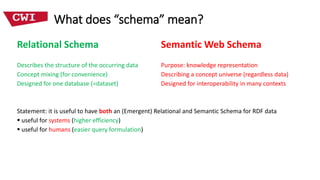
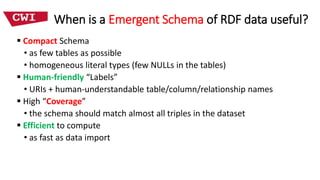
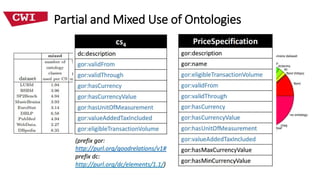
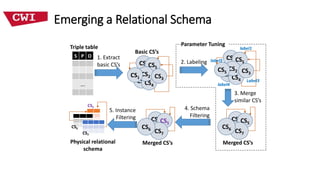
This document discusses deriving an emergent relational schema from RDF data. It describes extracting characteristic sets from RDF data to recognize classes and relationships between classes. These characteristic sets are then merged and labeled to create a logical relational schema. This emergent schema provides benefits for both systems through improved efficiency and humans through easier query formulation over the RDF data. Key aspects of a useful emergent schema are discussed such as being compact, having human-friendly labels, providing high coverage of the RDF data, and being efficient to compute. Experimental results on real-world RDF datasets show the approach produces compact schemas with high coverage and understandable labels that improve performance over the native RDF representation.

![ Bad query plans
Low storage locality
Lack of user schema insight
Main Problems in RDF Data Management [1]
[1] Minh-Duc Pham, Boncz P.A., " Self-organizing Structured RDF in MonetDB ," PhD Symposium, ICDE, 2013
RDF de-emphasizes the need for a schema
and the notion of structure in the data
Emergent Schema](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/emergentschemagraphta-150323090108-conversion-gate01/85/Deriving-an-Emergent-Relational-Schema-from-RDF-Data-2-320.jpg)