This document discusses employee testing and selection. It covers several key points:
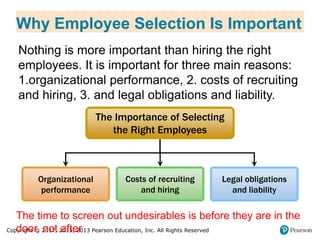
1. It explains why employee selection is important for organizational performance, costs of recruiting and hiring, and legal obligations and liability. The goal is to achieve person-job and person-organization fit by matching candidates' skills to the job requirements.
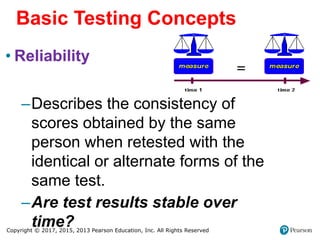
2. It defines reliability as the consistency of test scores over time and validity as whether a test actually measures what it intends to measure.
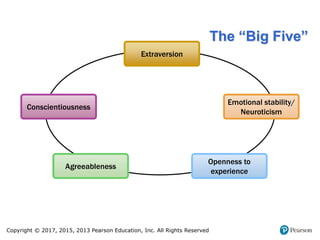
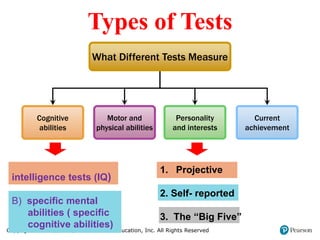
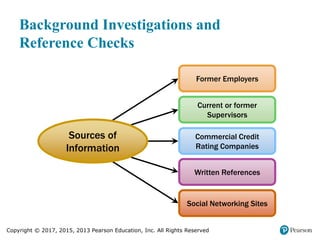
3. It lists and describes the basic categories of selection tests, including cognitive abilities, physical abilities, personality/interests, and achievement tests, providing examples of each type. It also discusses work samples, simulations, and background checks.