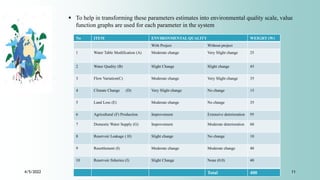
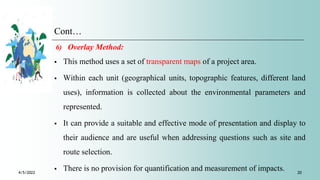
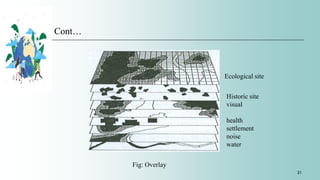
The document discusses various methodologies for environmental impact assessment (EIA), highlighting qualities like systematic approach, data organization, and predictive capability. It outlines methods such as baseline studies, checklists, matrices, and cost/benefit analysis, emphasizing their strengths and weaknesses in evaluating project impacts. Ultimately, the selection of an appropriate methodology should consider simplicity, comprehensiveness, and the ability to communicate results effectively.