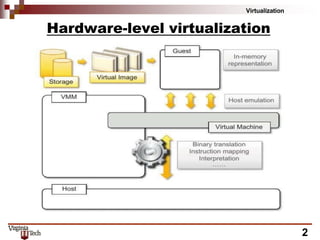
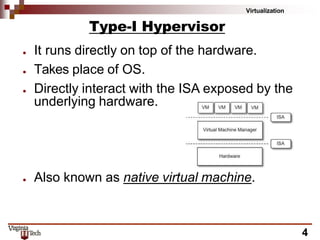
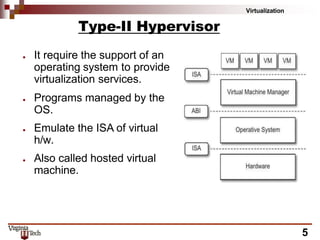
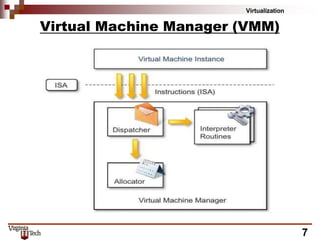
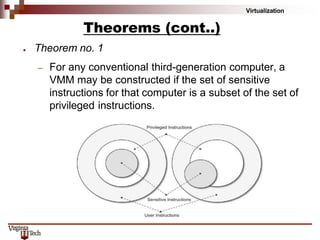
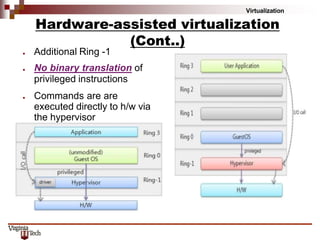
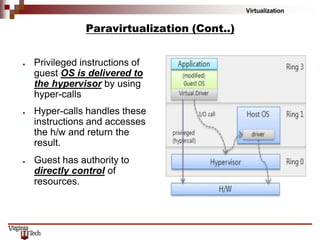
This document discusses hardware virtualization techniques. It describes hardware-level virtualization which provides an abstract execution environment for a guest OS on computer hardware. A hypervisor runs above the supervisor mode and enables multiple VMs to run on a physical server. There are two types of hypervisors: type-I runs directly on hardware while type-II requires an operating system. Virtual machine managers contain dispatcher, allocator, and interpreter modules. Popek and Goldberg's theorems define requirements for efficient virtualization based on instruction set classification. Hardware virtualization techniques include full virtualization, hardware-assisted virtualization, paravirtualization, and partial virtualization.