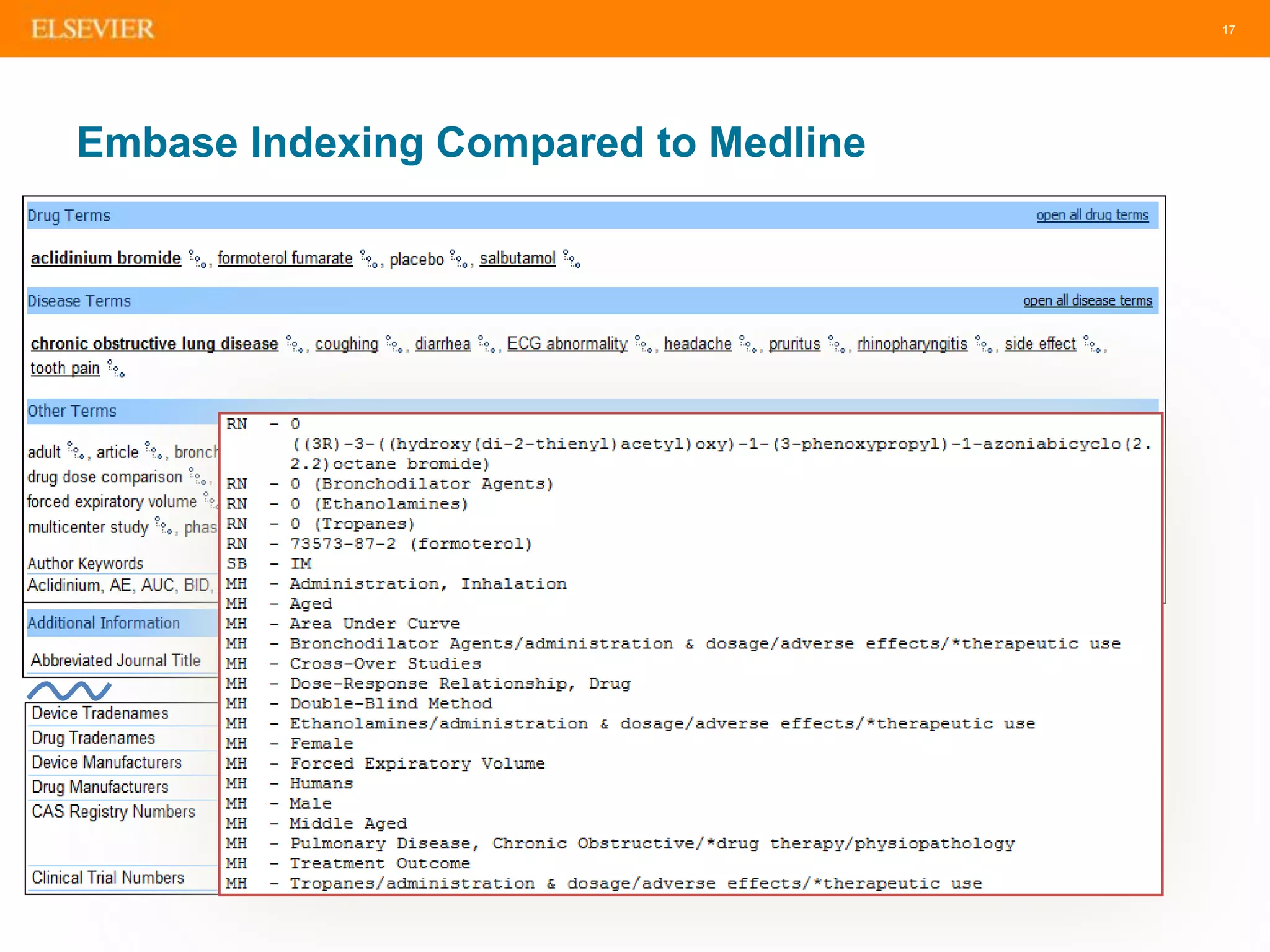
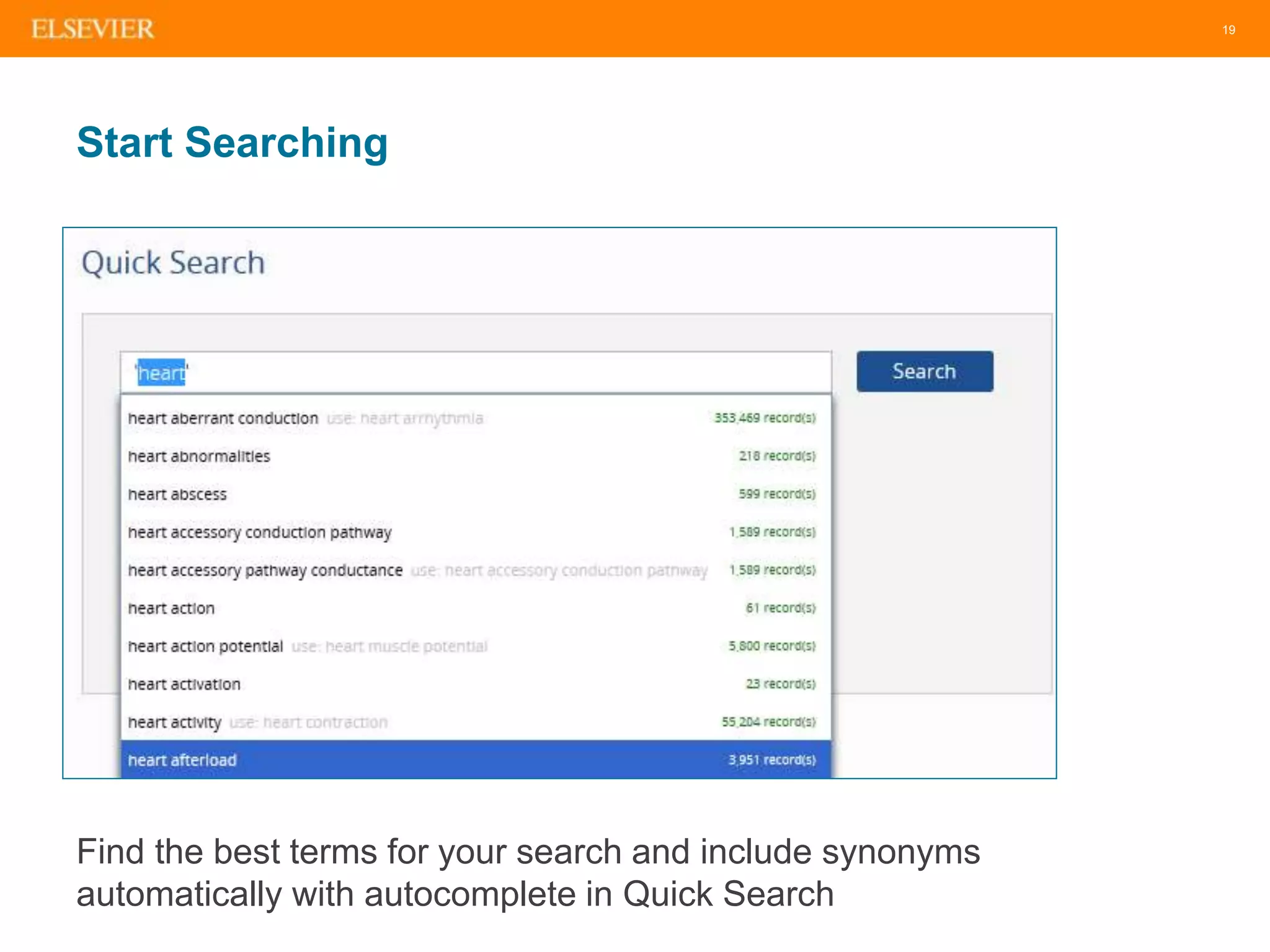
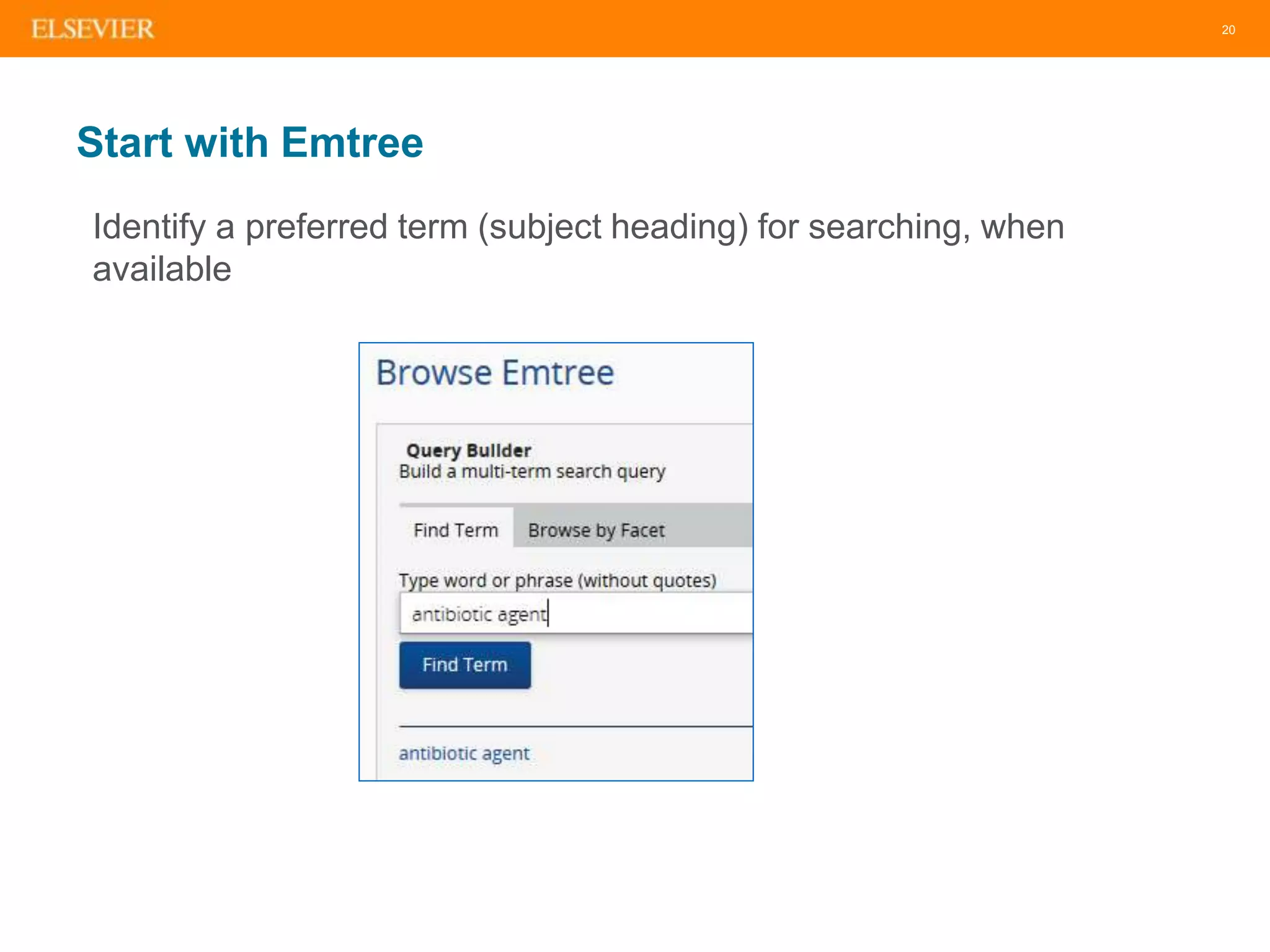
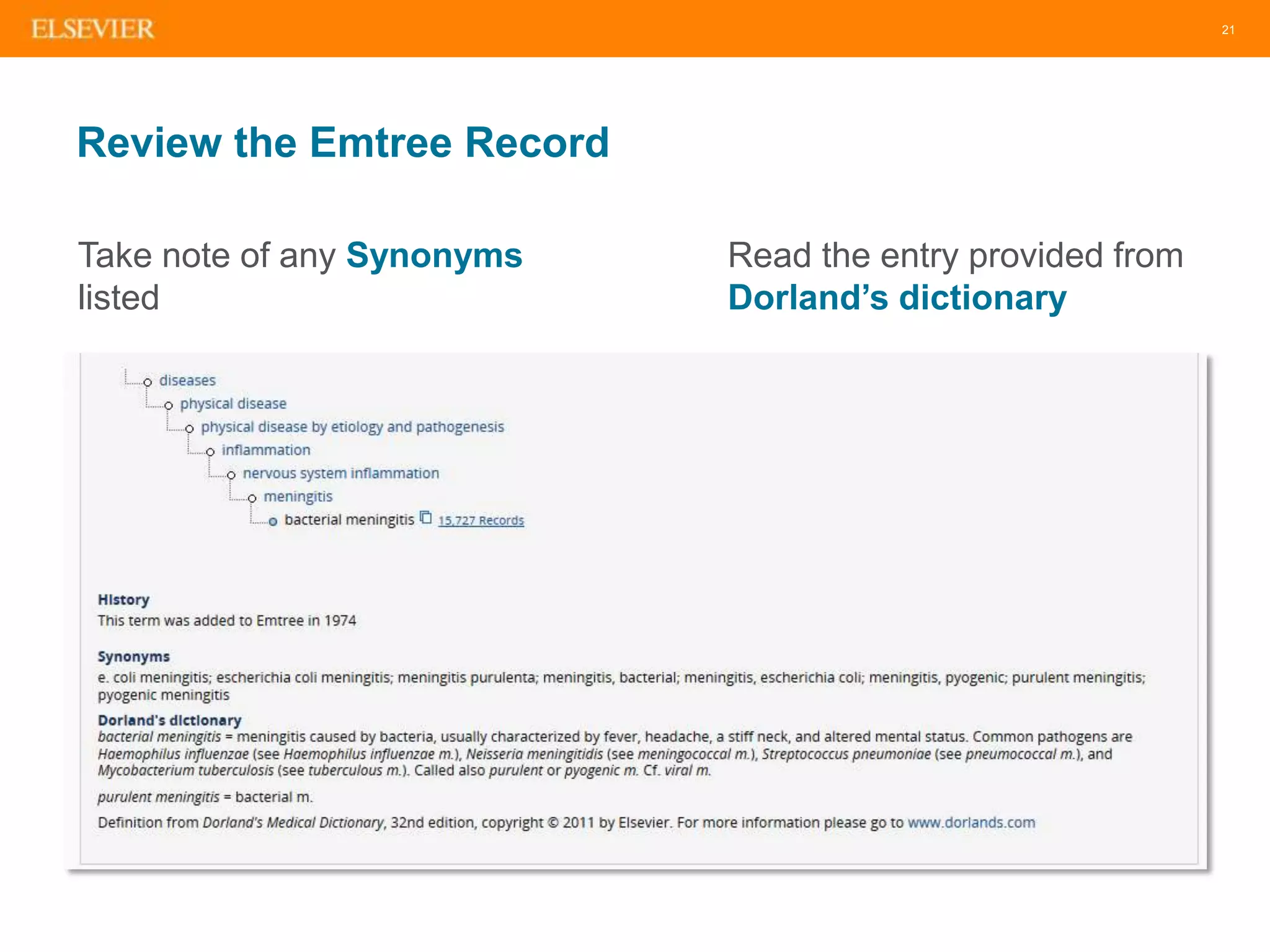
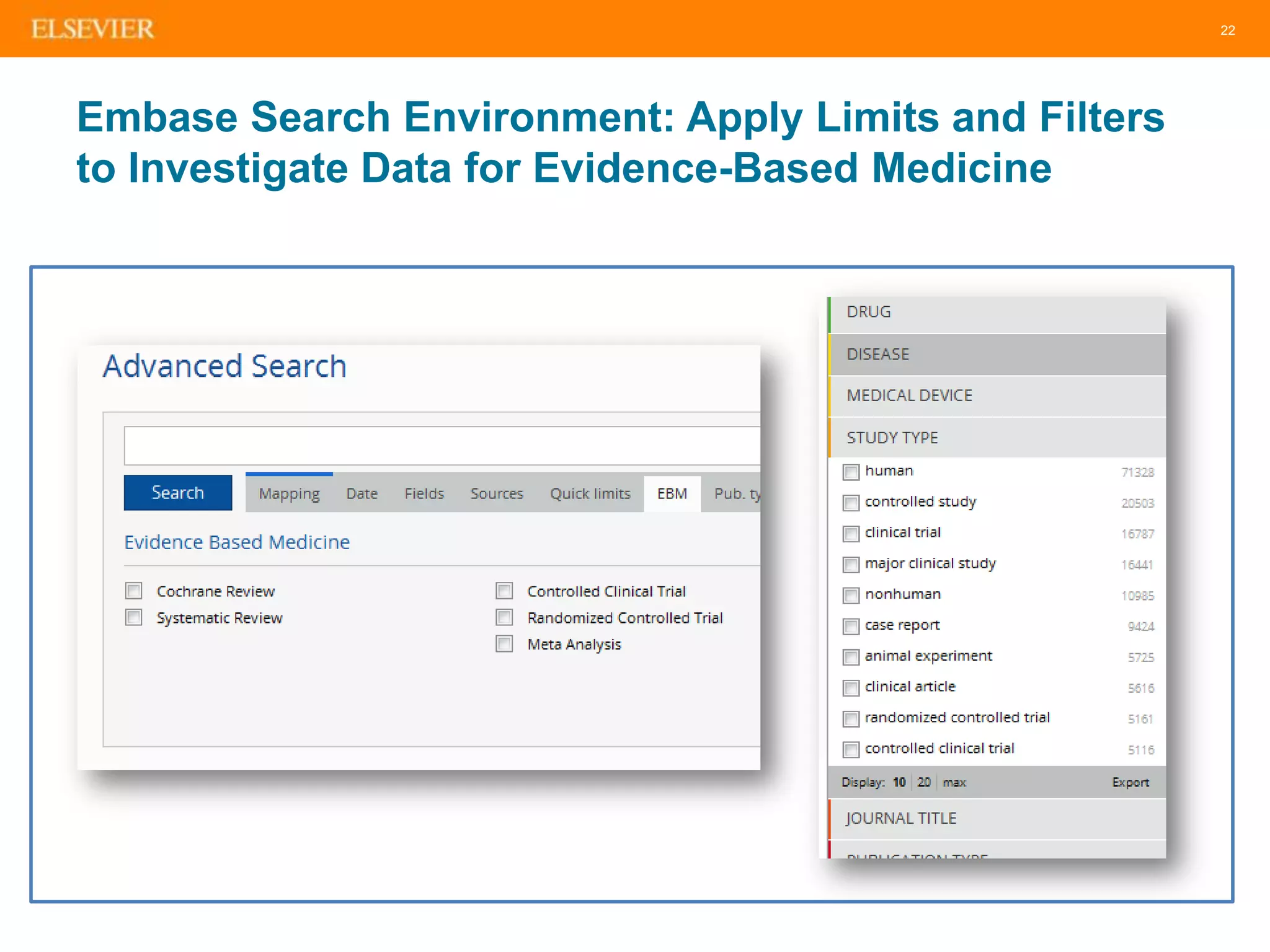
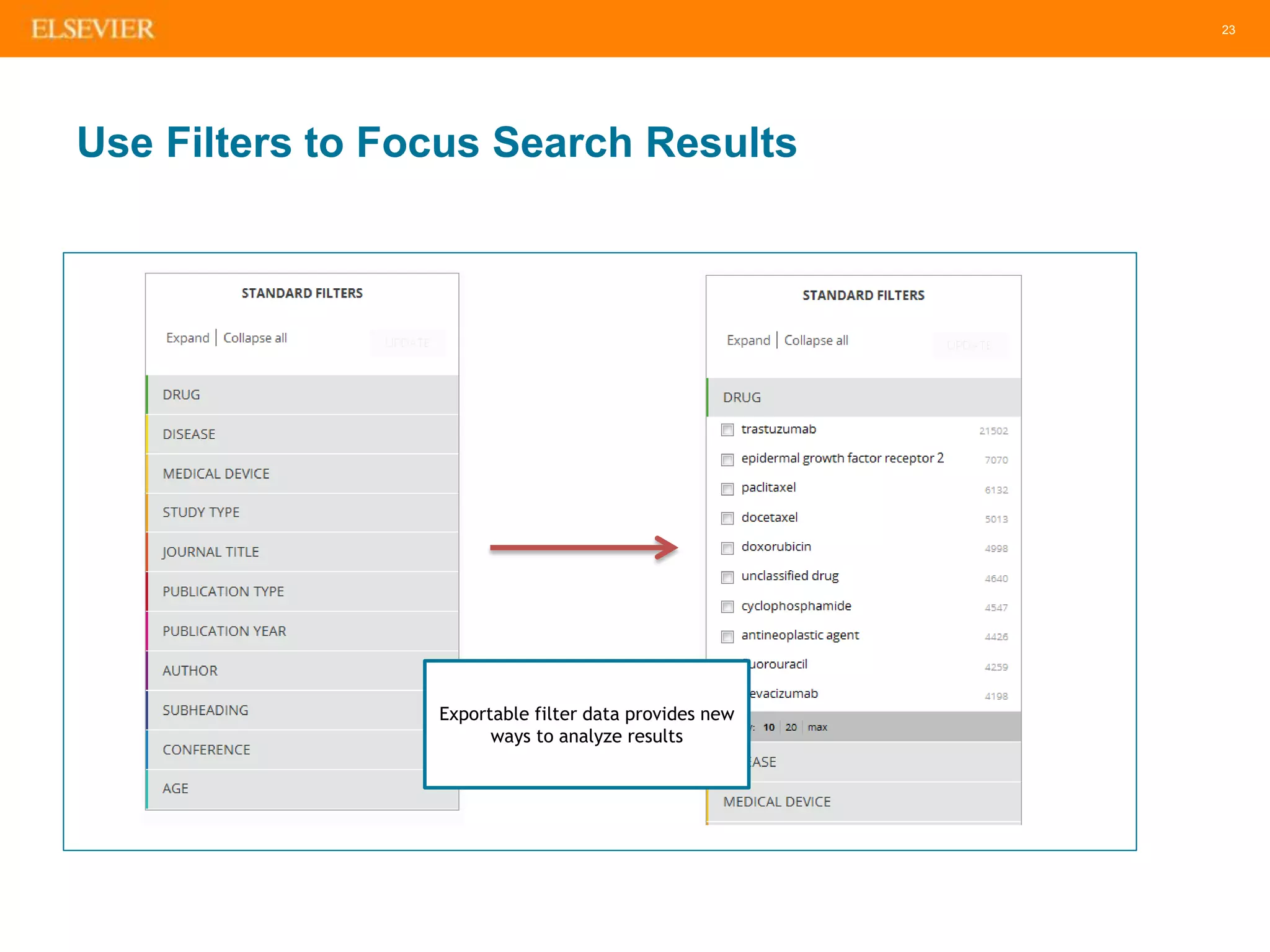
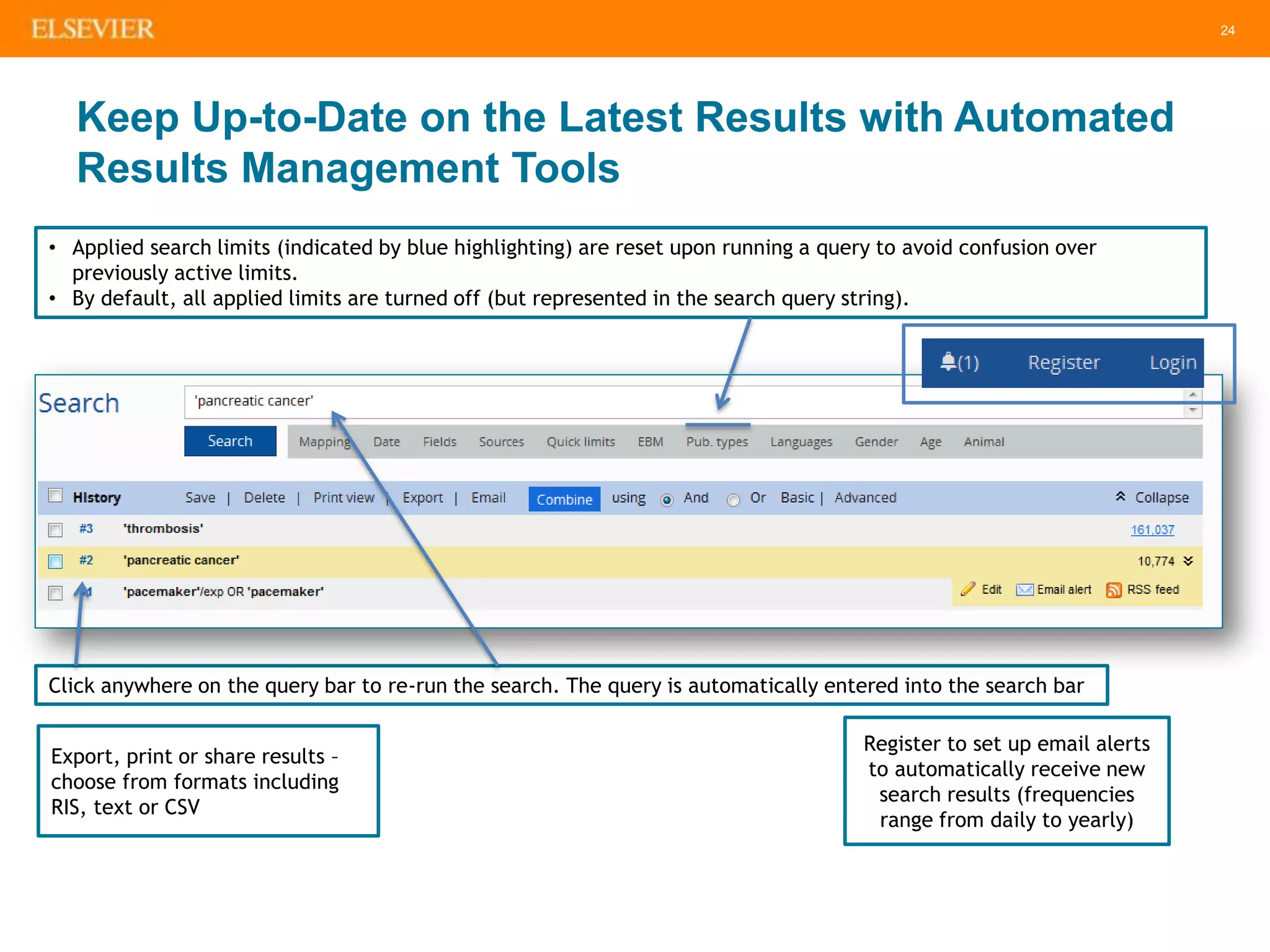
The document is an introduction to Embase, a comprehensive biomedical literature database that provides extensive journal and conference coverage, along with deep indexing for precise result retrieval. It outlines the key features and advantages of using Embase for biomedical research, including its unique content, advanced search capabilities, and automation tools. The session includes tips for effective searching and emphasizes the importance of Embase in systematic reviews and pharmacovigilance.







![11
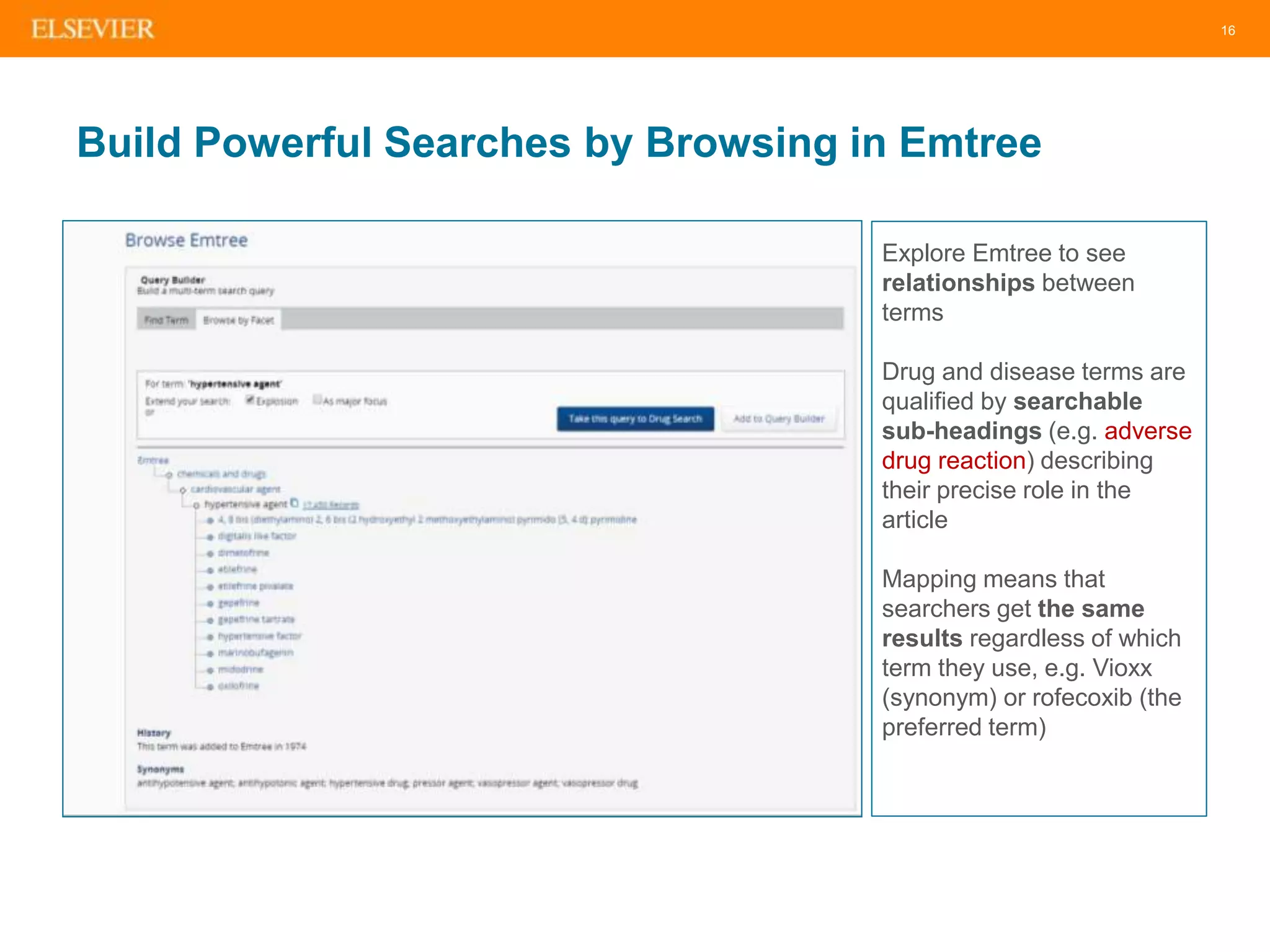
Embase Content – Includes all of MEDLINE
Plus Much More
• Over 2,800 journals not
indexed on MEDLINE,
especially from countries
outside North America
• Over 1.9m conference
abstracts from >5,5000
conferences (added since
2009)
• In-depth drug and medical
device indexing based on
the Emtree Life Science
thesaurus, which has over
twice as many terms as the
PubMed (MEDLINE) thesaurus
(MeSH)
Embase
Unique
MEDLINE
on Embase
Embase &
MEDLINE
6.7m records
2,800 journals
12m records
3,000 journals
8.5m records
2,500 journals
[embase]/lim NOT
[medline]/lim
[embase]/lim AND
[medline]/lim
[medline]/lim NOT
[embase]/lim](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/embaseintrowebinarjuly2015-150722171202-lva1-app6891/75/Embase-intro-webinar-july-2015-11-2048.jpg)