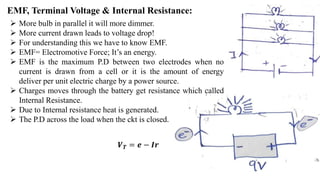
1) Electromagnetic induction is the process of using magnetic fields to produce voltage and electric current. It occurs whenever there is a change in magnetic flux through a loop of wire.
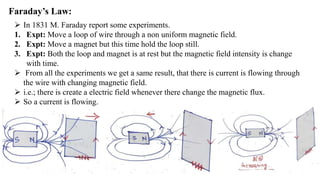
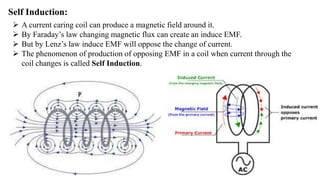
2) Faraday's experiments in 1831 showed that a changing magnetic field can induce an electromotive force (EMF) in a loop of wire. This established the principle of electromagnetic induction.
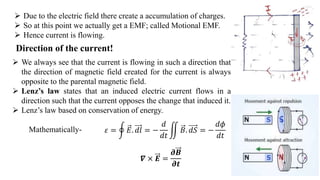
3) Lenz's law describes the direction of induced current in a conductor due to an external changing magnetic field. It states that the induced current will flow in a direction that creates its own magnetic field opposing the change that caused it.