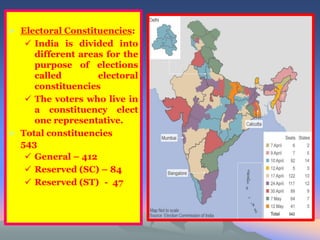
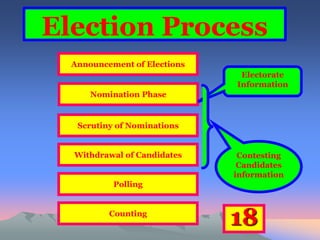
India holds regular free and fair elections to determine the composition of government. The country is divided into 543 electoral constituencies where voters elect one representative to the Lok Sabha. Elections follow a process where candidates are nominated, an election campaign occurs, voting takes place at polling stations on a single day, and votes are counted afterwards to determine the winner in each constituency. The Election Commission of India oversees the entire process and enforces rules to ensure free and fair elections.