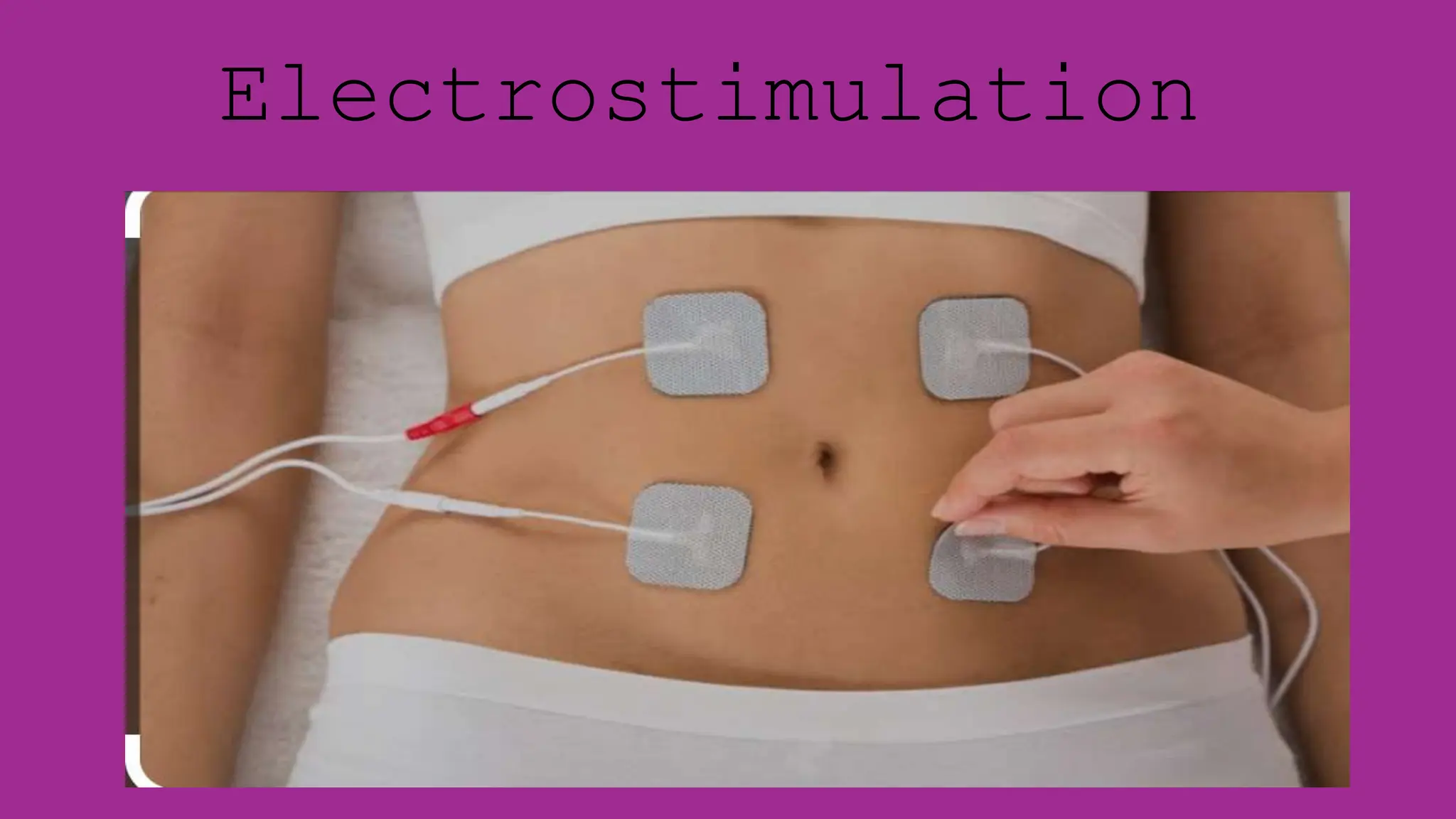
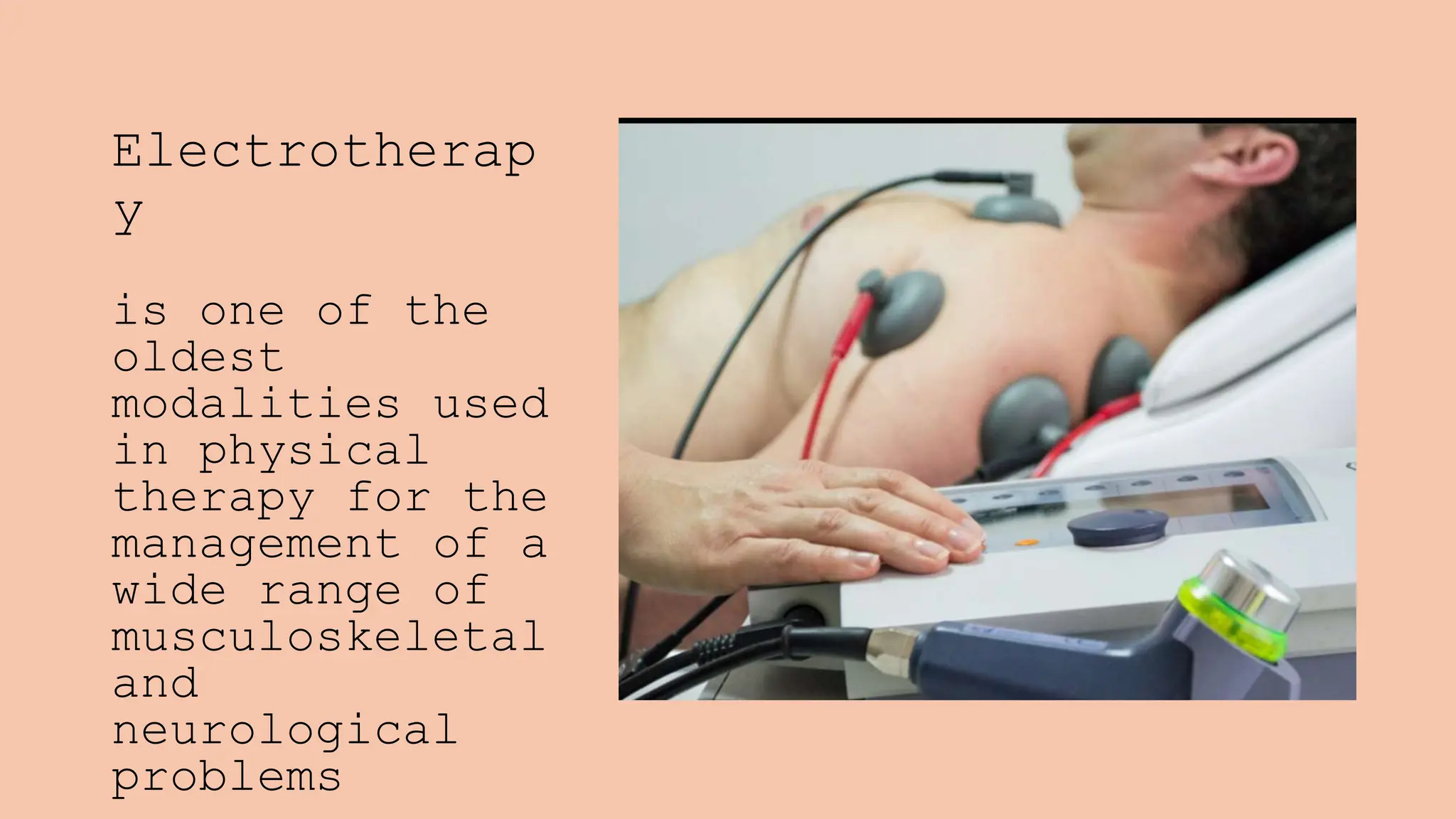
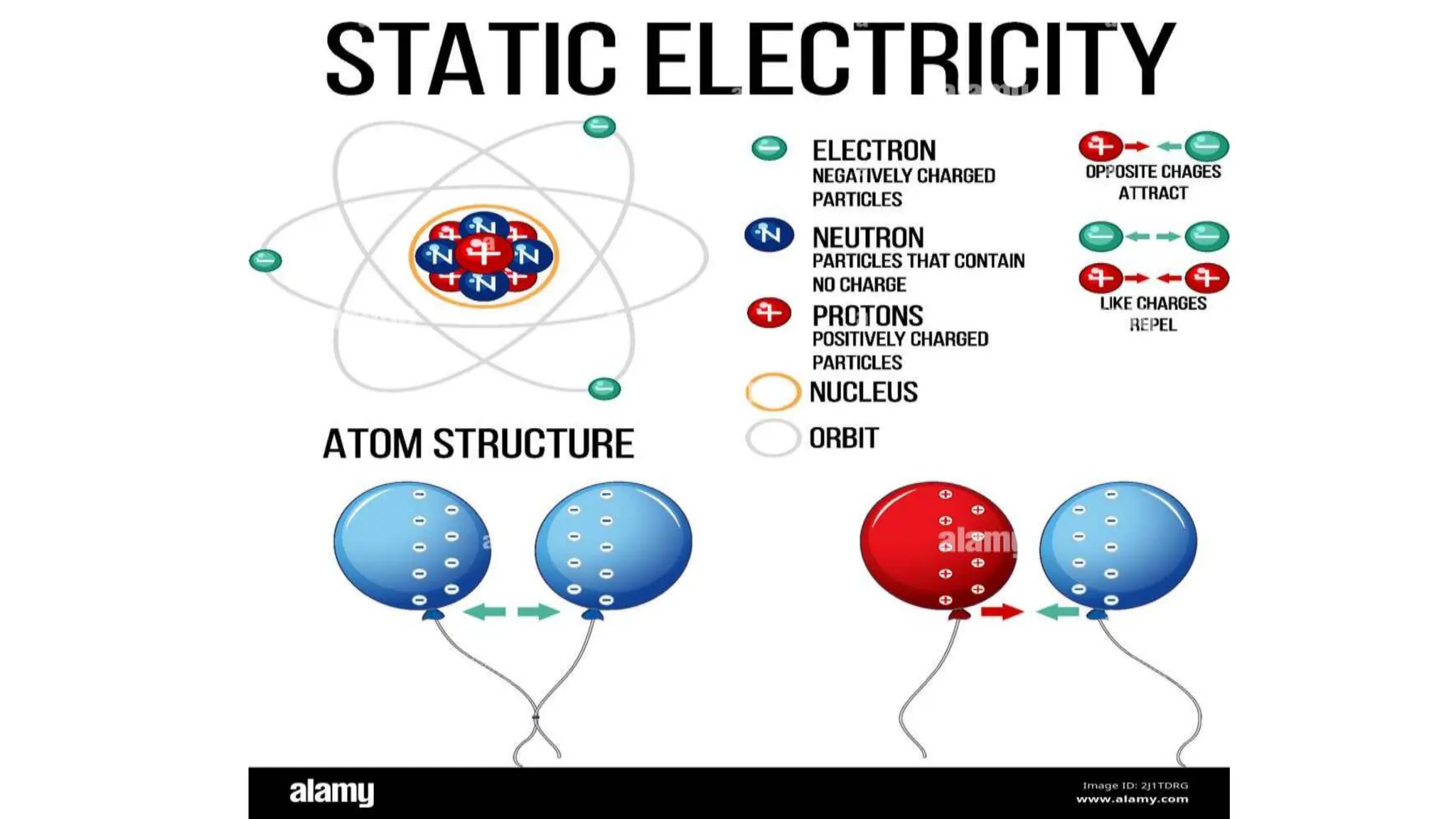
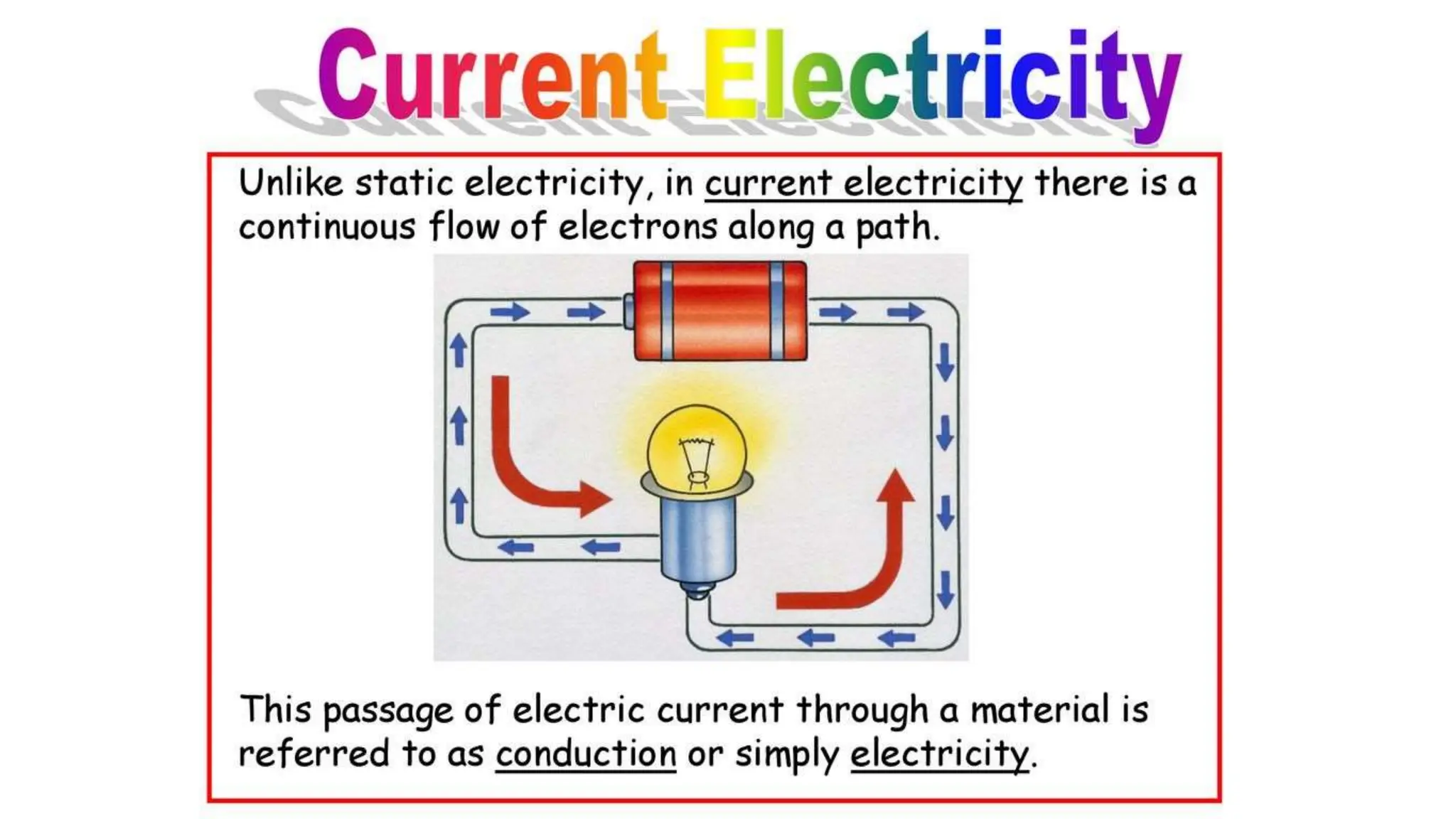
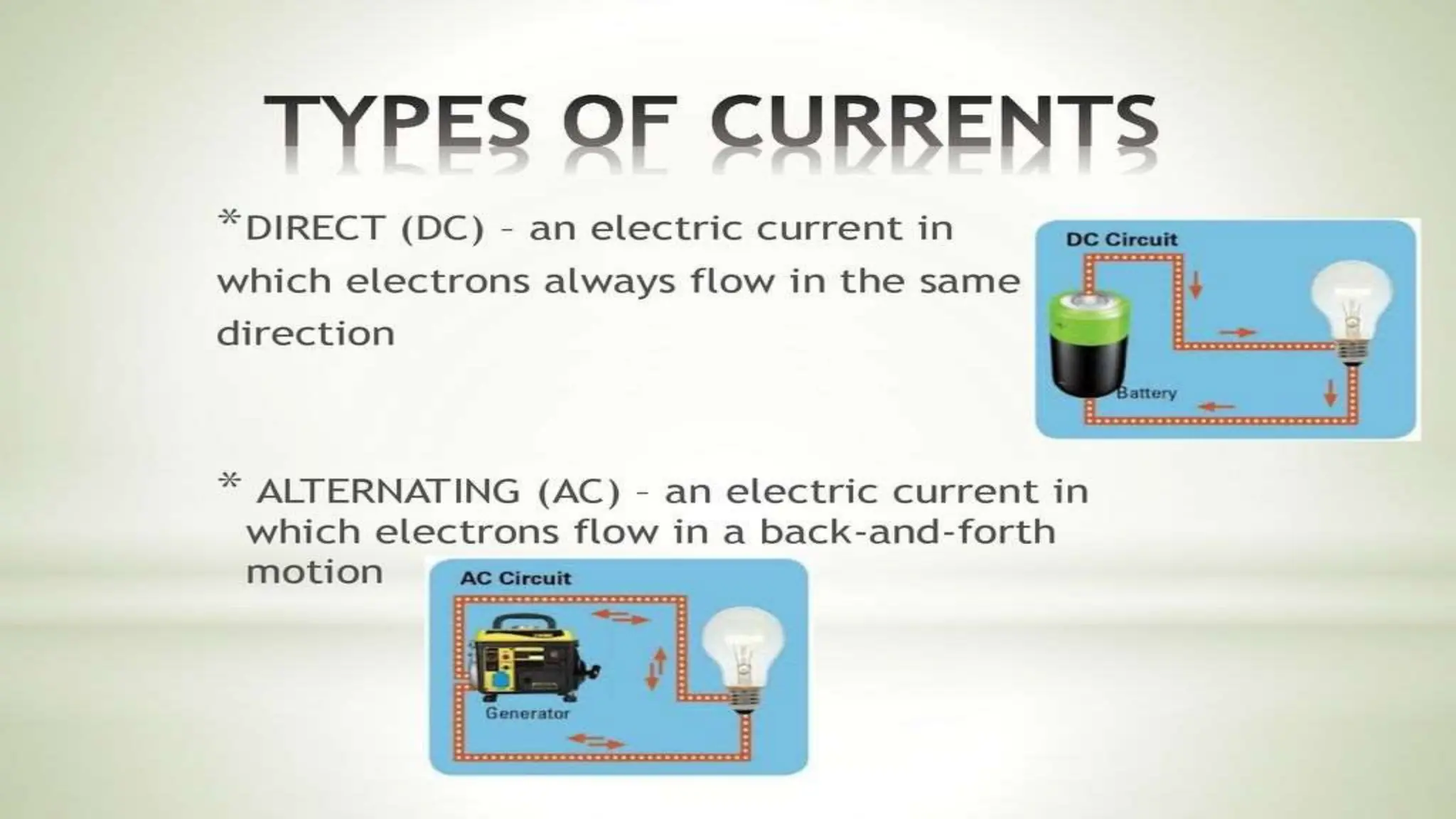
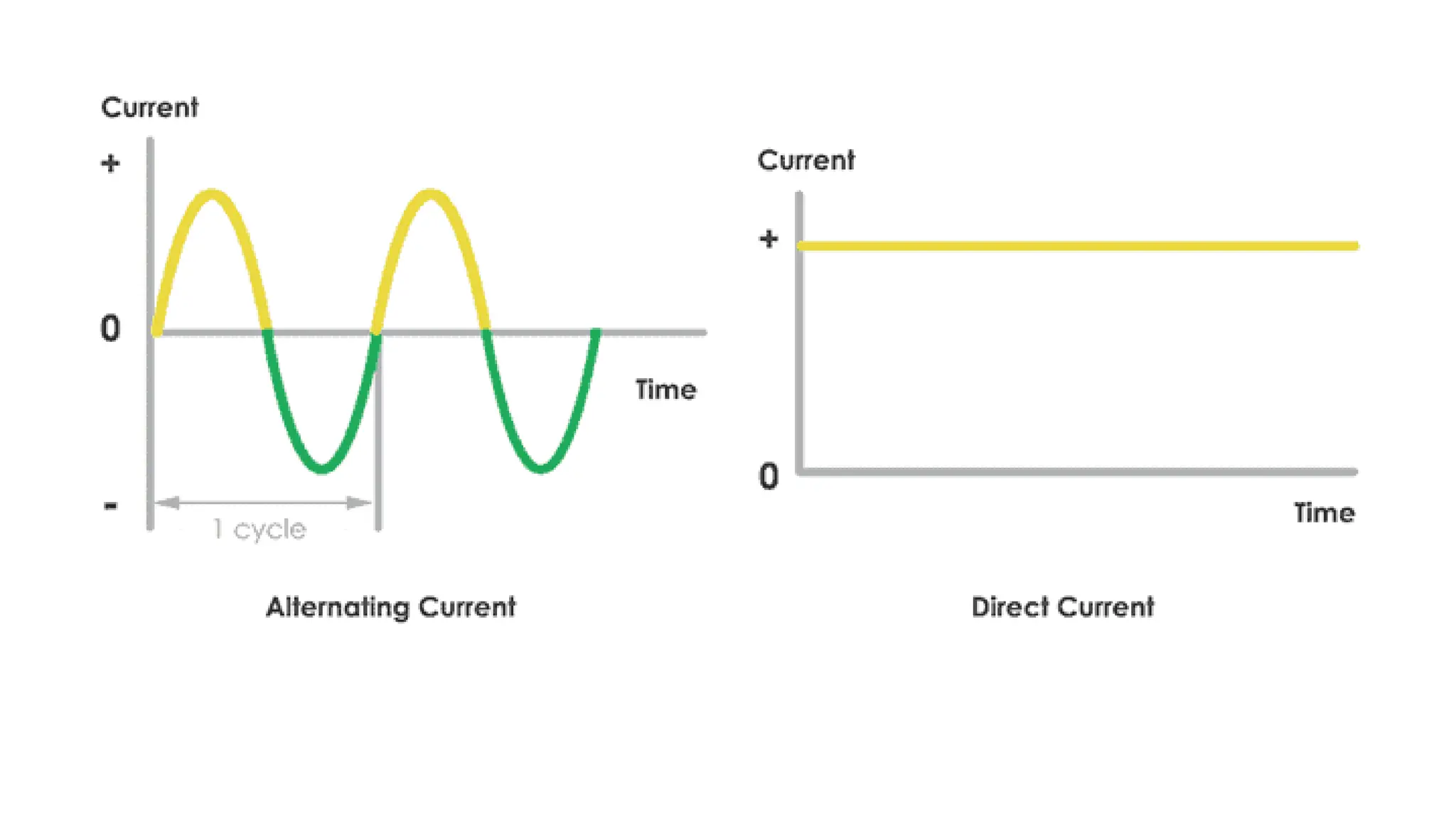
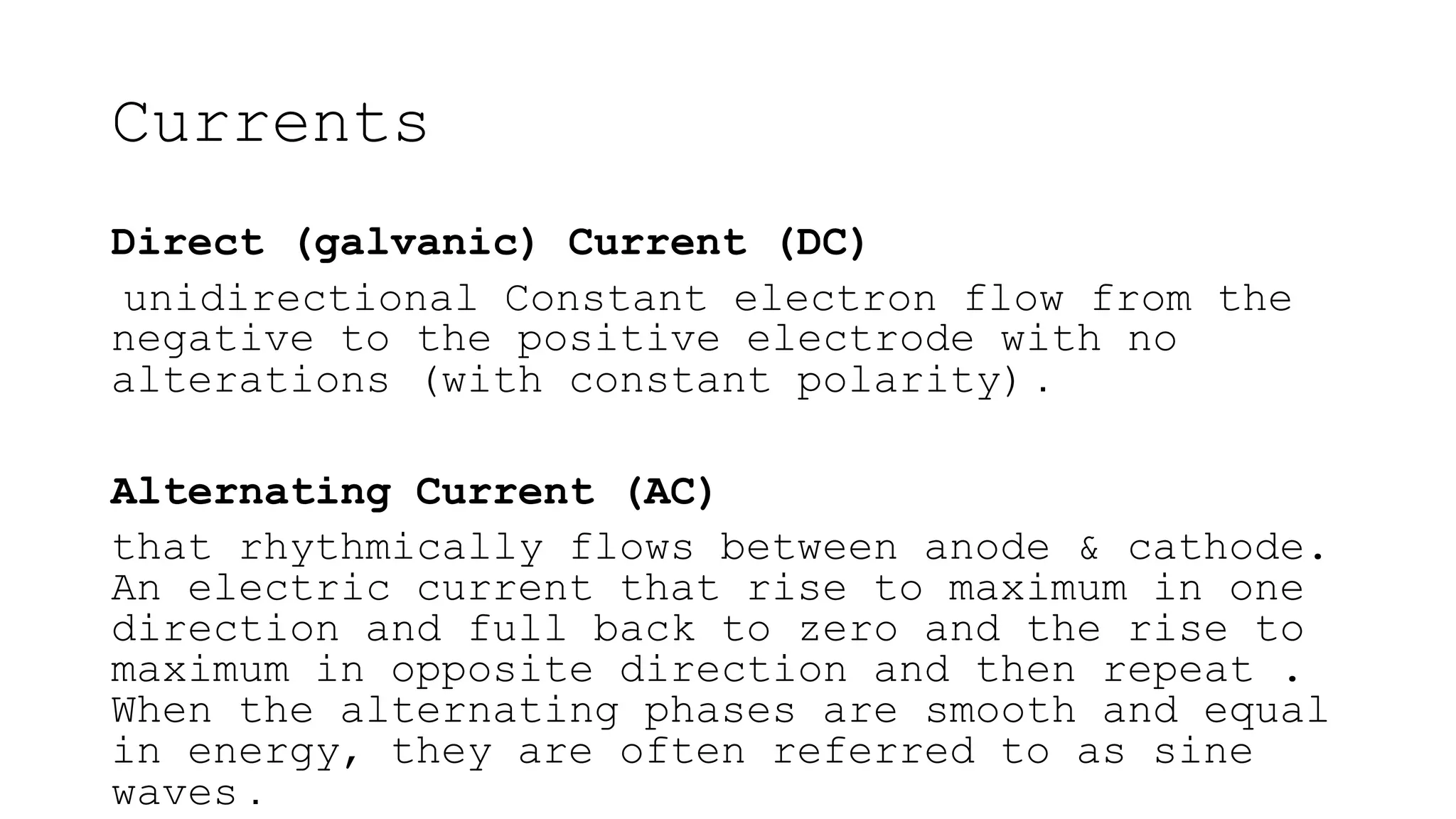
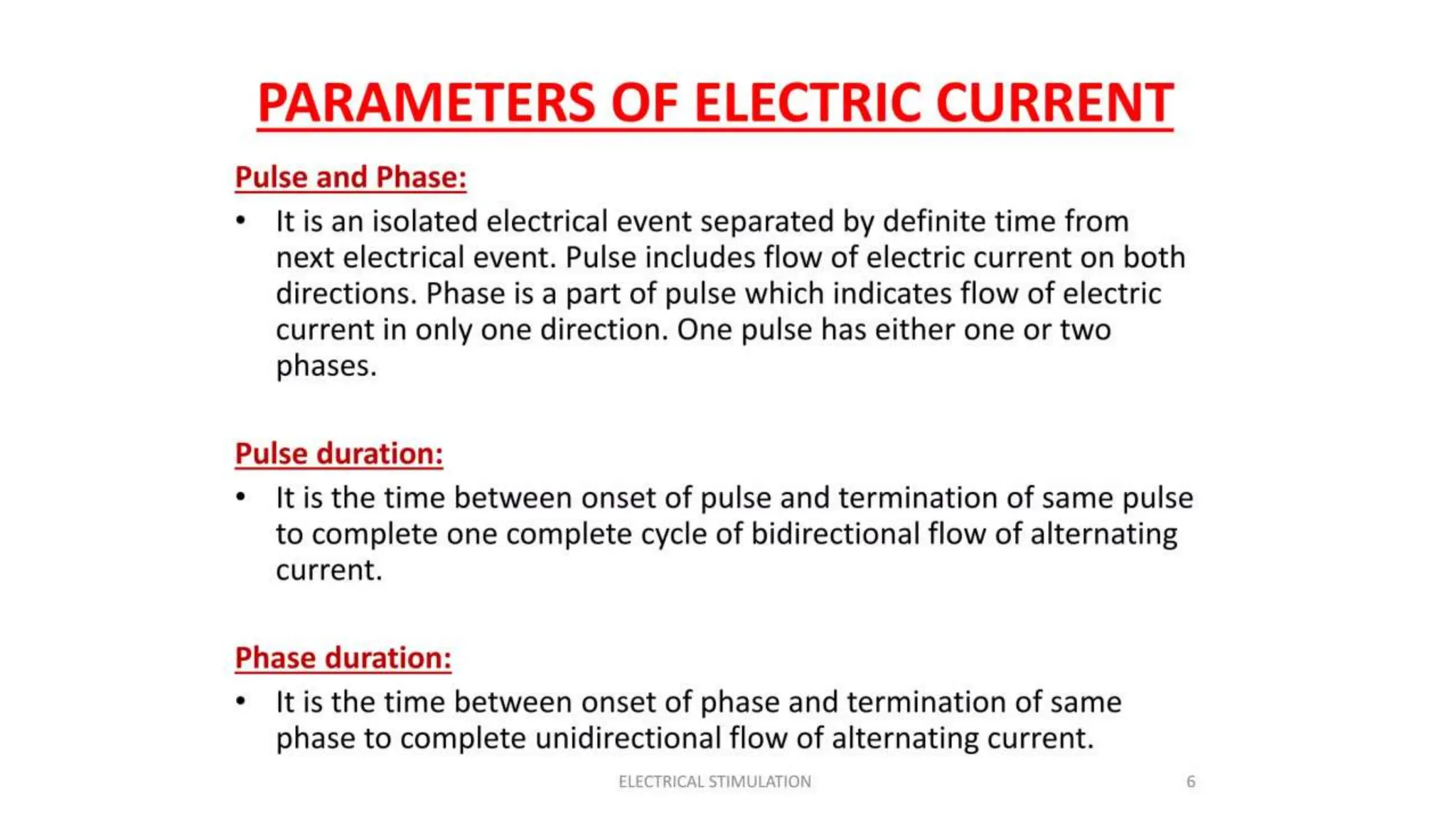
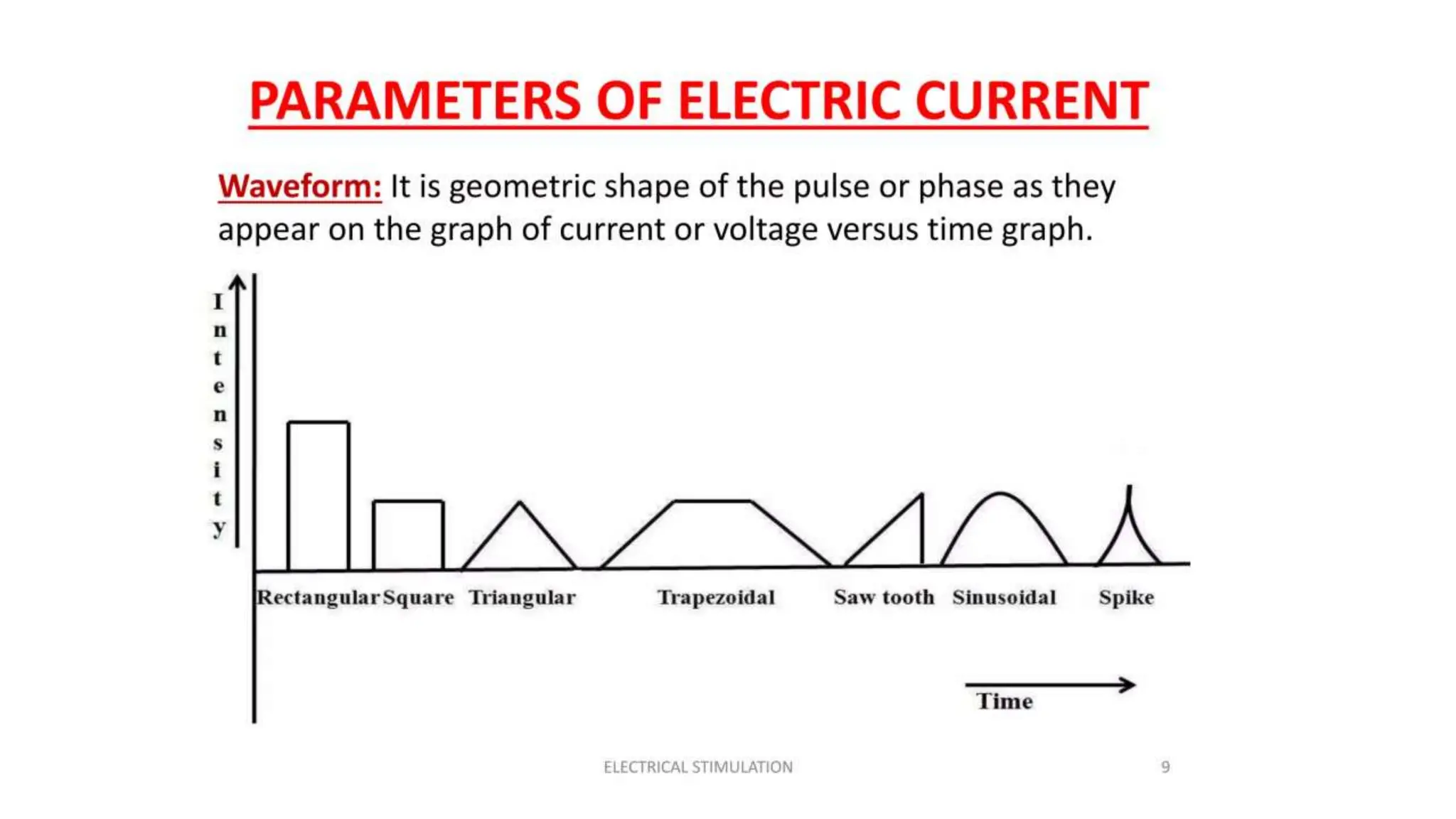
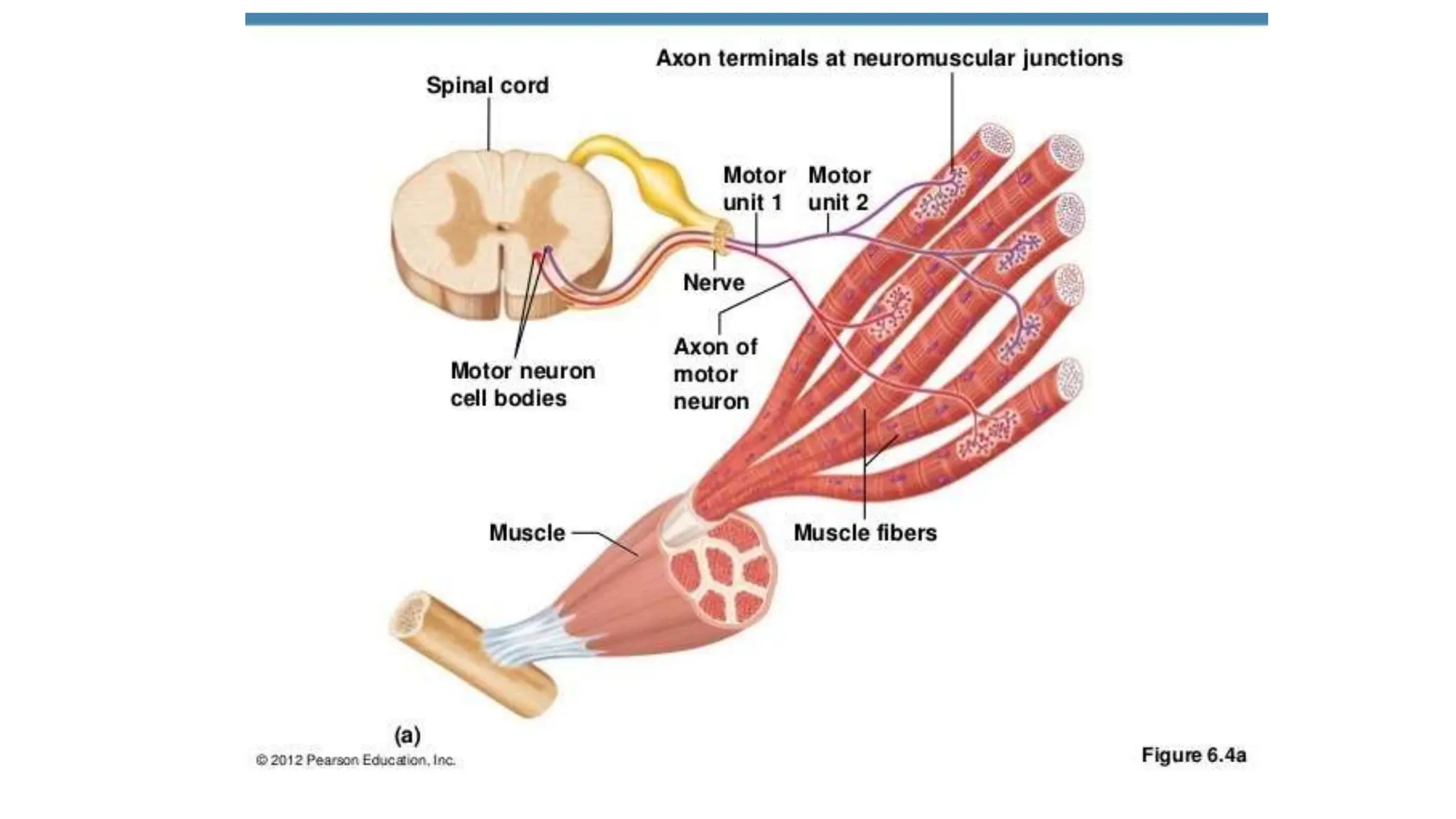
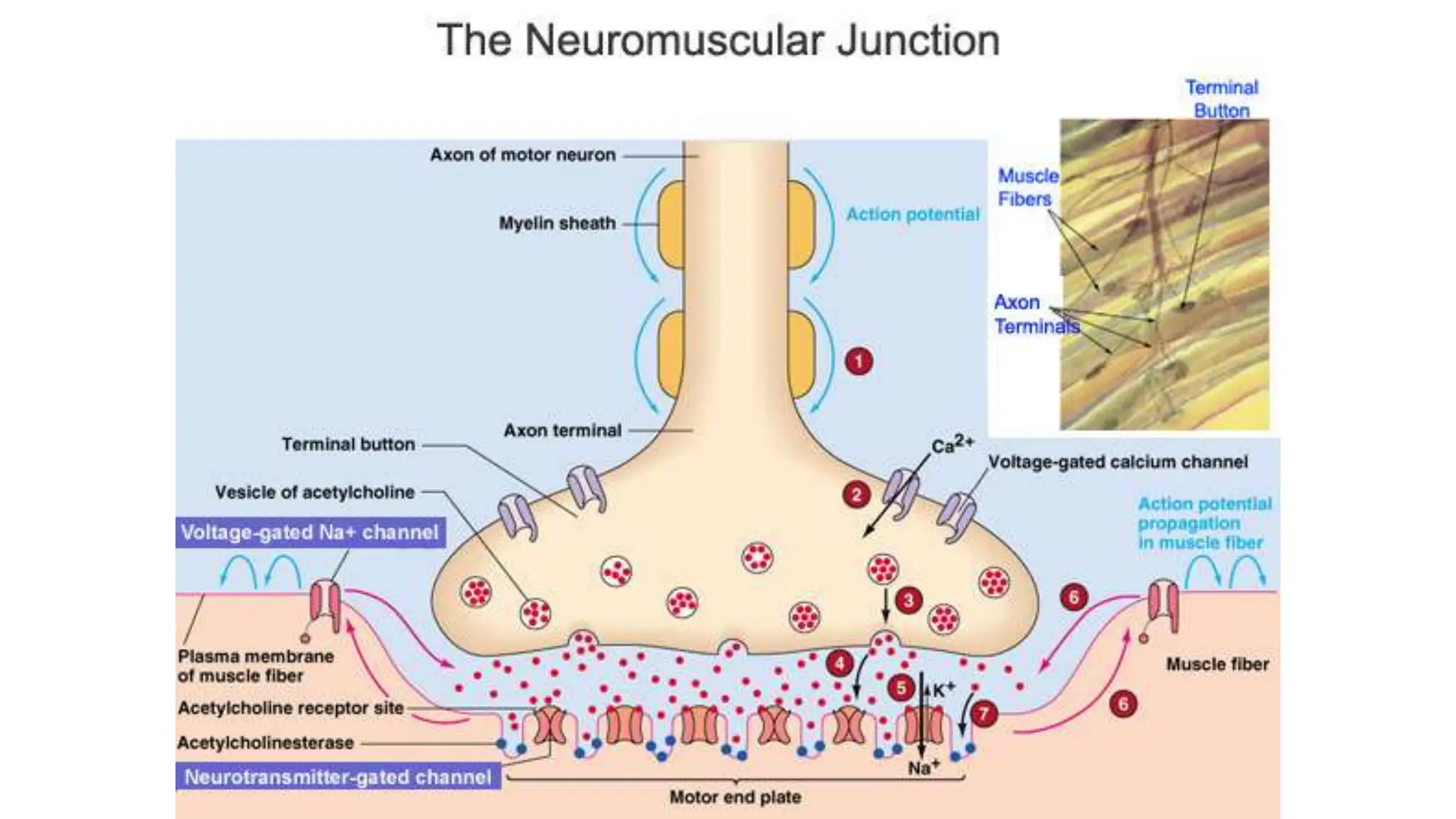
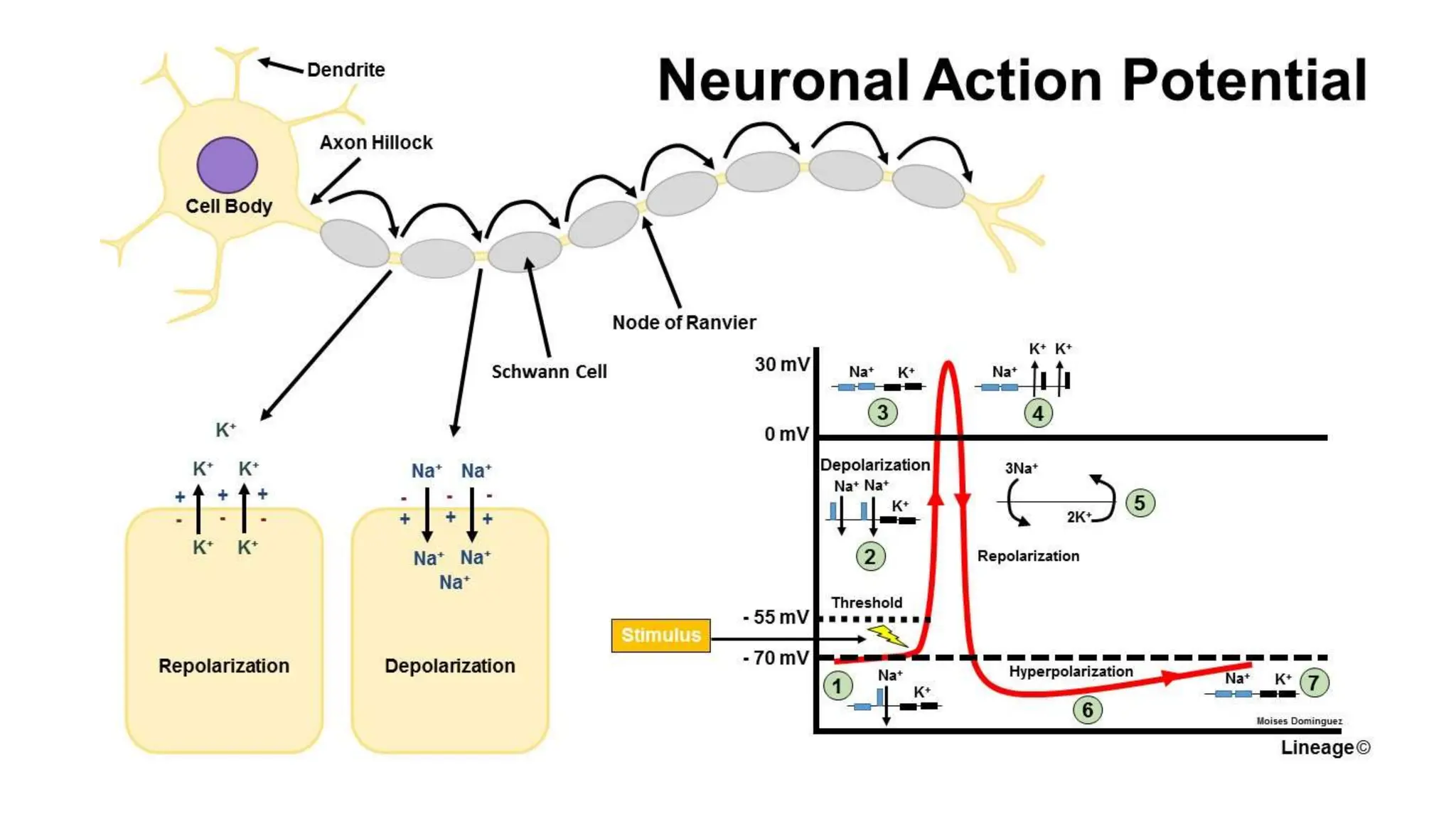
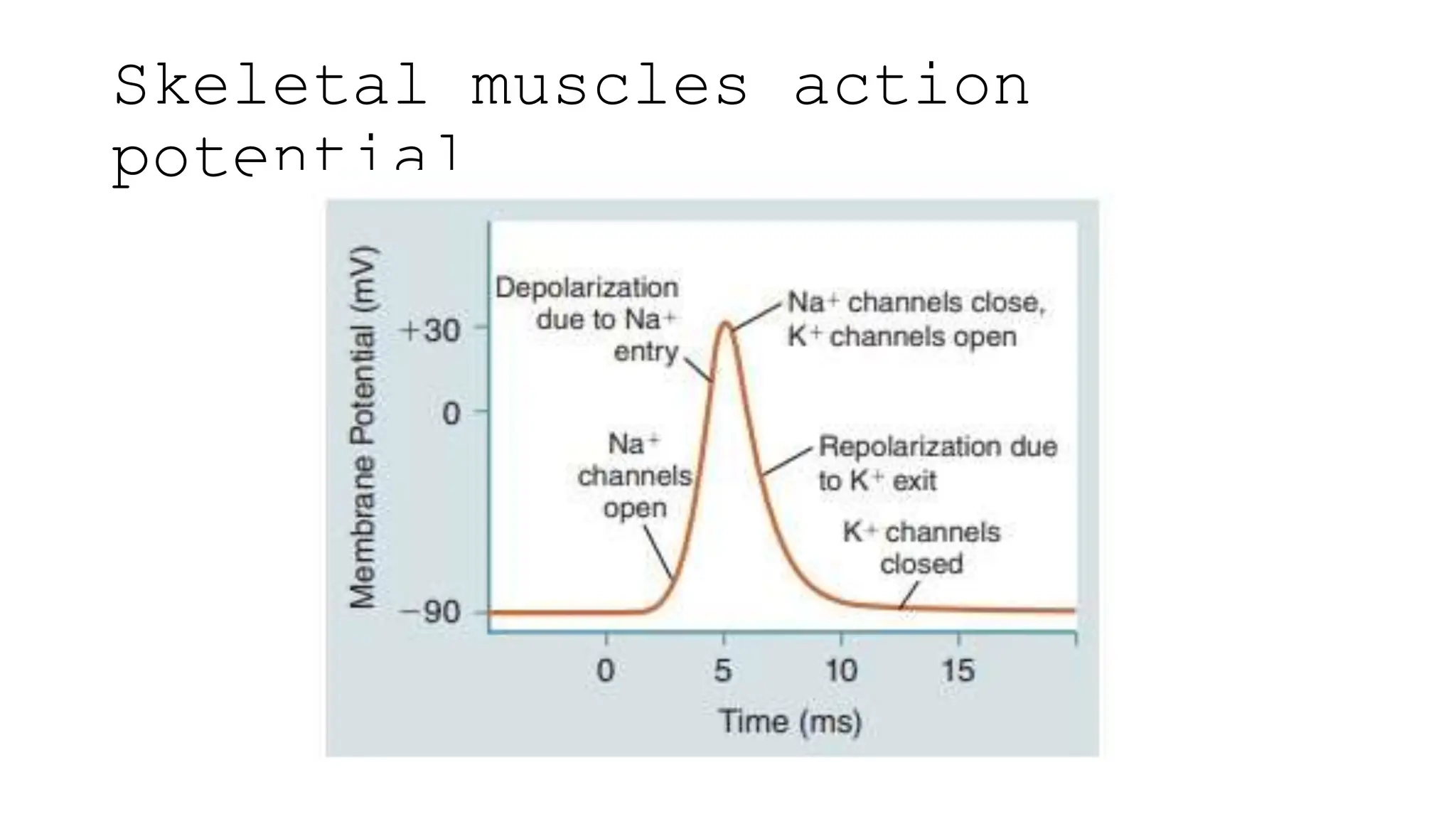
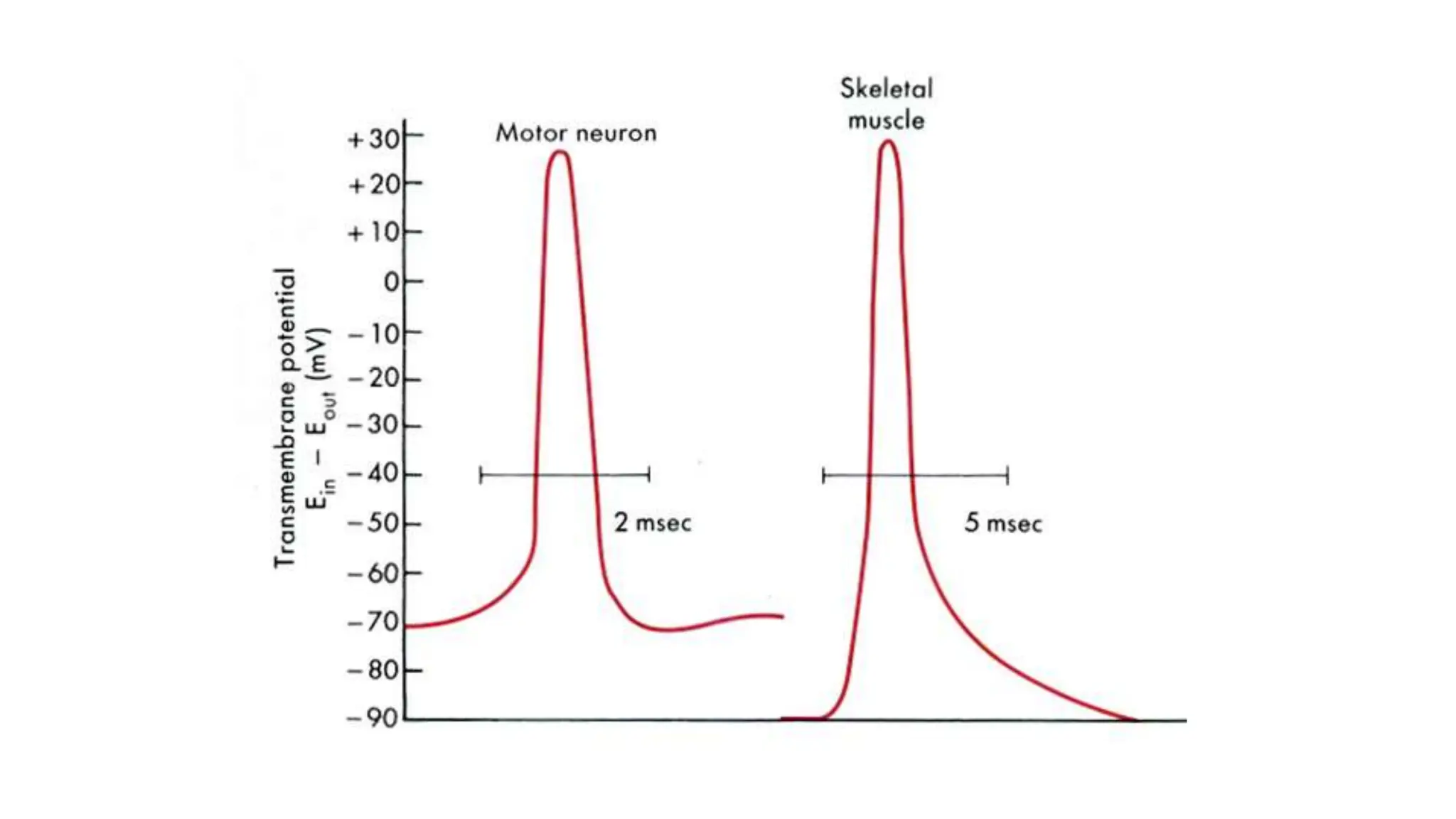
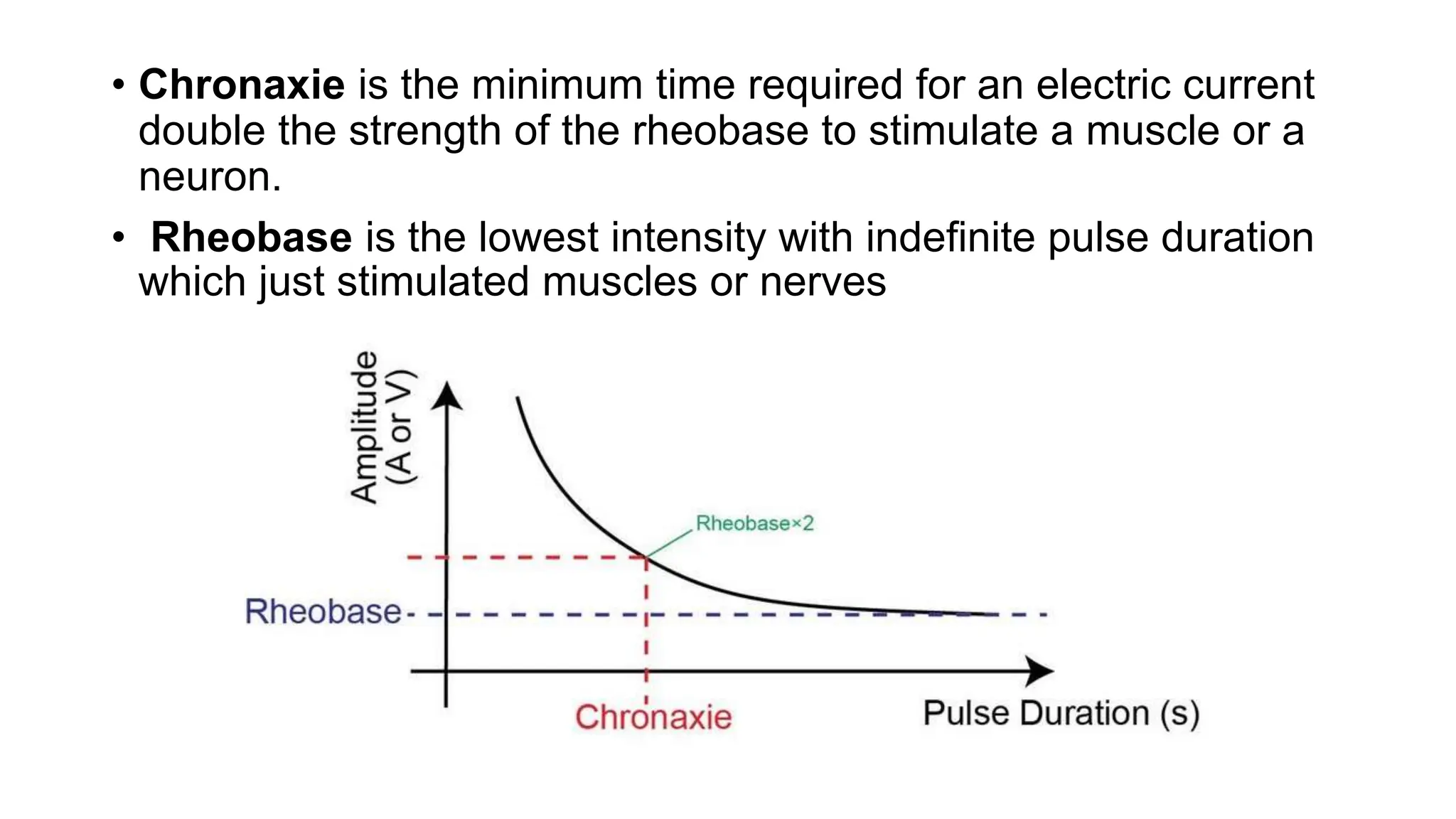
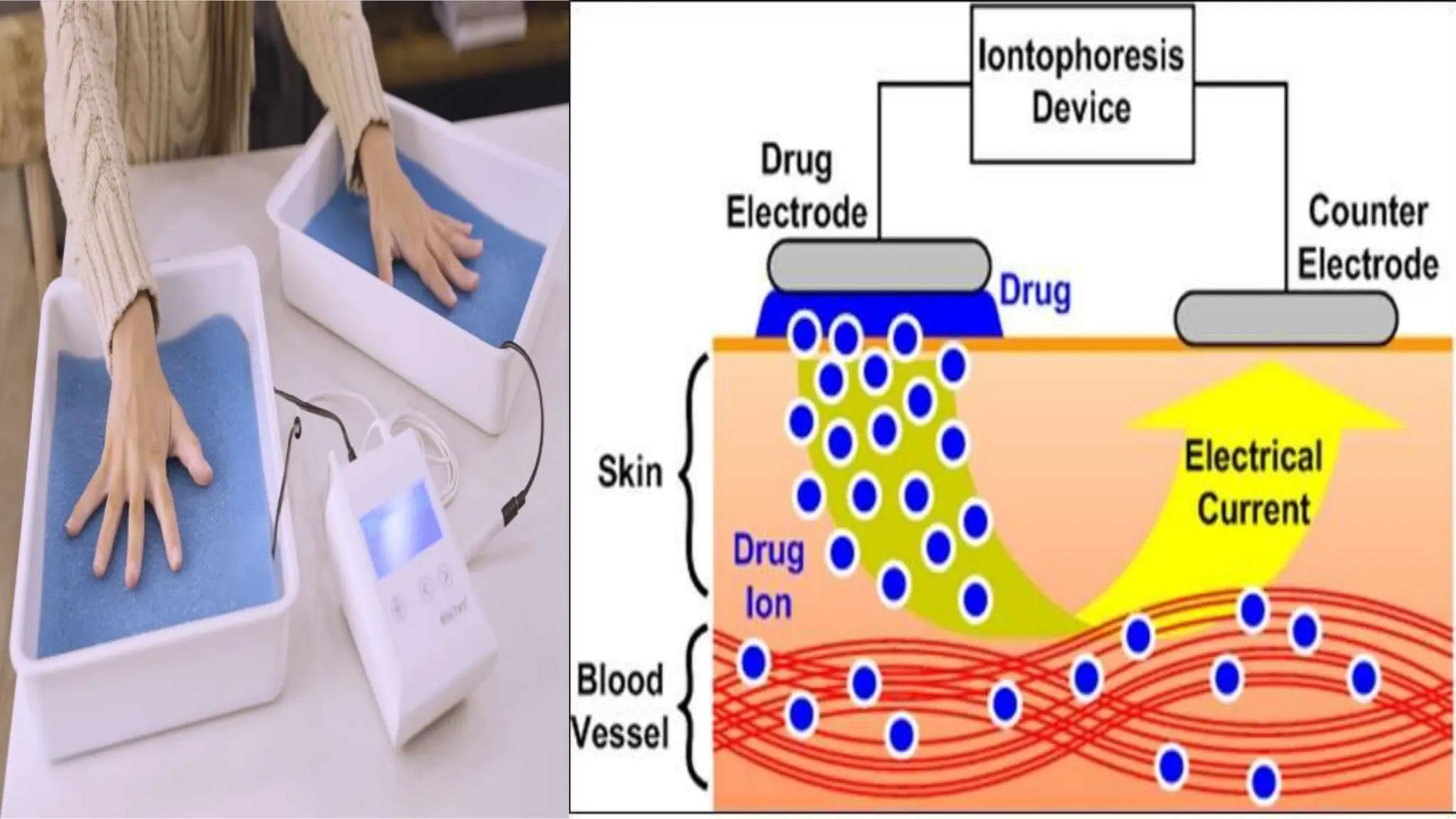
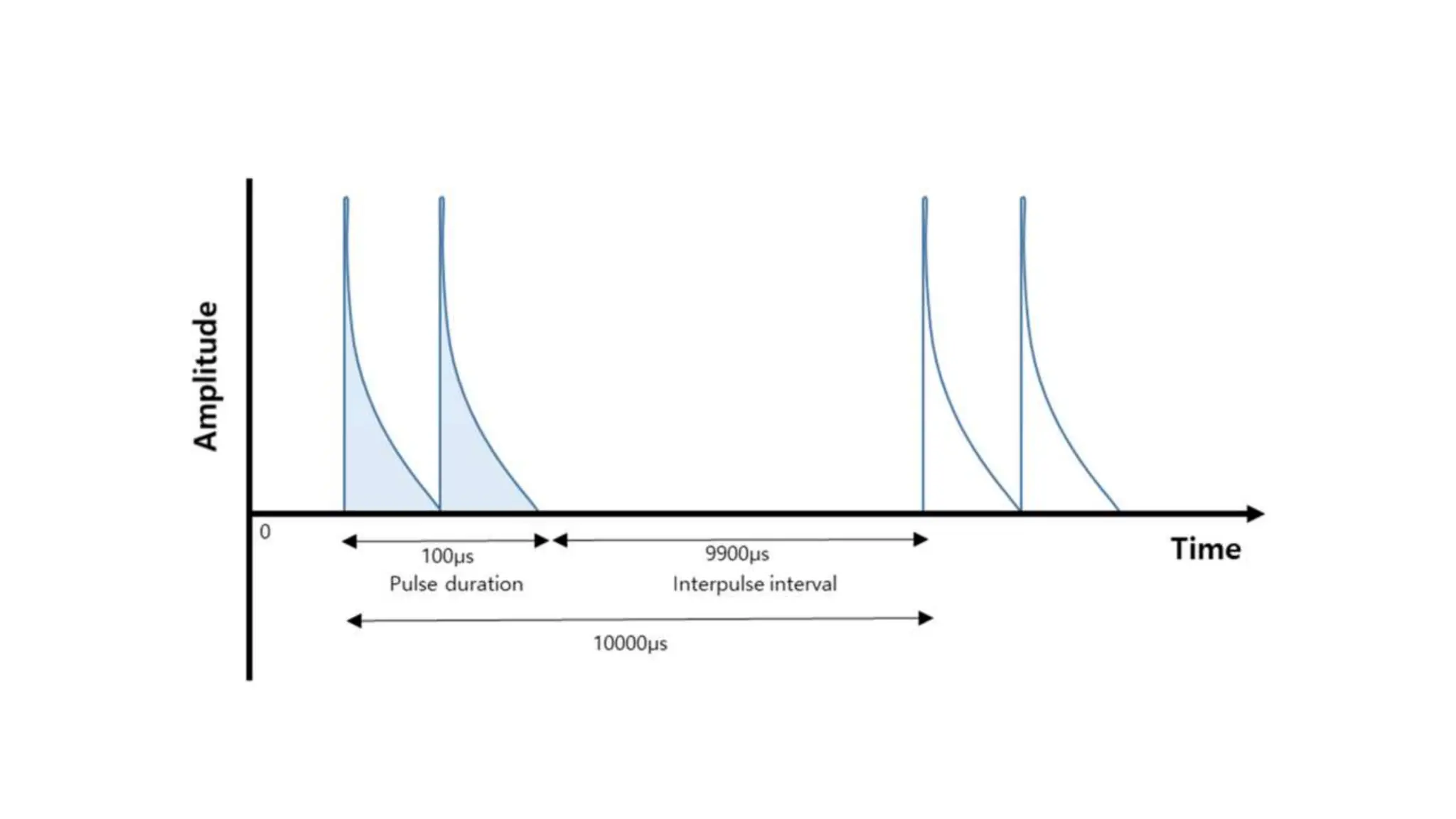
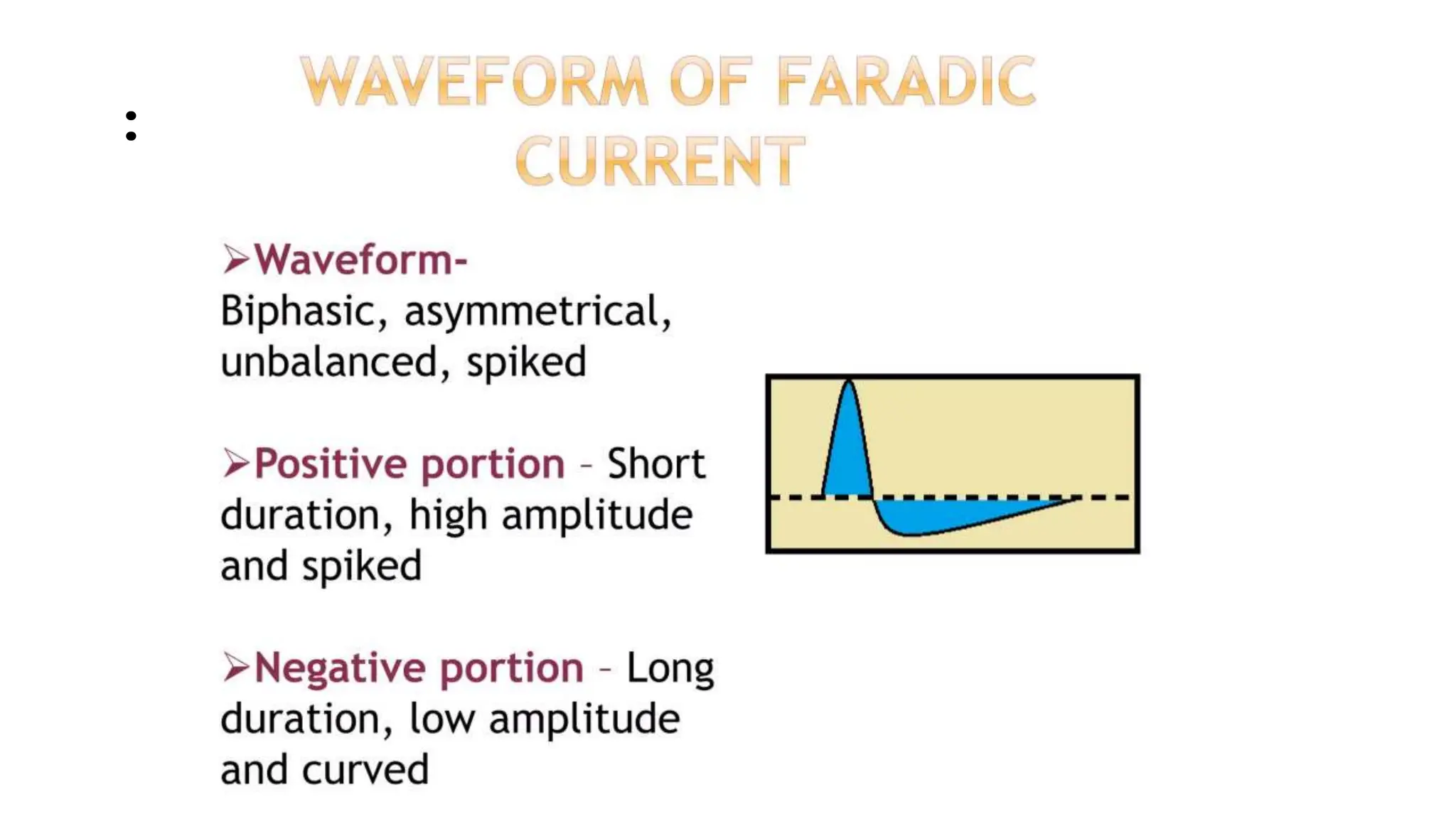
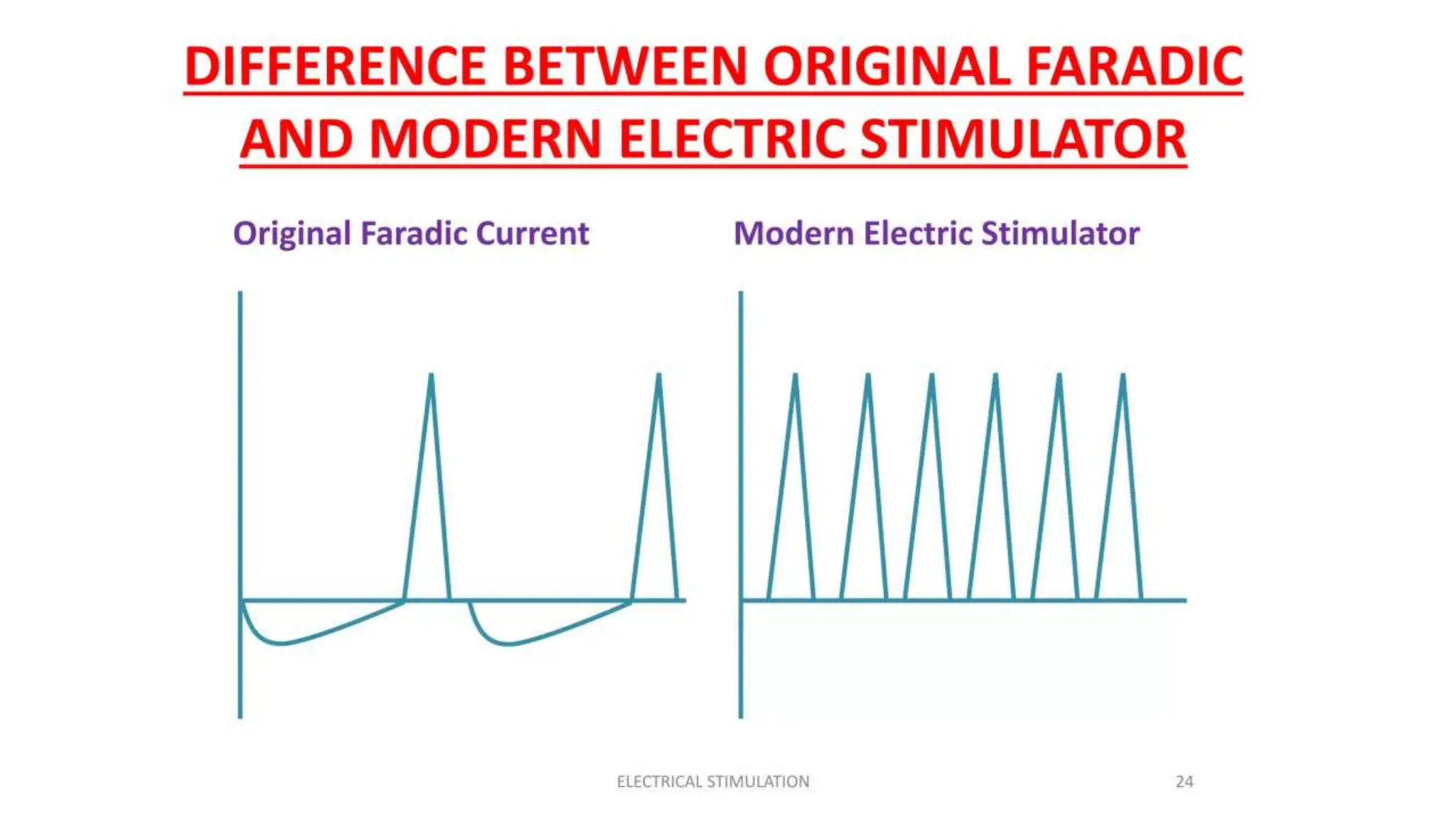
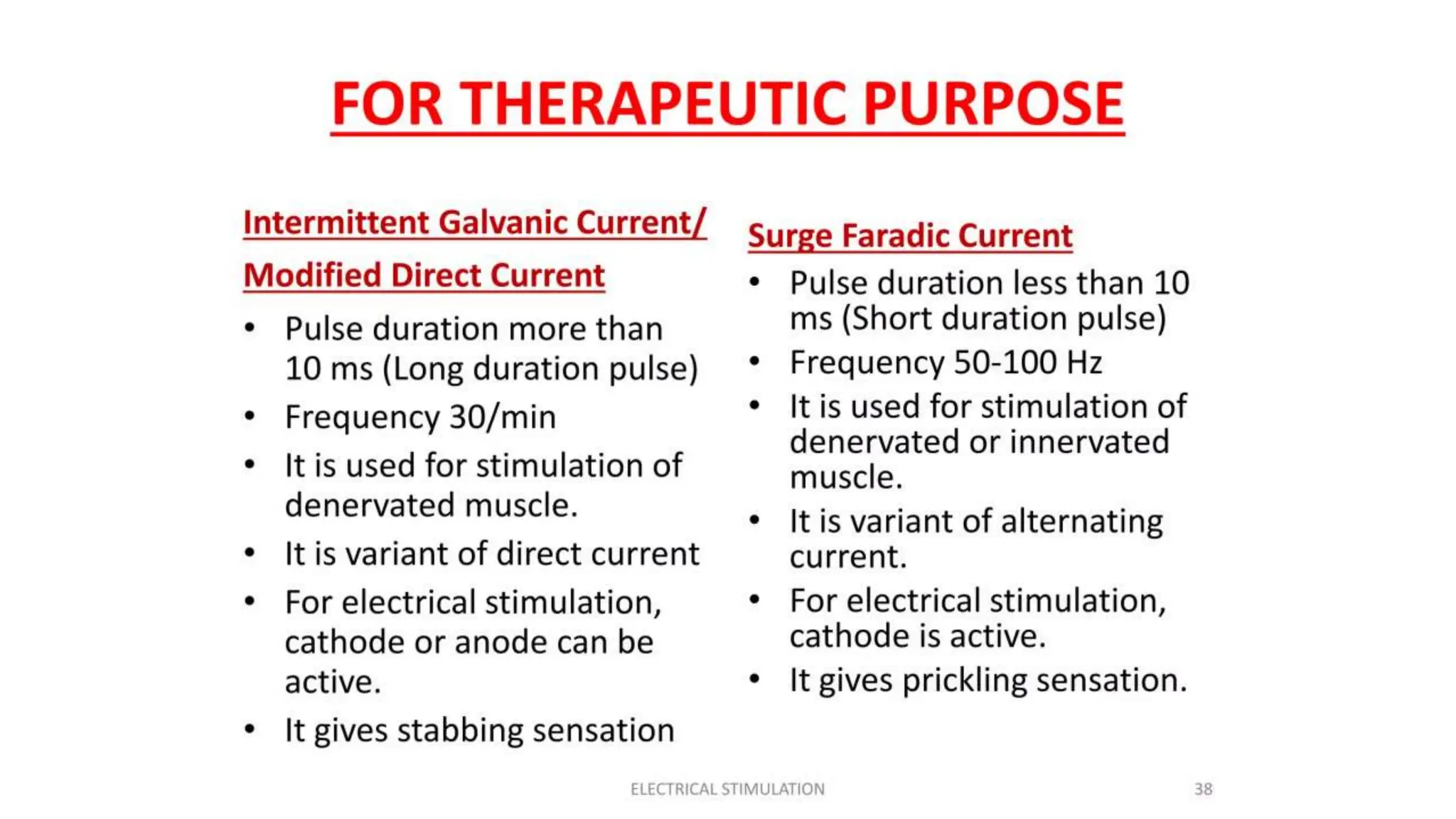
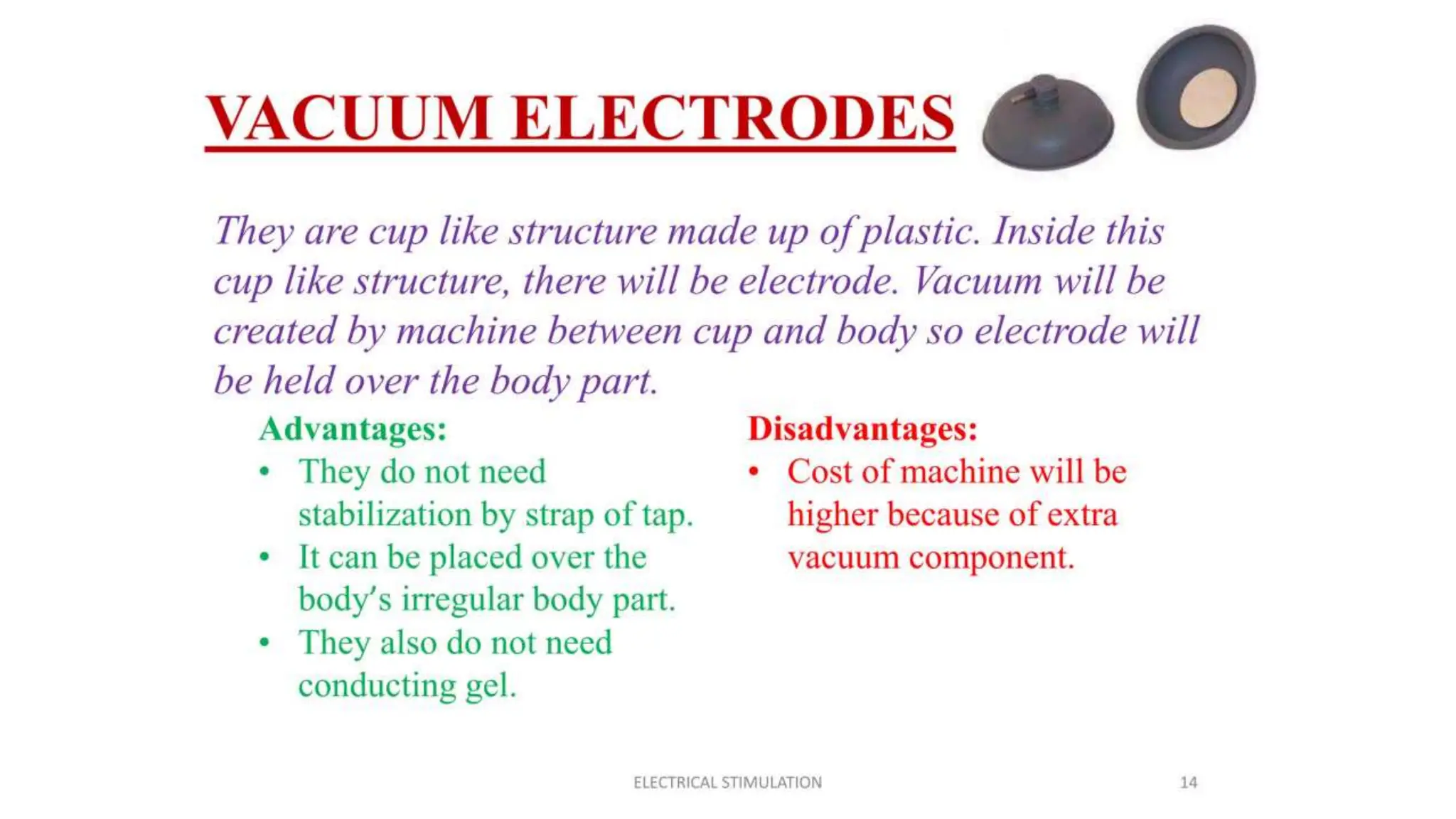
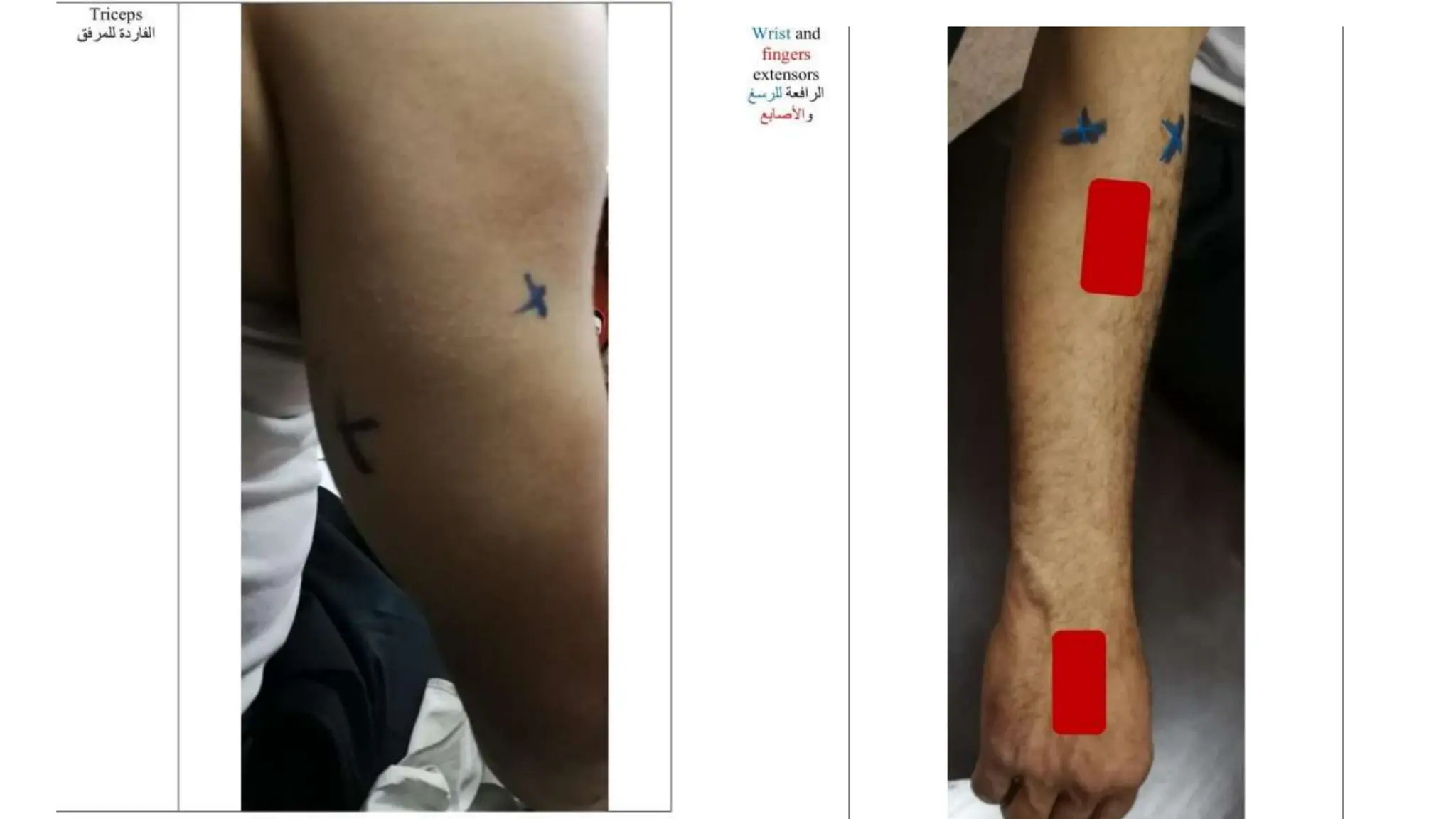
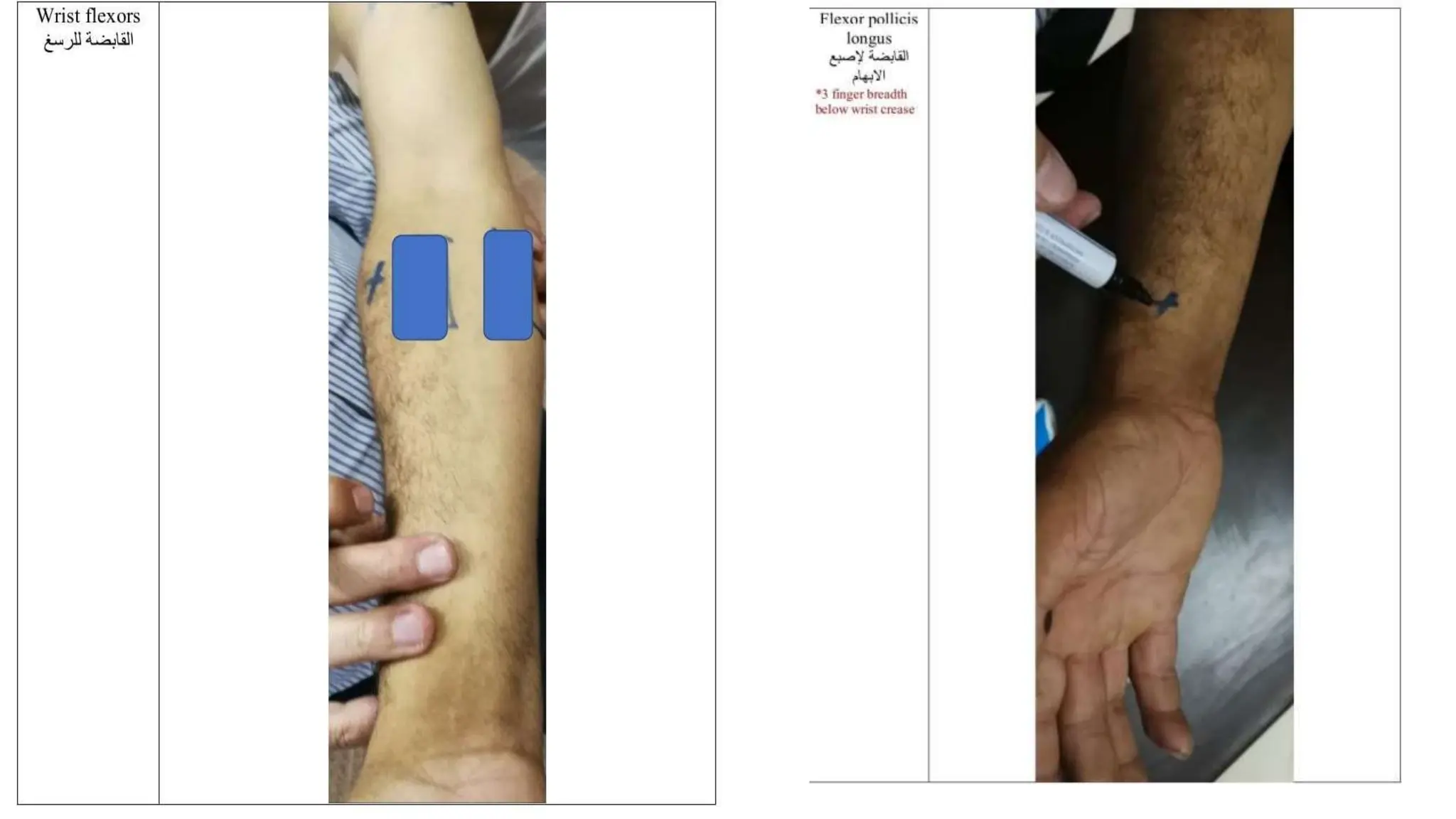
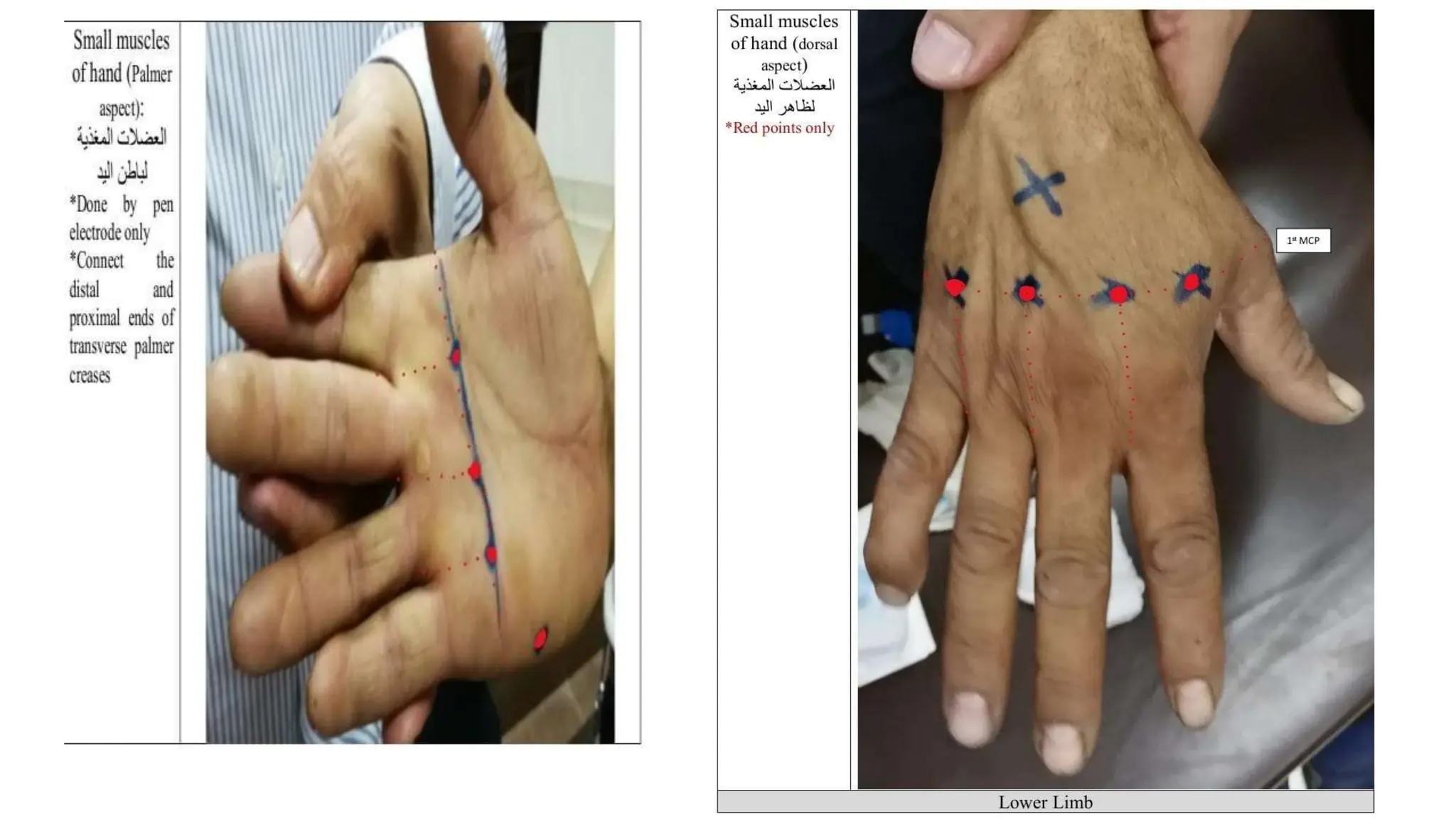
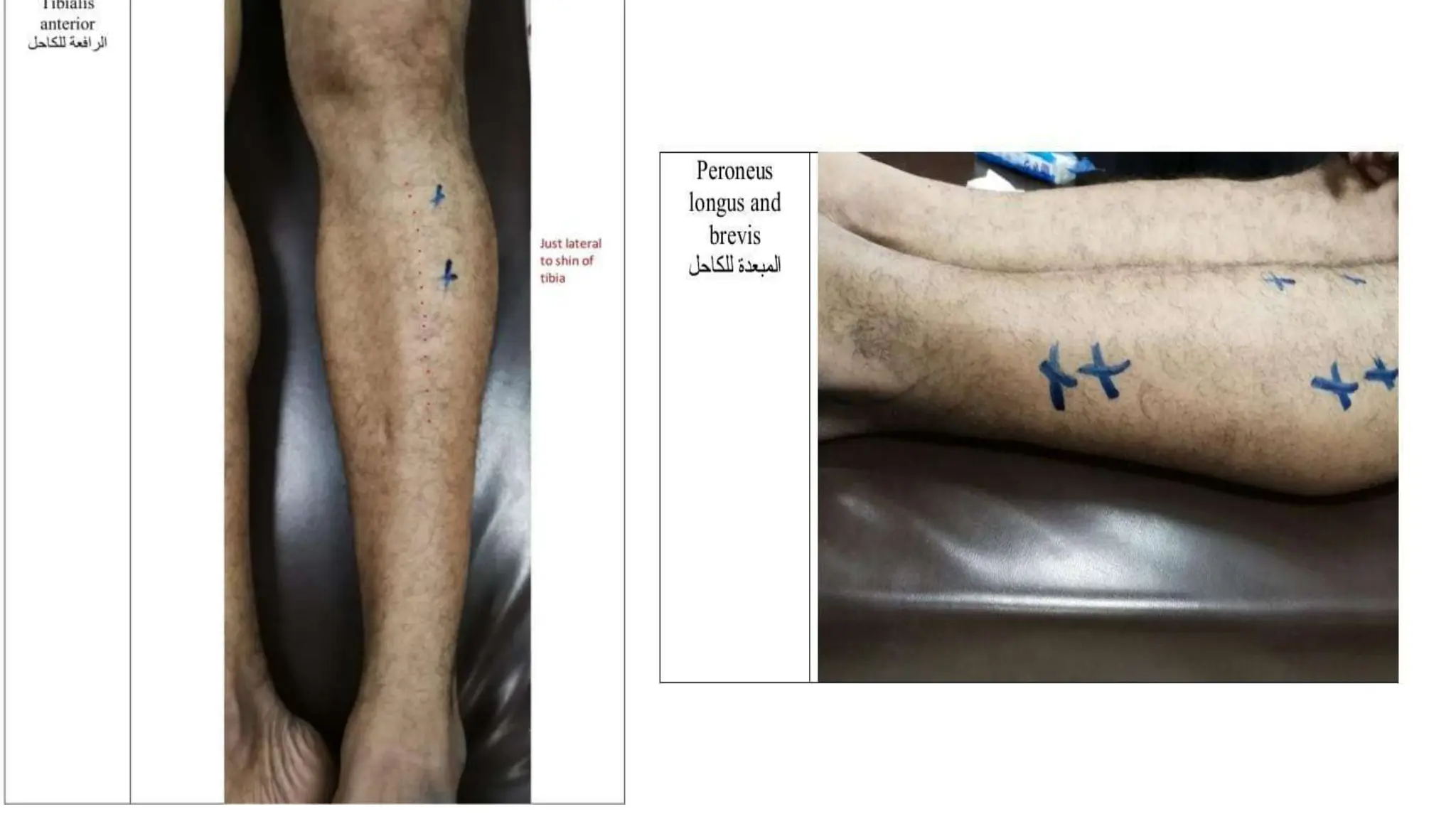
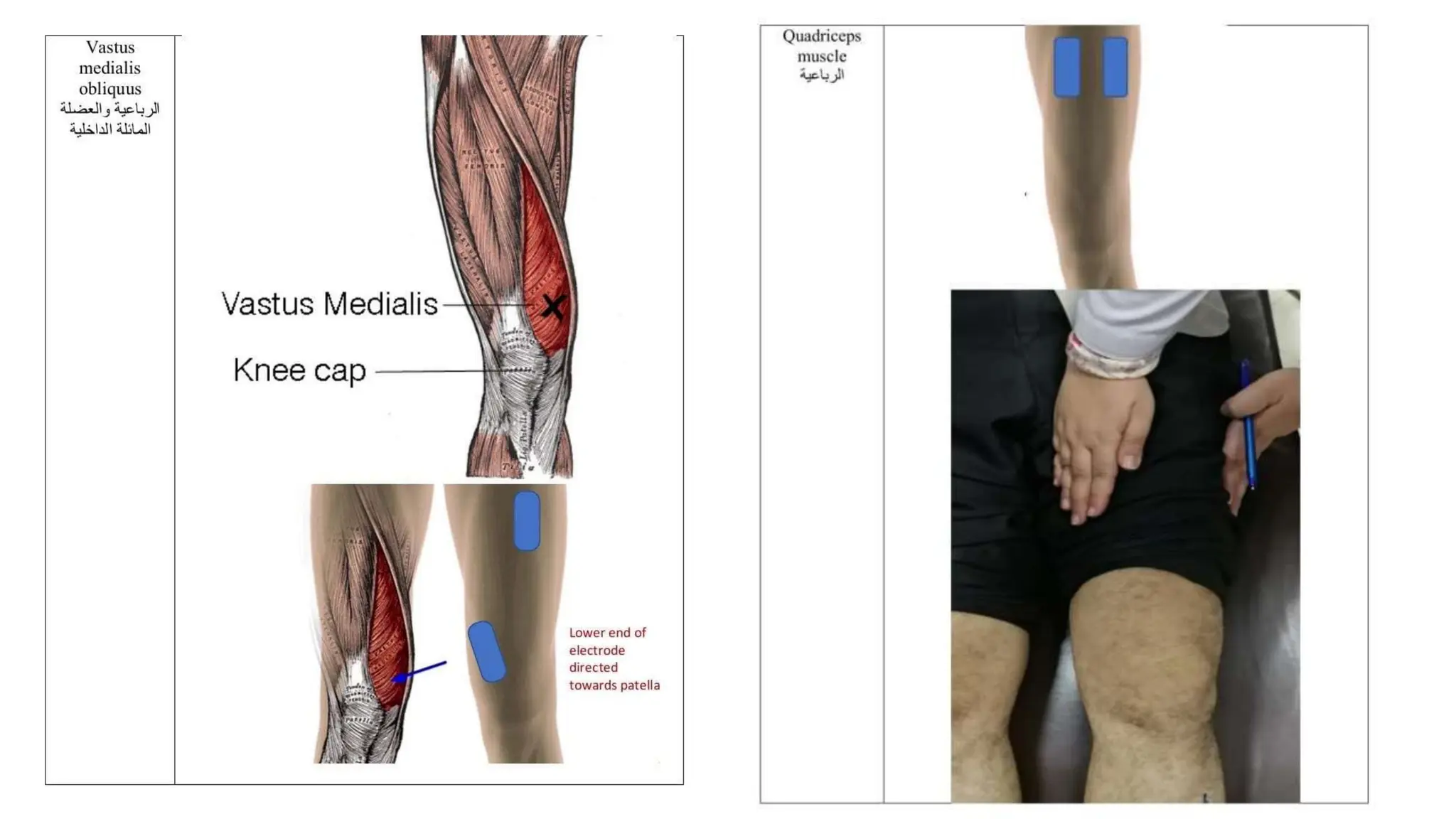
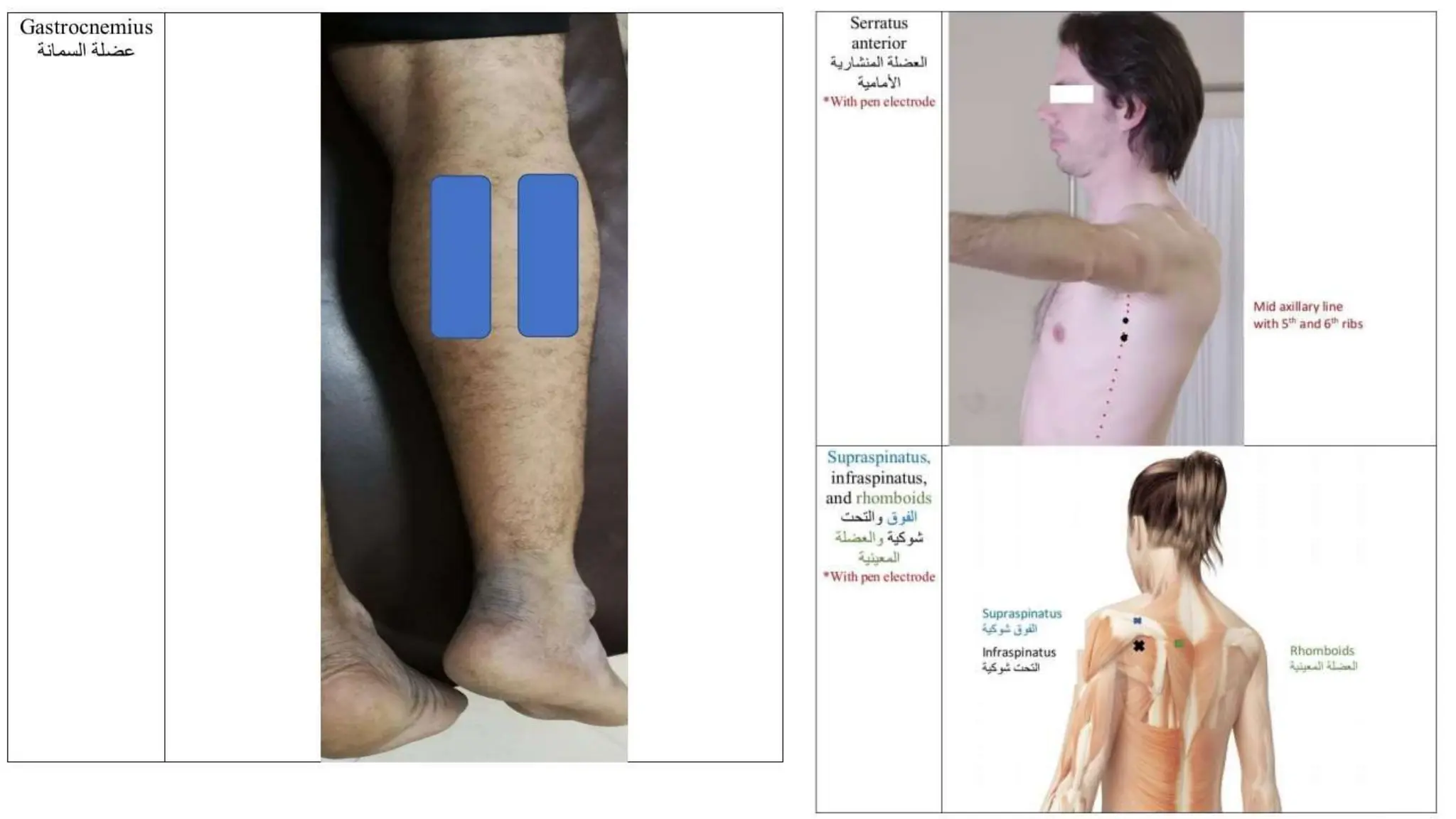
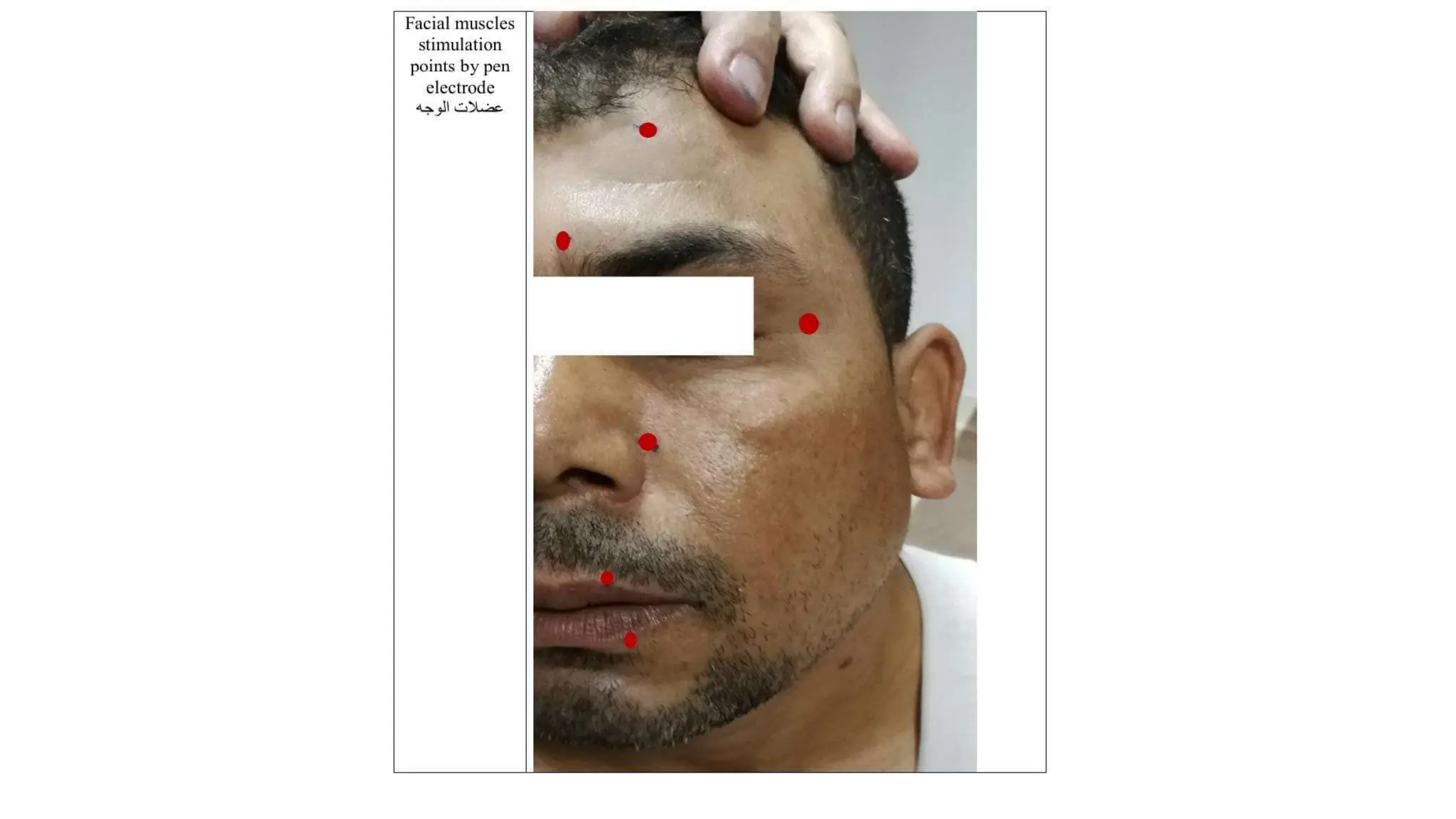
Electrostimulation therapy is a well-established physical therapy technique utilizing direct and alternating current to manage musculoskeletal and neurological issues. Key concepts include galvanic and faradic currents for muscle stimulation, with specific applications for pain relief, muscle re-education, and enhancing wound healing. Proper electrode placement and precautions are essential for effective treatment, ensuring patient safety and optimal stimulation.