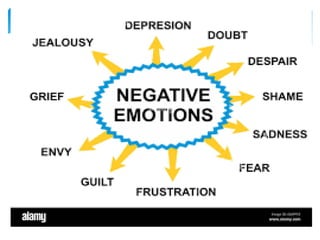
This document discusses emotions from an etymological, definitional, and theoretical perspective. It defines emotions as agitated states of mind and body that stir us to act in certain ways. Emotions have cognitive, affective, and behavioral components. There are positive and negative emotions that can influence health and illness through physiological and psychological changes. Theories like James-Lange, Cannon-Bard, and Schachter-Singer propose different views of the relationship between physiological arousal and emotional experience. Nurses must understand emotions to care for patients, as illness can impact emotional control and nurses must help substitute negative emotions with positive ones.