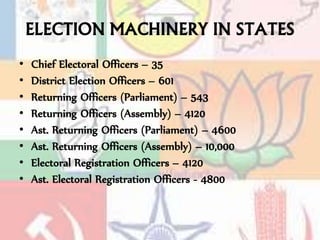
The Election Commission of India is responsible for administering elections in the country. It consists of a Chief Election Commissioner and two Election Commissioners. The key functions of the Commission include being the guardian of free and fair elections through measures like the Model Code of Conduct, registering political parties, setting limits on election expenses, and prohibiting the publication of opinion polls. It also has quasi-judicial powers. The Commission aims to ensure that elections are held regularly and democratically through a large election machinery across states.




![FUNCTIONS & POWERS
3. Registration of Political Parties
• A law regarding to this registration process was enacted in 1989 and number of
parties got registered with Commission.[8] It helps to avoid confusion and headache
of the administrative machinery as well as confusion of the electorate. It ensures
that political parties can practice democracy only by their registration.
4. Limits on Poll Expenses
• To get rid of the growing influences and vulgar show of money during elections the
Election Commission has made many suggestions in this regard. The Election
Commission has fixed the legal limits on the amount of money which a candidate
can spend during election campaigns. These limits have been revised from time to
time. The Election Commission by appointing observers keeps an eye on the
individual account of election expenditure. The contestants are also required to give
details of expenditure with 30 days of declaration of results. However, political
parties do not adhere to the financial ‘Lakshman Rekha’ as huge amount are spent
by parties under the garb of their supporters.
• The campaign period was reduced by the Election Commission from 21 to 14 days
for Lok Sabha and Assembly elections; it is for to trim down election expenditure.
The Election Commission’s this attempt to impose these measures has been a move
in the right direction. Moreover, Election Commission takes details of the
candidate's asset on affidavit at the time of submitting nomination paper.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electioncommision-140608232150-phpapp01/85/Election-commision-India-5-320.jpg)