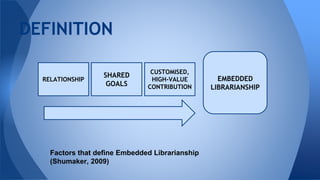
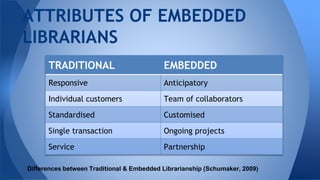
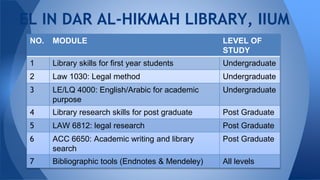
This document discusses the role and definition of embedded librarianship in higher education, emphasizing the importance of collaboration between librarians and academic teams to enhance information access and support. It contrasts traditional librarianship models with embedded approaches, highlighting attributes such as ongoing partnerships and customized contributions. The conference included topics on the integration of librarians in distance education and various library programs, aiming to foster better relationships and understanding of user needs.