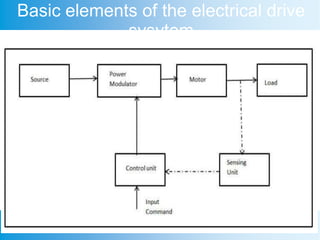
This document discusses electrical drives. It defines an electrical drive as a system that uses an electric motor to control motion for various industrial processes. The key components of an electrical drive system are a power source, power modulator, controller, motor, sensing unit, and mechanical load. The power source provides energy, typically from a 3-phase AC supply. The power modulator interfaces the motor to the power source and provides adjustable voltage, current and frequency. Common types of power modulators include controlled rectifiers, inverters, AC voltage regulators, DC choppers, and cycloconverters. Electrical drives offer advantages like flexible control, easy starting and braking, wide speed and torque ranges, and no exhaust emissions.