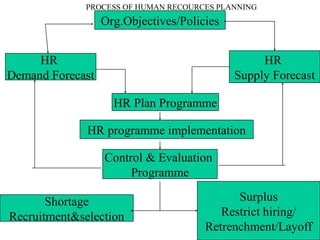
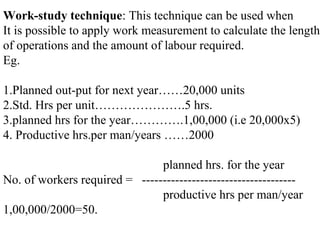
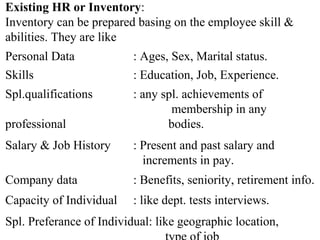
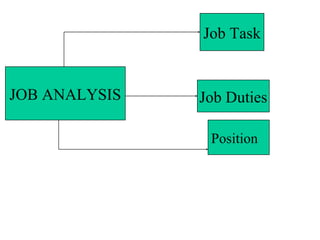
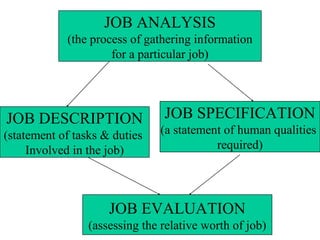
Human Resources Planning involves forecasting an organization's future human resource needs and ensuring the right people are available. It includes forecasting demand and supply of human resources. Demand forecasting considers internal factors like production levels and external factors like the economy. Supply forecasting analyzes existing employees and potential internal and external candidates. Job analysis is the process of gathering information about specific jobs through methods like interviews, observation, questionnaires and panels of experts. It involves creating job descriptions of tasks and duties and job specifications of required qualifications.