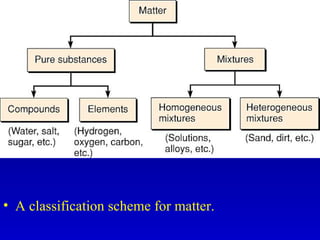
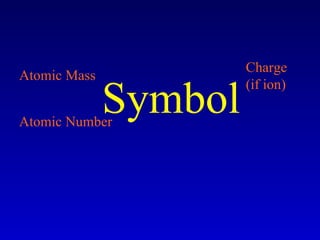
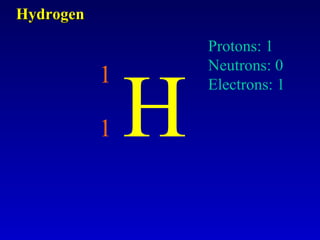
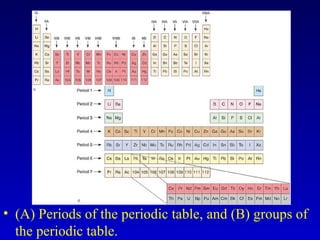
The document discusses elements and the periodic table. It provides information on the names of elements, their symbols, atomic mass and number. It explains that the periodic table is organized into rows and columns, with elements identified by their symbol and atomic properties. Key chemical families are also outlined, including alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens and noble gases. Cations and anions are defined as ions with positive and negative charges respectively.