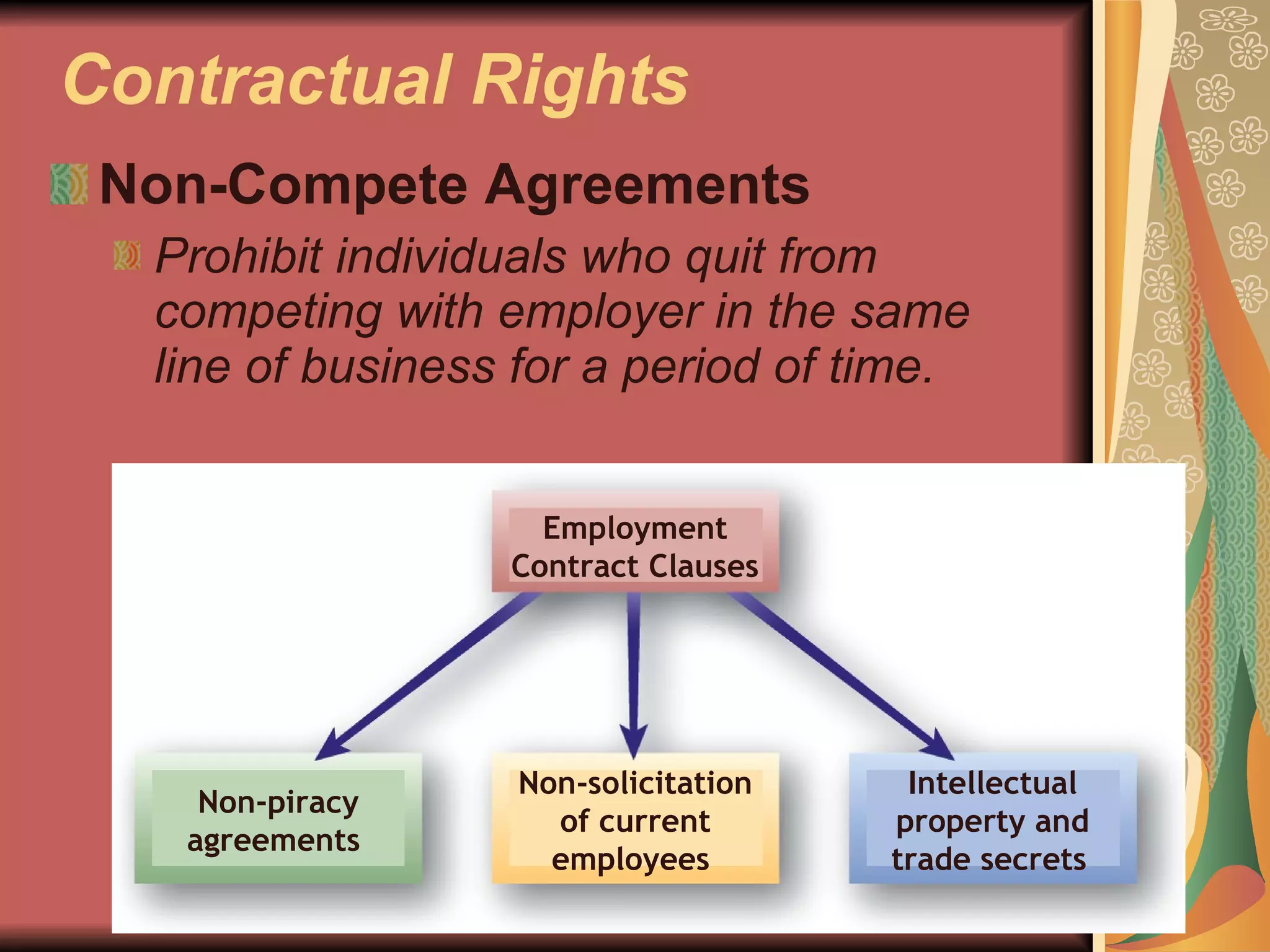
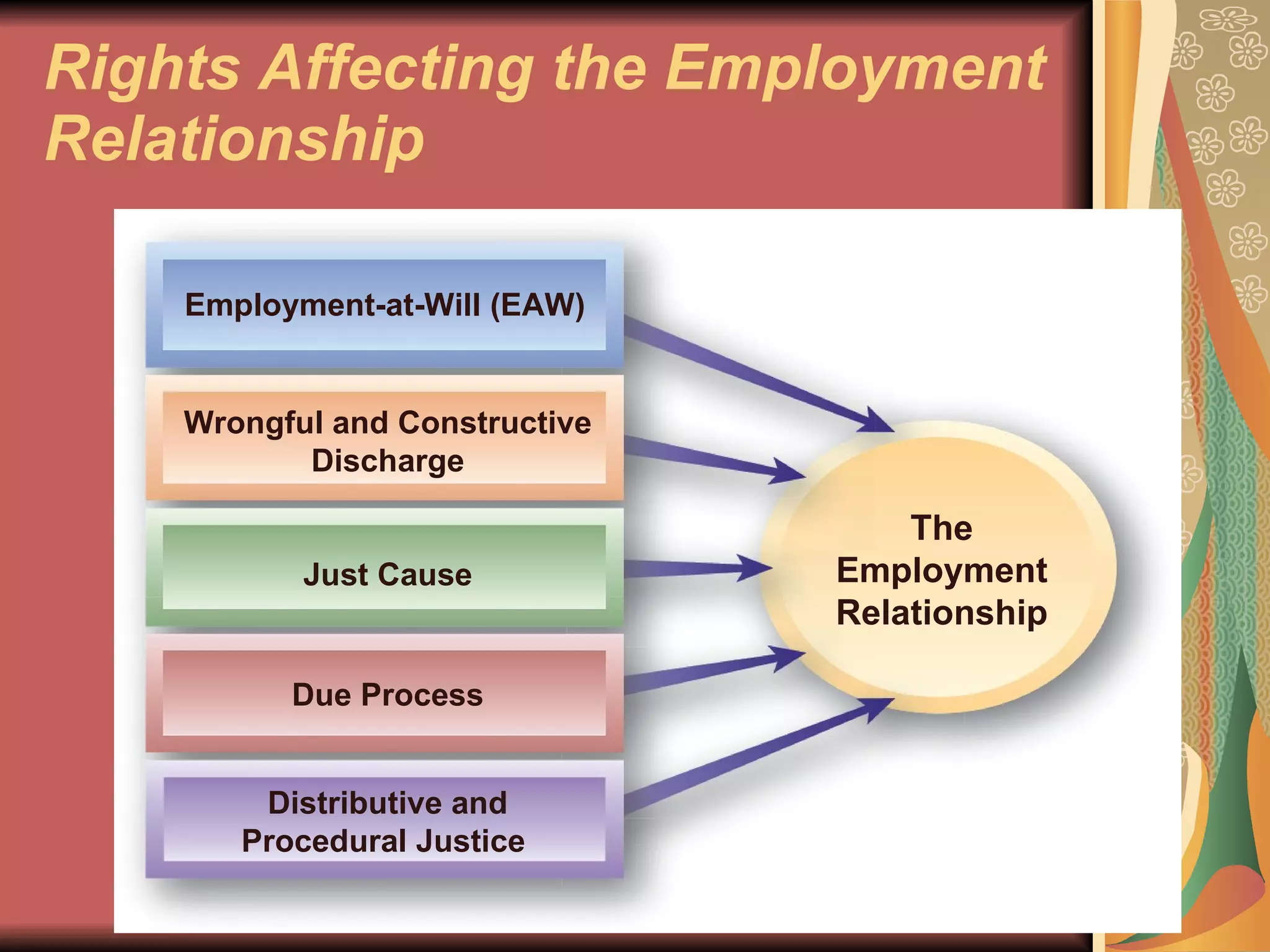
The document discusses various employee rights and responsibilities in the workplace. It covers statutory rights based on laws, contractual rights based on employment agreements, and implied rights based on promises made by employers. It also discusses employment-at-will, exceptions to at-will employment, wrongful discharge, constructive discharge, and ensuring fairness and due process. Finally, it outlines policies, procedures, rules, discipline processes, and other HR responsibilities regarding employees.