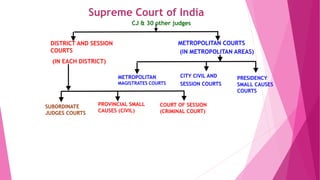
This document provides information about the structure and functions of the Supreme Court of India. It begins by explaining that the judiciary is one of three branches of the Indian state and discusses the pyramidal structure of the court system with the Supreme Court at the apex. It then describes some key responsibilities of the independent judiciary in India. The document goes on to explain the different types of jurisdiction exercised by the Supreme Court, including original, appellate and advisory jurisdiction. It also discusses the appointment and qualifications of Supreme Court judges, as well as the independence of the judiciary. In addition, it covers public interest litigation and the process for impeachment of a judge.