Embed presentation


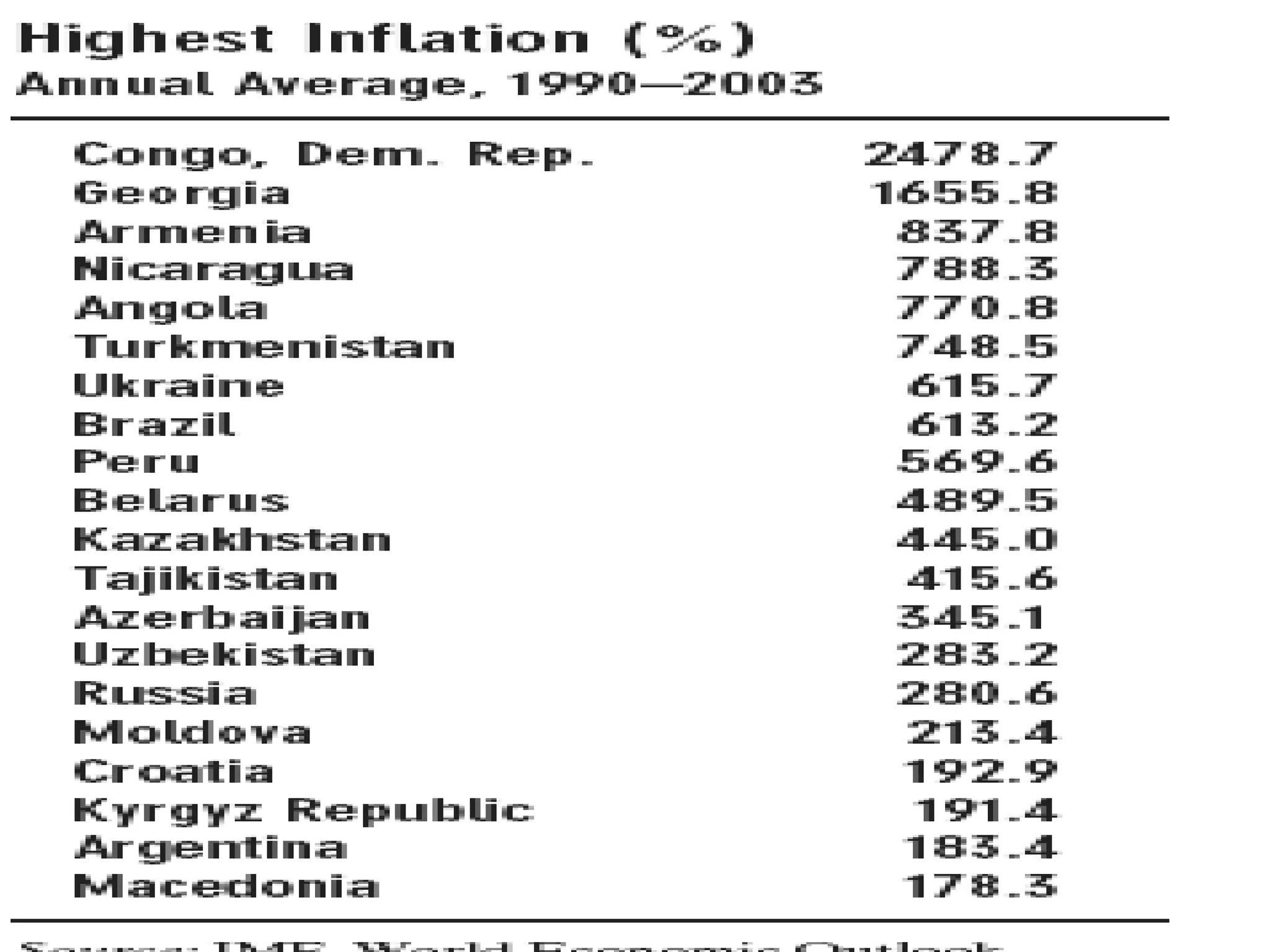
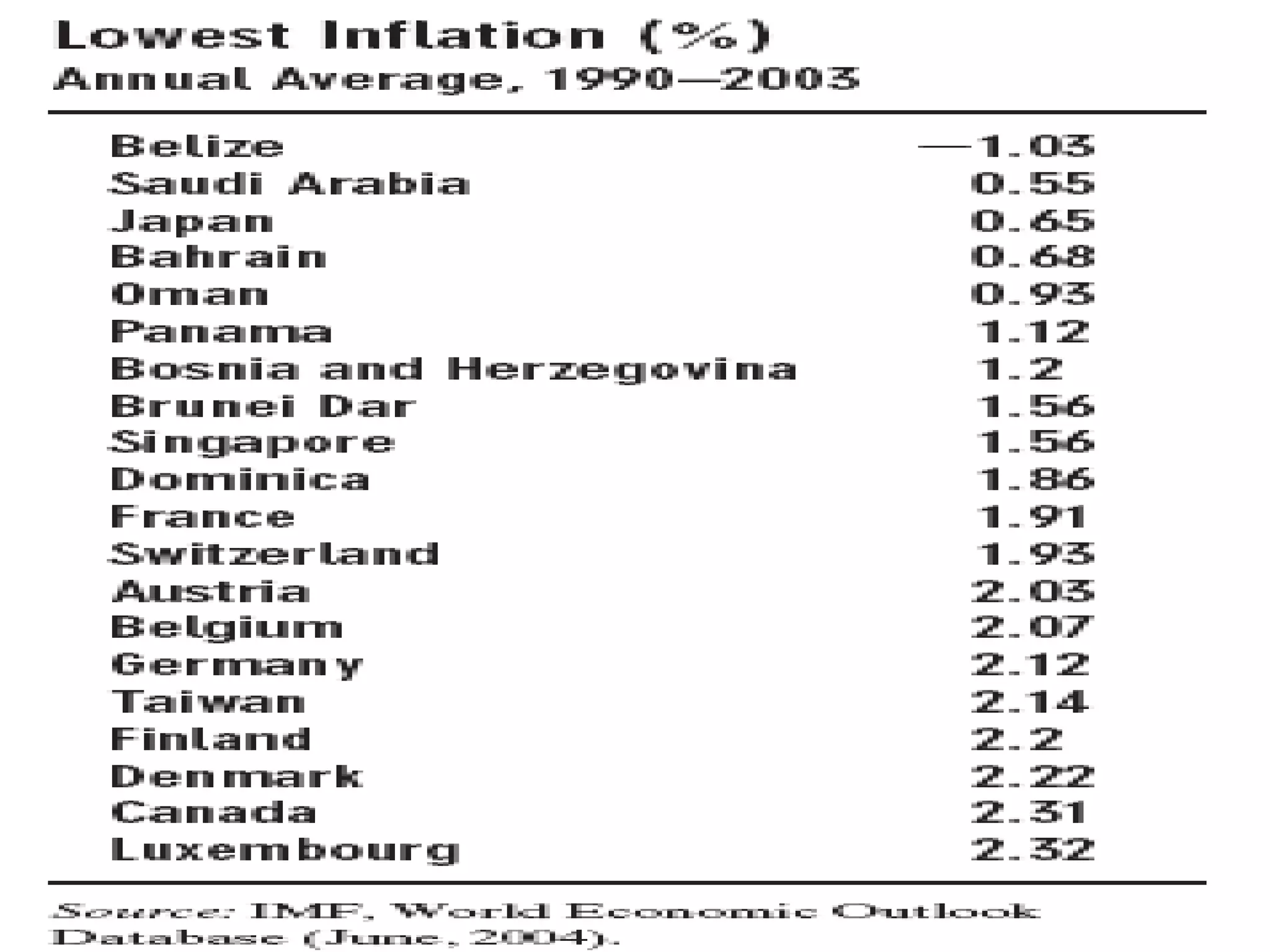





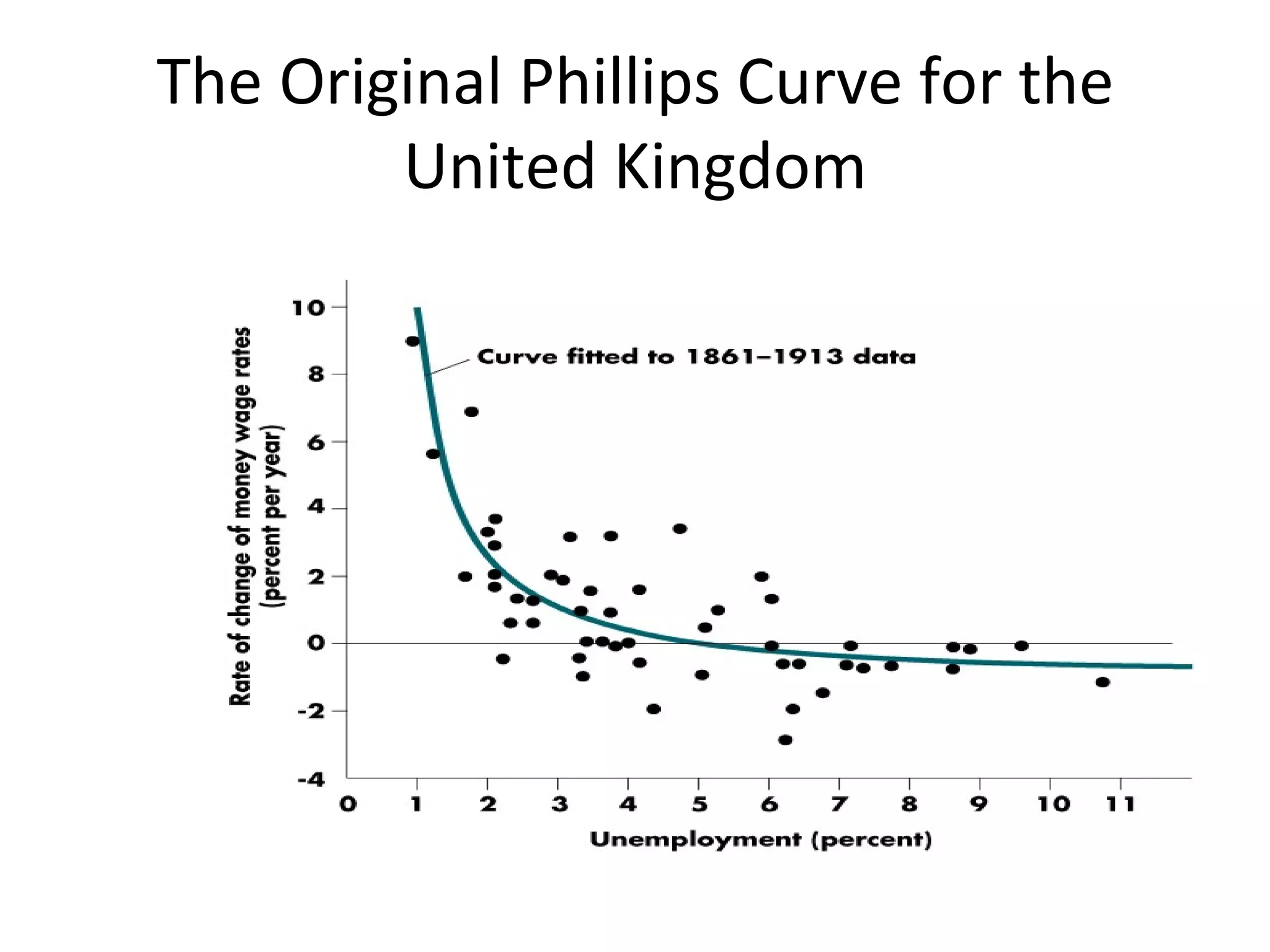
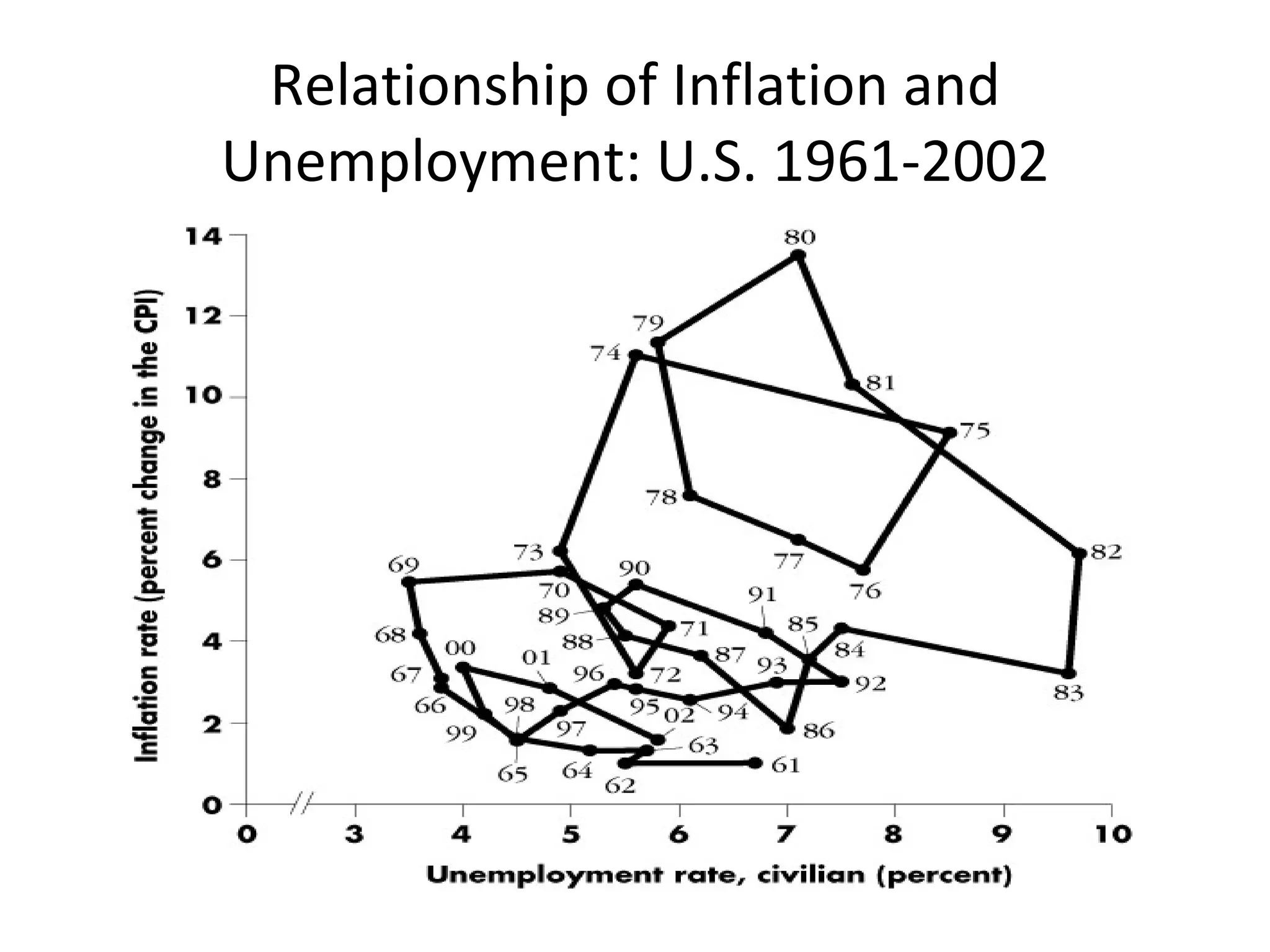


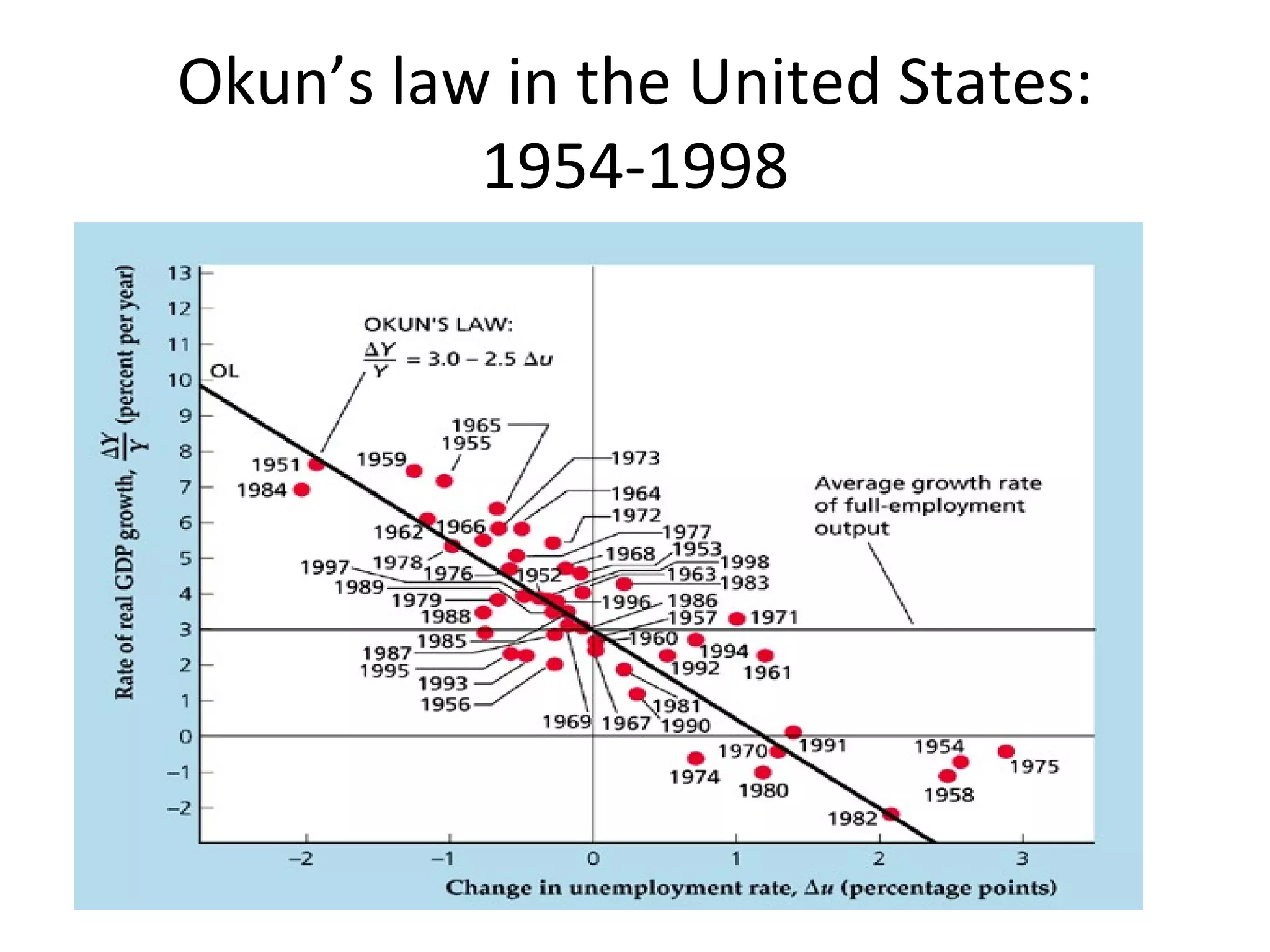


The document discusses the relationships between inflation, unemployment, and output. It covers topics like the types and measurement of unemployment, the Phillips curve relationship between inflation and unemployment, Okun's law linking changes in unemployment to economic growth, and the sacrifice ratio measuring the output lost from reducing inflation.















