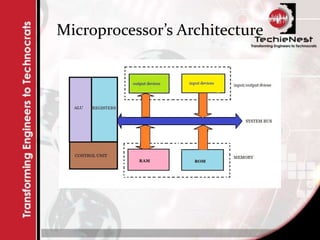
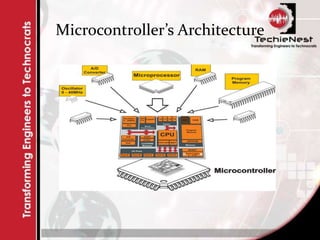
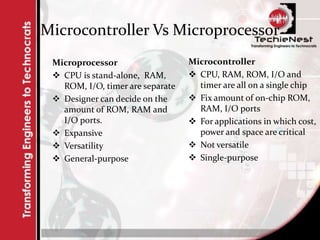
An embedded system combines computer hardware and software designed for a specific function, prevalent in devices ranging from household appliances to industrial machines. These systems can vary from simple with limited interfaces like switches to complex systems using microcontrollers, and they are optimized for size, cost, and performance. Key components of an embedded system include input devices (sensors), processing units (microprocessors or microcontrollers), and output devices that provide results based on the processed input.