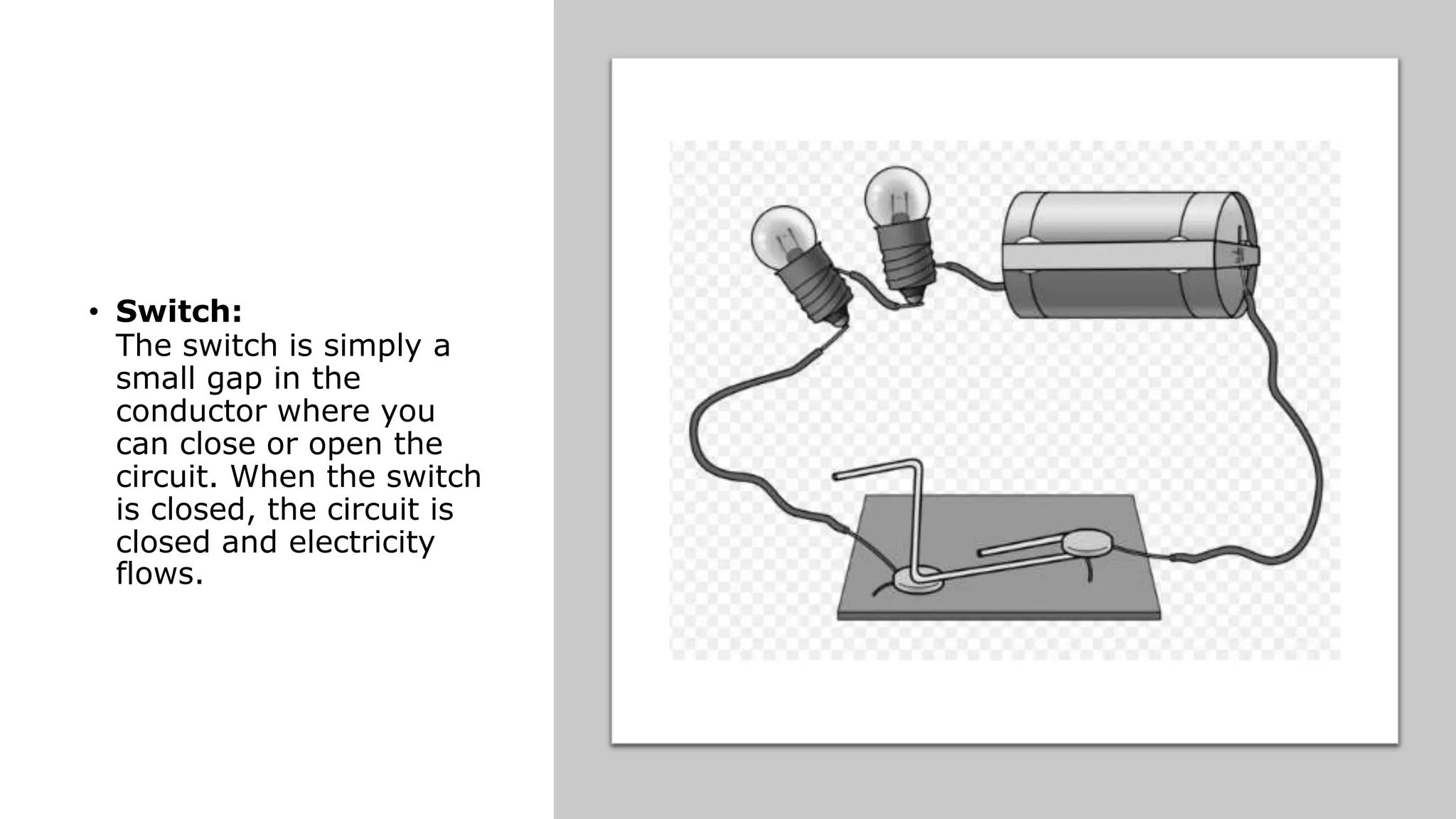
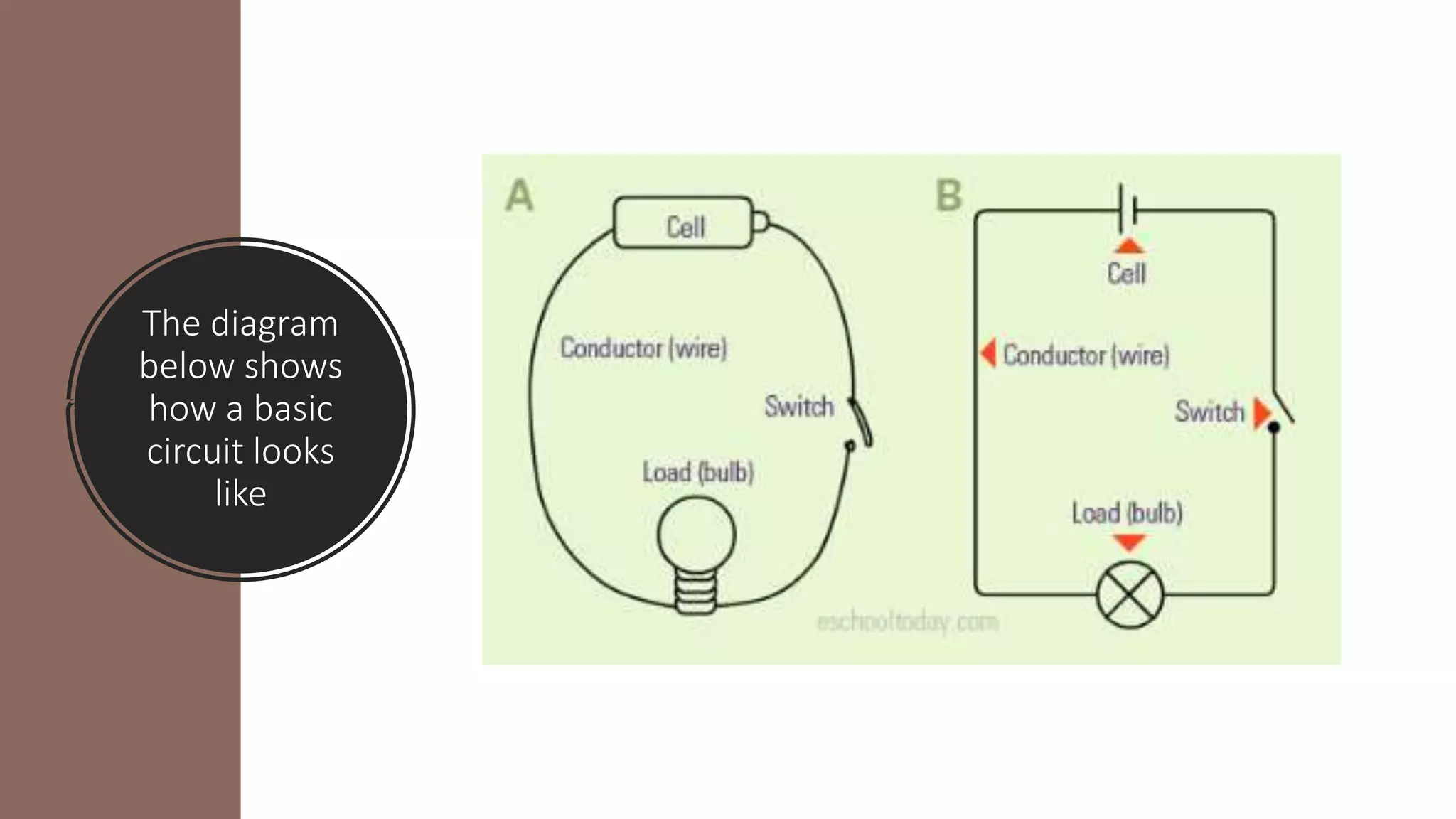
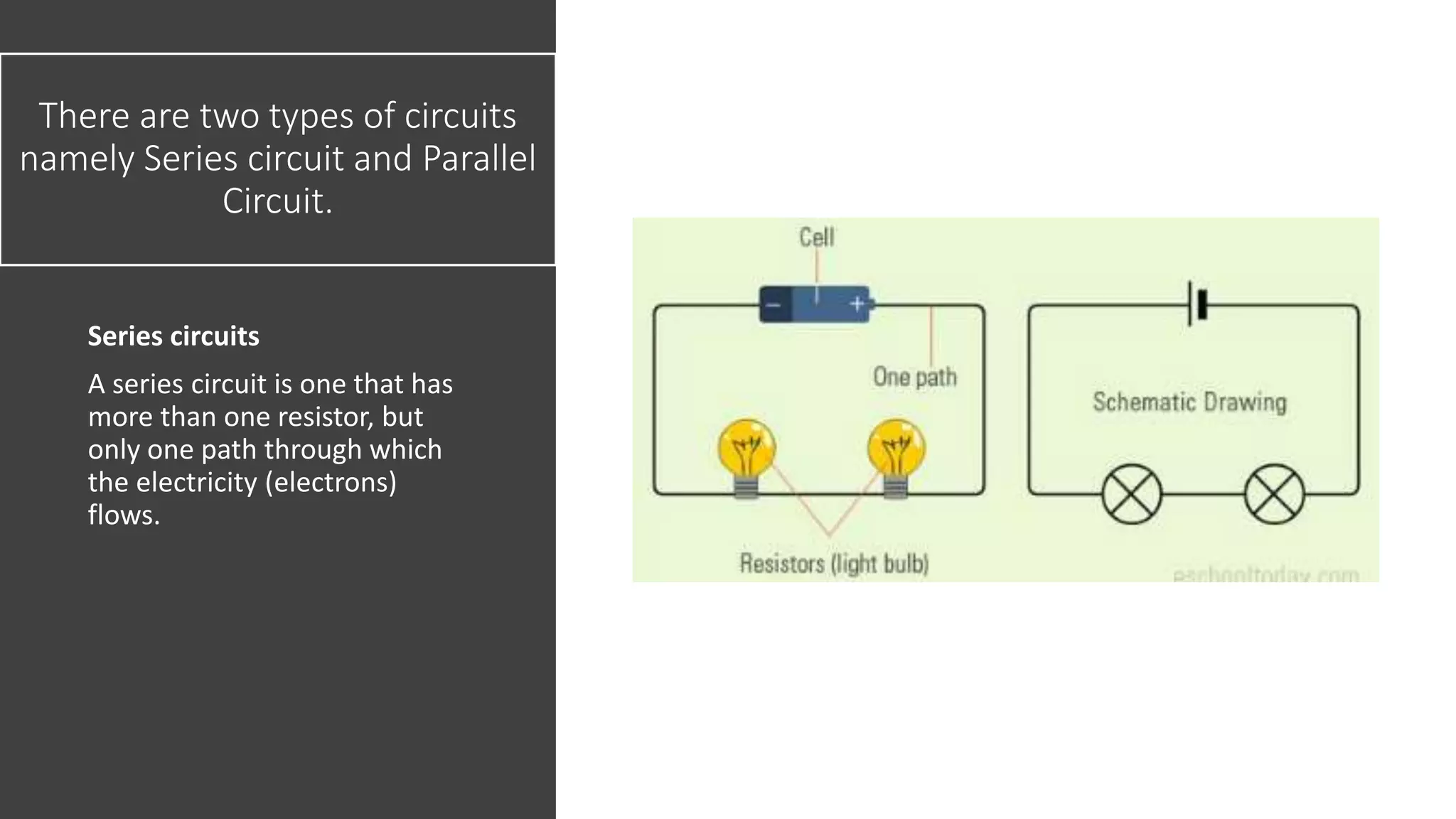
An electrical circuit is a path through which electrical current can flow. It requires a power source, conductors to carry the current, and a load. There are two main types of circuits - series and parallel. A series circuit has one path for current to flow through components sequentially. A parallel circuit has multiple paths and components connected across the power source. Short circuits occur when there is no load and wires contact each other, allowing high voltage to flow directly back to the power source and cause overheating. Circuits are protected using fuses, circuit breakers, or thermal breakers to open the circuit if excess current flows.