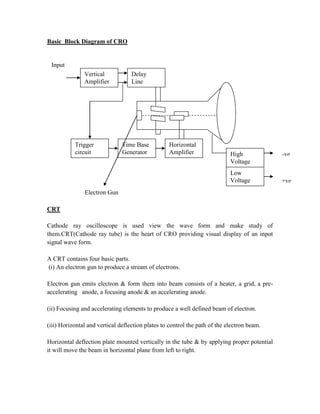
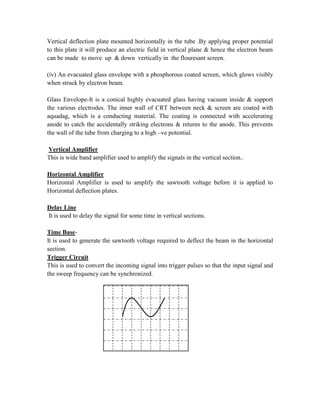
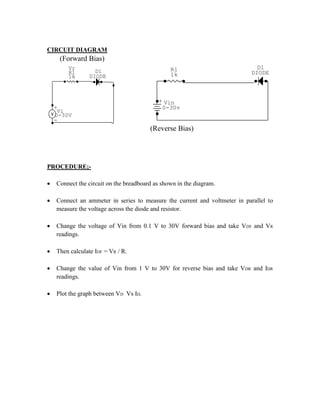
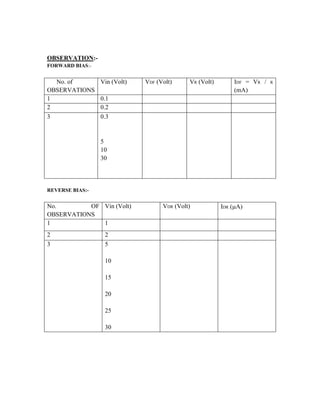
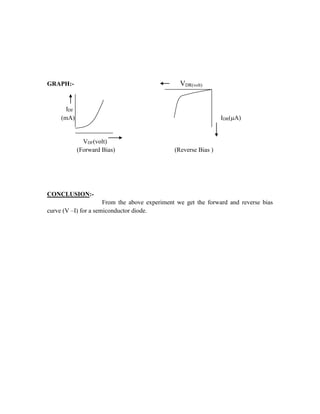
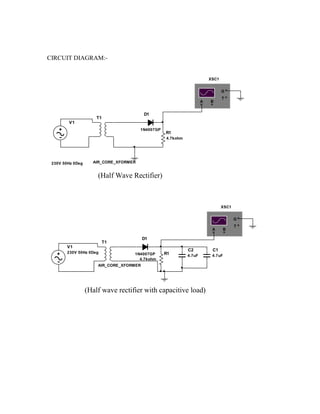
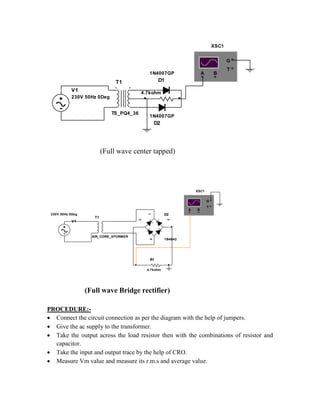
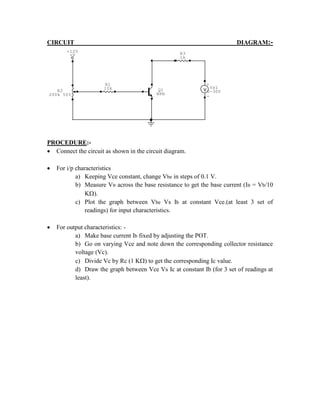
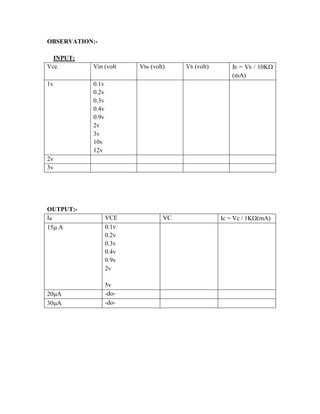
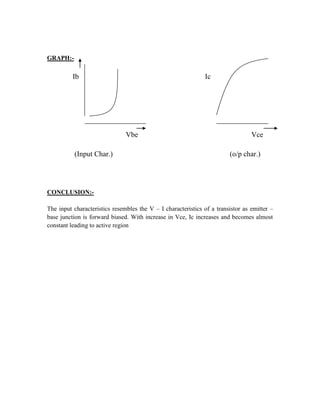
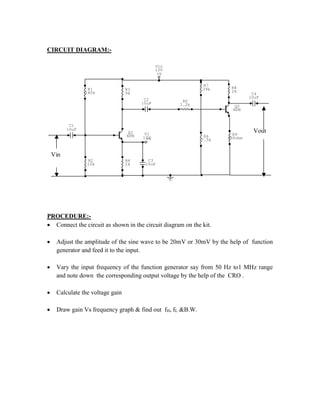
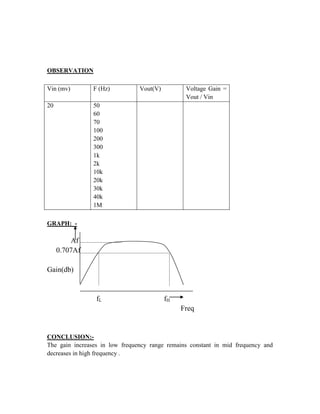
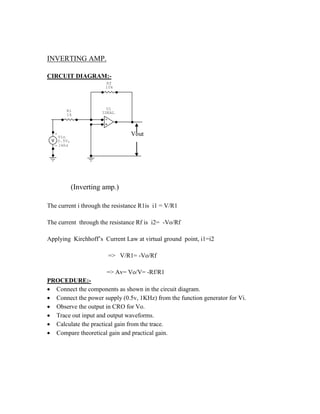
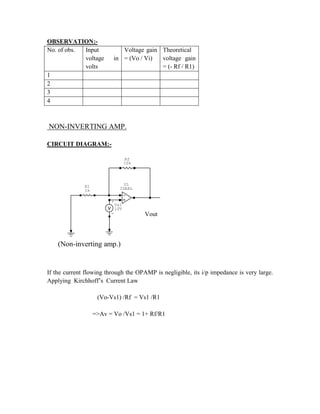
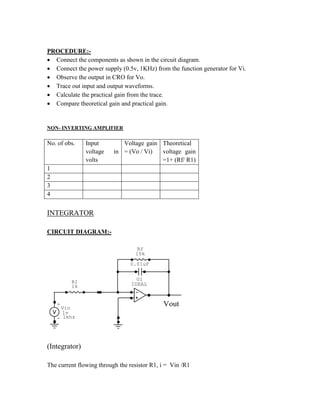
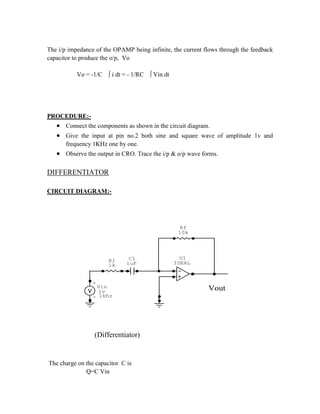
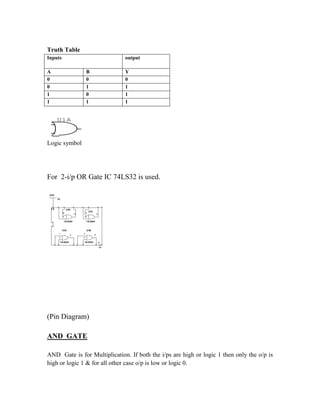
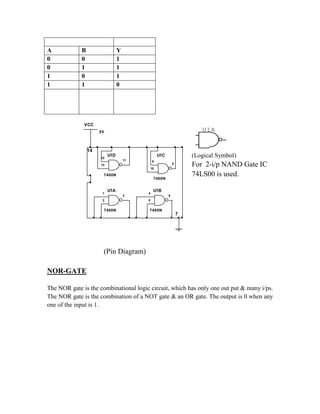
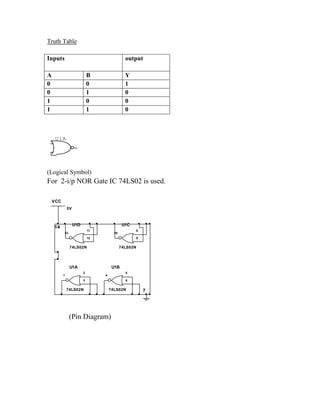
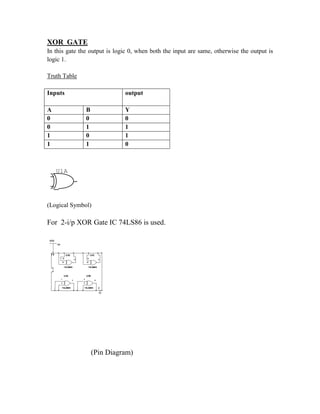
This document provides instructions for experiment 2 which involves using an oscilloscope (CRO) to view waveforms and measure amplitude and frequency. It describes the basic components of a CRO including the electron gun, CRT, horizontal and vertical deflection plates. The CRO uses an electron beam that is deflected along the X and Y axes to provide a two-dimensional display on the fluorescent screen, allowing the amplitude and time-varying behavior of electrical signals to be observed. Students will use a CRO, probes, and function generator to view waveforms and take amplitude and frequency measurements.