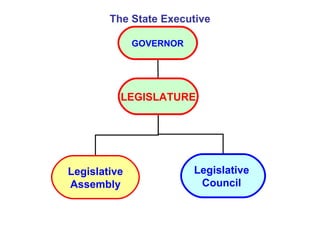
The document discusses the structure and composition of state legislatures in India. It outlines that some states have bicameral legislatures consisting of a Legislative Assembly (lower house) and Legislative Council (upper house). The Legislative Assembly is comprised of elected members representing territorial constituencies. It has powers to make laws on matters in the state and concurrent lists. The Legislative Council consists of members elected by different groups like local bodies, graduates and teachers. It is a permanent body with 1/3 of its members retiring every 2 years. Both houses have presiding officers and certain powers to conduct proceedings and pass laws.


![State Legislature [Art.169]: Creation or Abolition of the Legislative Council If Legislature passes a resolution majority of total membership and not less than 2/3 members present and voting. Transmitted to the Parliament [Art.170]: Composition of Legislative Assembly ( LA ) Each State shall have a LA Not more than 500 members Not less than 60 members Direct election from territorial constituencies. Ratio seats : population uniform Delimitation-- end of each decennial Census Universal Adult Franchise; fixed no (1) Anglo-Indian](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/state-legislature-1233675867865972-3/85/State-Legislature-4-320.jpg)
![State Legislature [Art.172]: Term of LA 5 years from date of FIRST meeting During 5 years if emergency is in operation- extension by Parliament not exceeding one year at a time in any case not extending beyond by six months from end of emergency Qualifications: Citizen of India: 25 years of age Such Qualification as may be prescribed by Parliament by law. Sessions: At least twice a year —interval not more than six months](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/state-legislature-1233675867865972-3/85/State-Legislature-5-320.jpg)




![State Legislature [Art.171]: Composition of Legislative Council ( LC ) Not more than 1/3 rd the members of LA of the State Not less than 40 members unless Parliament provides by Law. Until such law by the Parliament [Art.171] clause c provides for 1/3 rd elected by electorate of Municipalities, District Boards & local authorities specified by Law 1/12 th graduates of any university in territory of India - 3 yrs Residence in state. 1/4 th Teachers Constitution -3yrs-not below secondary school – equivalent by law-Parliament 1/3 rd non LA members-elected by LA members. Remaining nominated by Governor Literature, Art, Science, Social Service, co-op movement](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/state-legislature-1233675867865972-3/85/State-Legislature-10-320.jpg)
