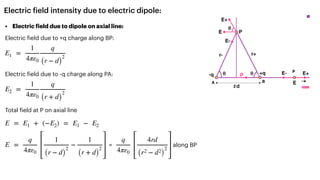
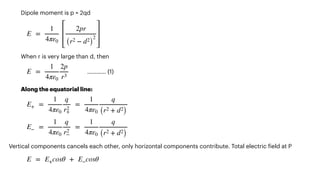
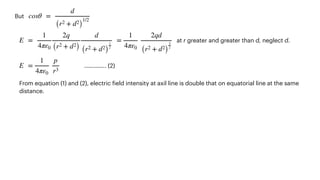
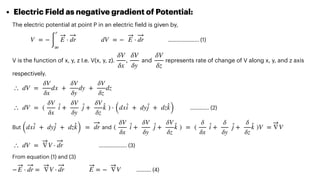
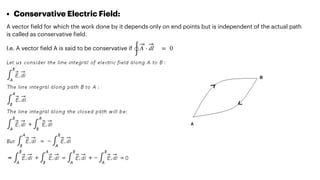
The document covers the principles of electrostatics, including Coulomb's law, electric fields, electric dipoles, and potential energy associated with dipoles in electric fields. It explains concepts such as electric field intensity, electric potential, and the behavior of dipoles in uniform electric fields, including calculations of torque and potential energy. Additionally, it addresses electrostatic energy storage, electric flux, and the representation of electric fields through lines of force.