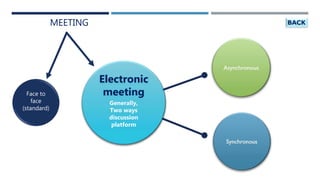
The document discusses the evolution and significance of electronic meetings since the 1980s, highlighting their role in enhancing group decision-making through technology. It outlines the structure, tools, and benefits of electronic meeting systems (EMS) and group support systems (GSS), emphasizing increased participation, equity in decision-making, and the ability to mitigate biases. The challenges of managing virtual teams and ensuring effective communication through these systems are also addressed.