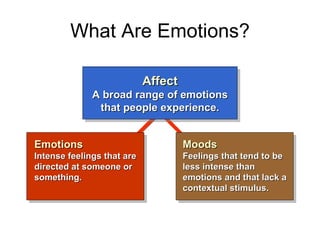
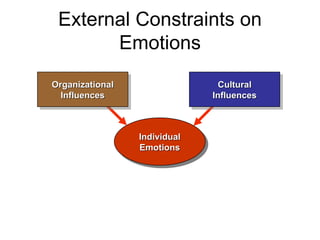
Emotional intelligence involves being self-aware of one's emotions and managing them well. It also includes skills like empathy, social skills, and motivation. Studies show emotional intelligence competencies are twice as effective as IQ in determining success, especially for executives where there is an 85% correlation between emotional intelligence and success. The document defines concepts like emotions, moods, affect, and discusses gender differences and constraints on expressing emotions. It also outlines abilities within self-awareness, self-management, and social skills that comprise emotional intelligence.