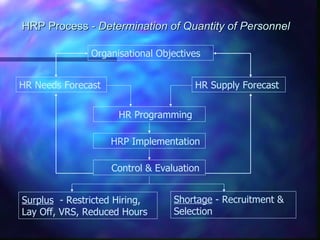
Human resource planning involves determining the quantity and quality of personnel needed by an organization. It is done through forecasting future human resource needs and available supply, then developing programs to address any gaps. The key steps are analyzing jobs to understand skill requirements, forecasting demand and supply, balancing needs with available staff, implementing recruitment and development plans, and monitoring results against targets. The goal is to ensure the right people are available at the right time and place to achieve organizational objectives.