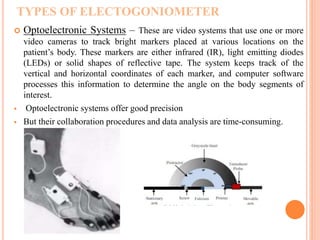
An electrogoniometer uses angle sensors to objectively measure human joint motion. It has two arms attached to the proximal and distal segments of the joint, connected to a potentiometer that measures the angular position as voltage. This voltage is sampled and converted to an angle. Electrogoniometers include optoelectronic systems using cameras, potentiometers measuring resistance, and strain gauges using flexible springs. They are portable, lightweight, and adapt to different body segments but can interfere with natural movement. Electrogoniometers provide precise dynamic joint angles and are reliable for laboratory studies.