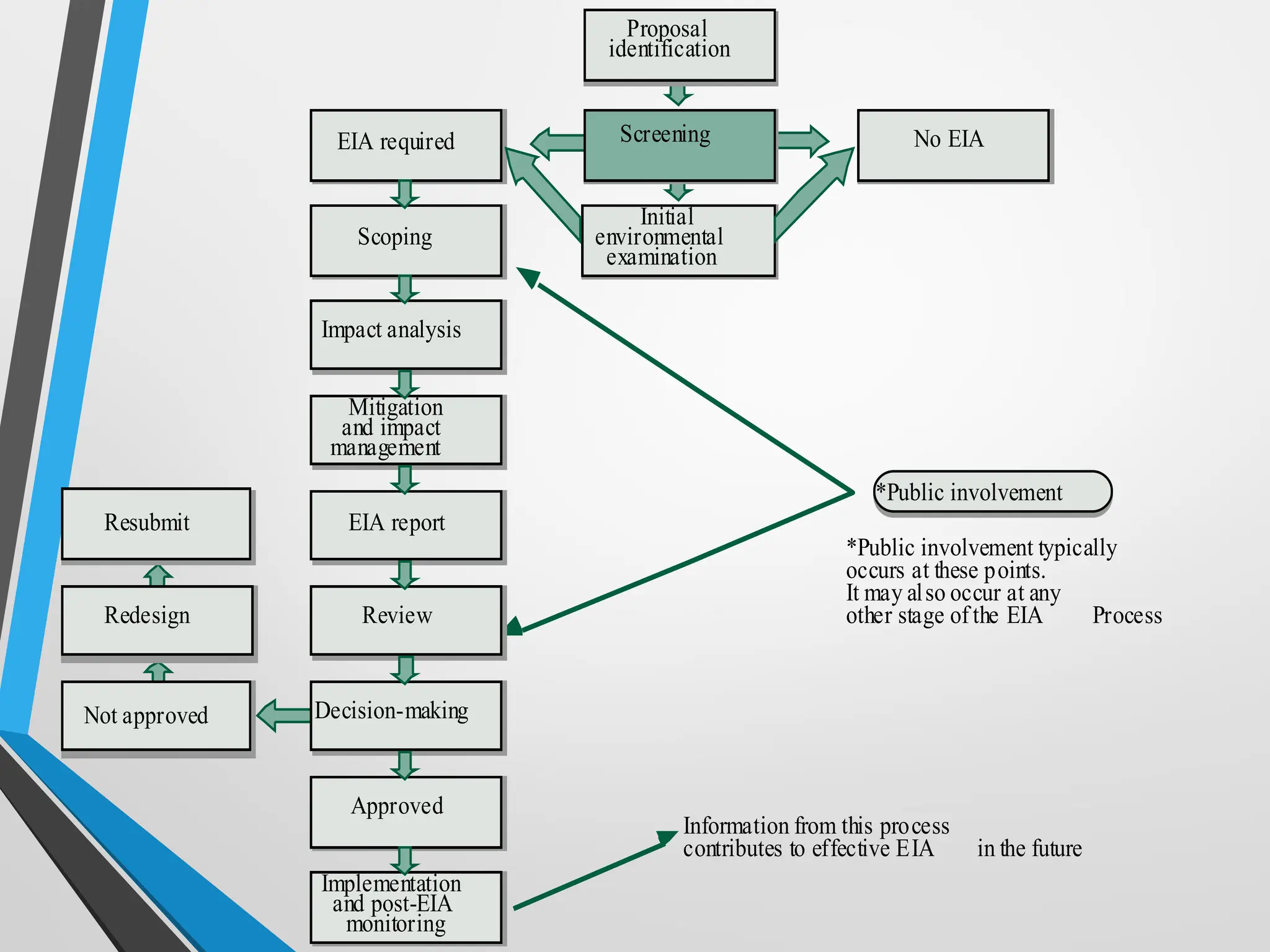
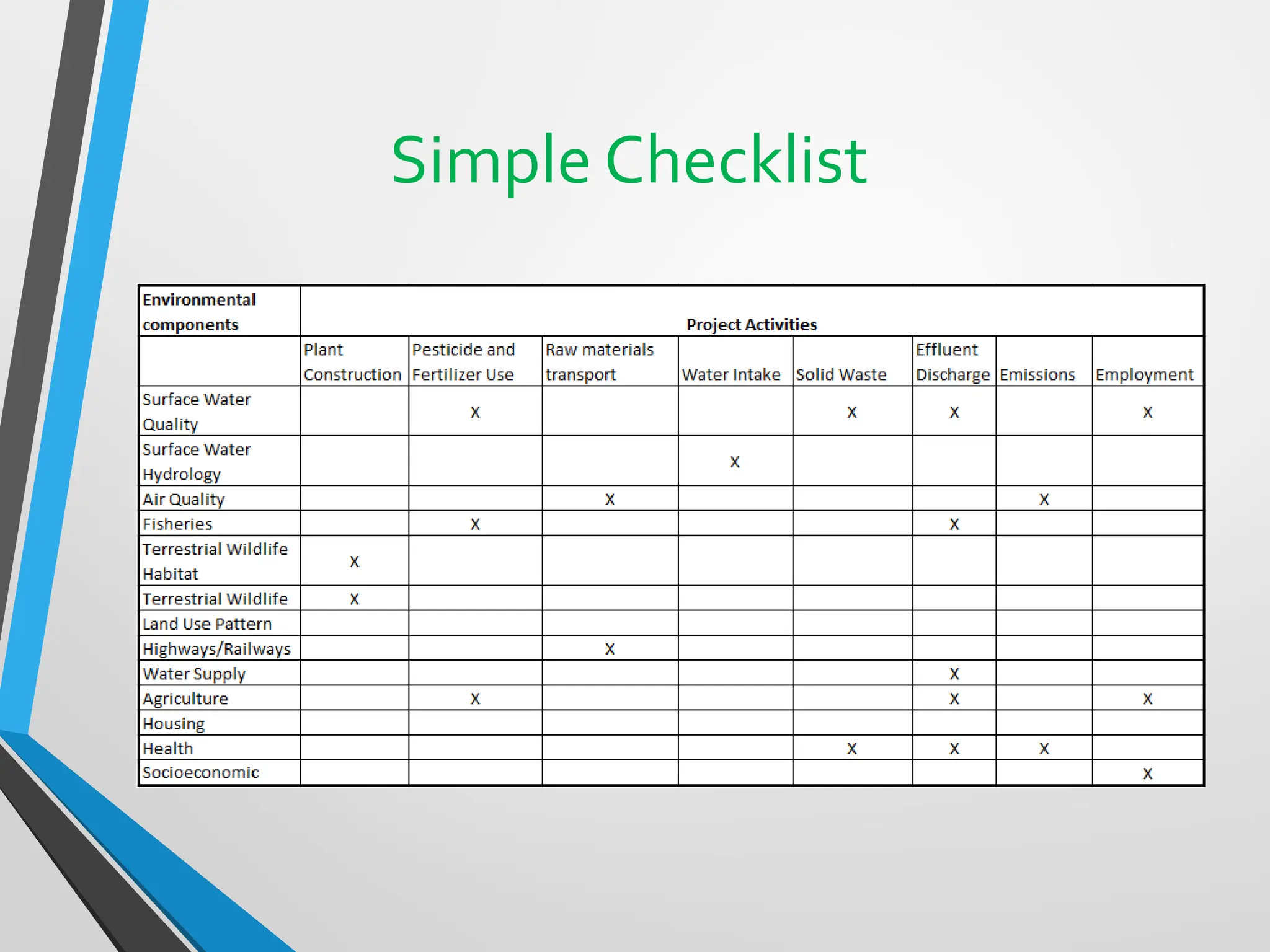
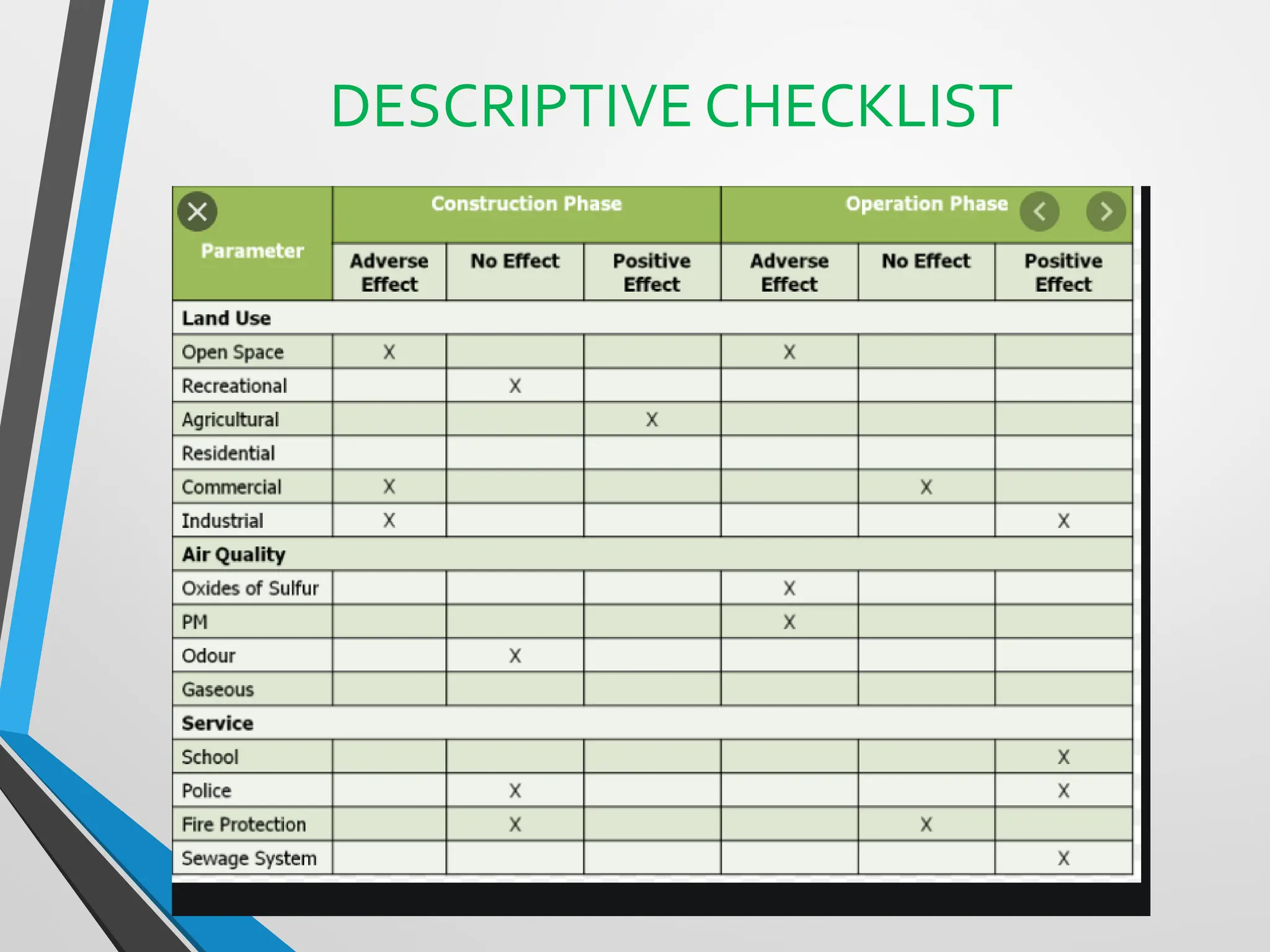
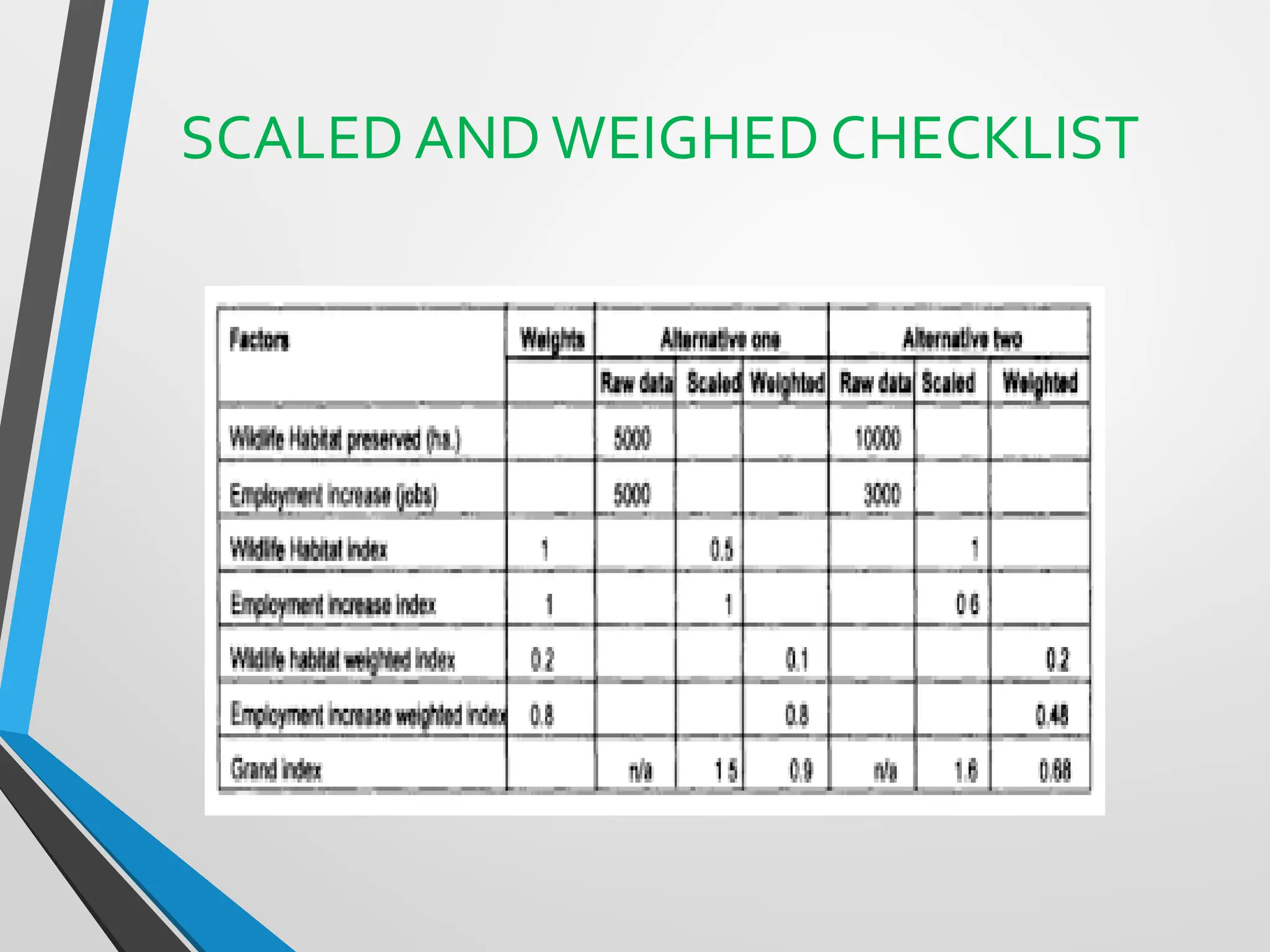
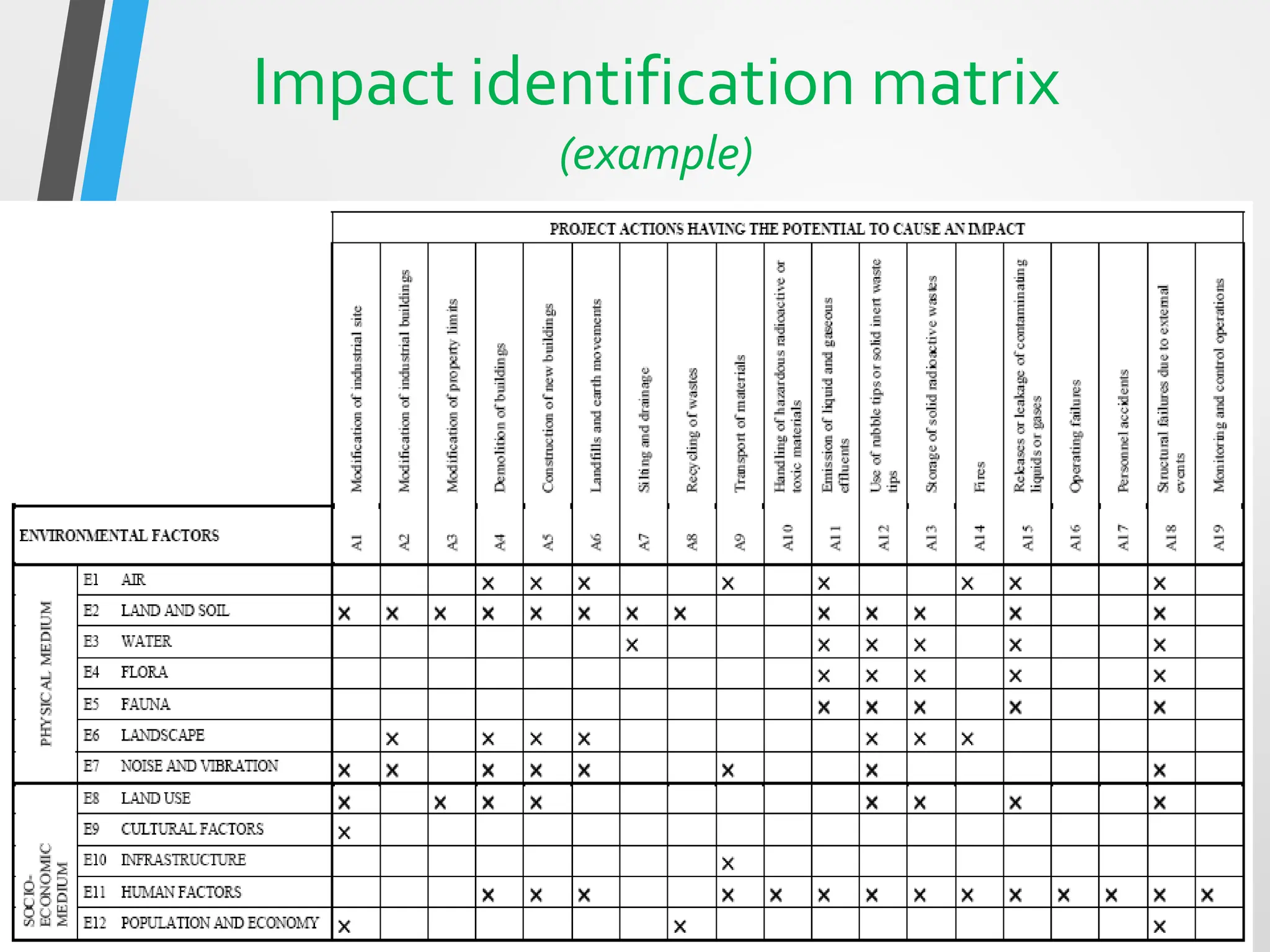
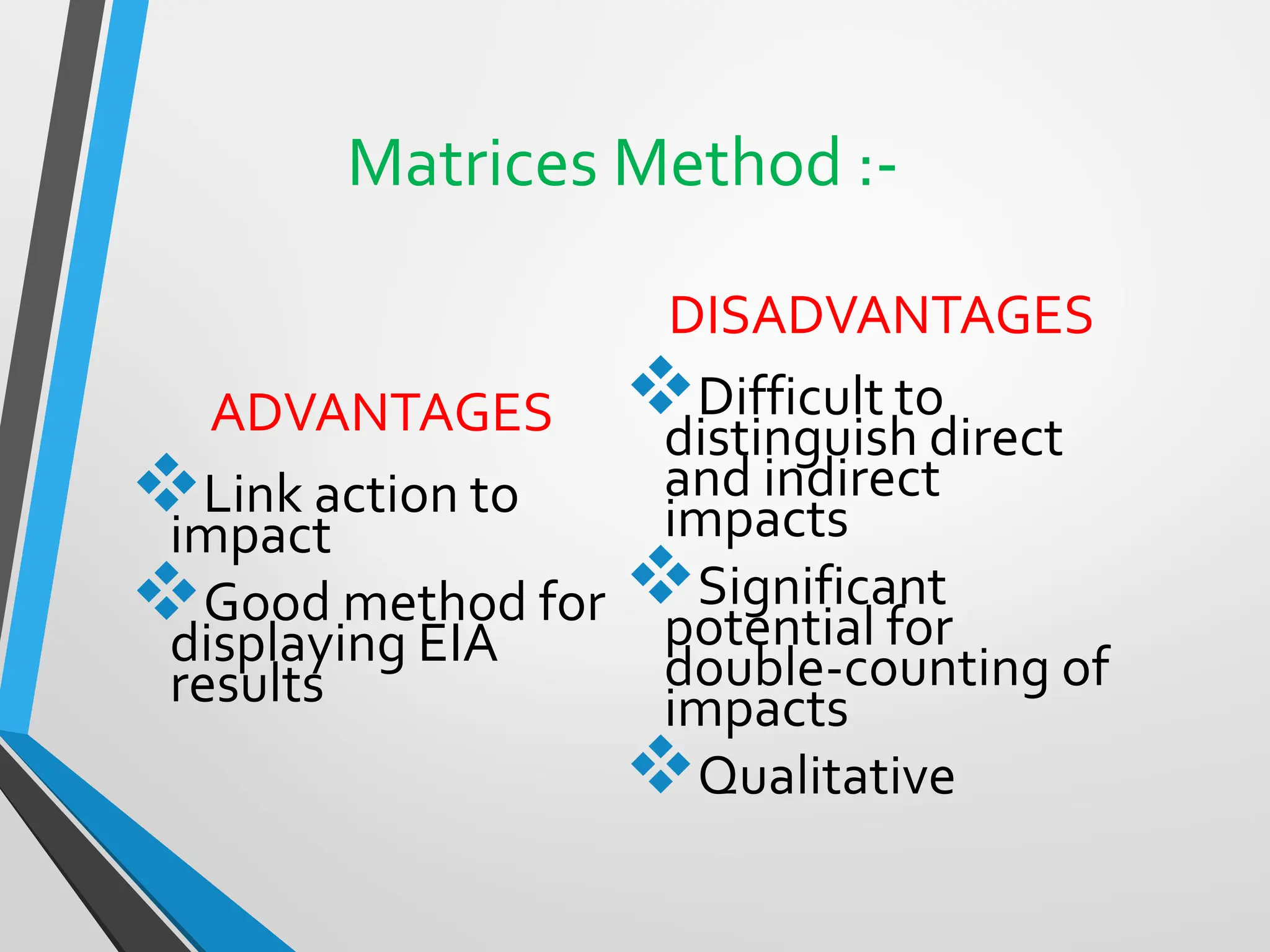
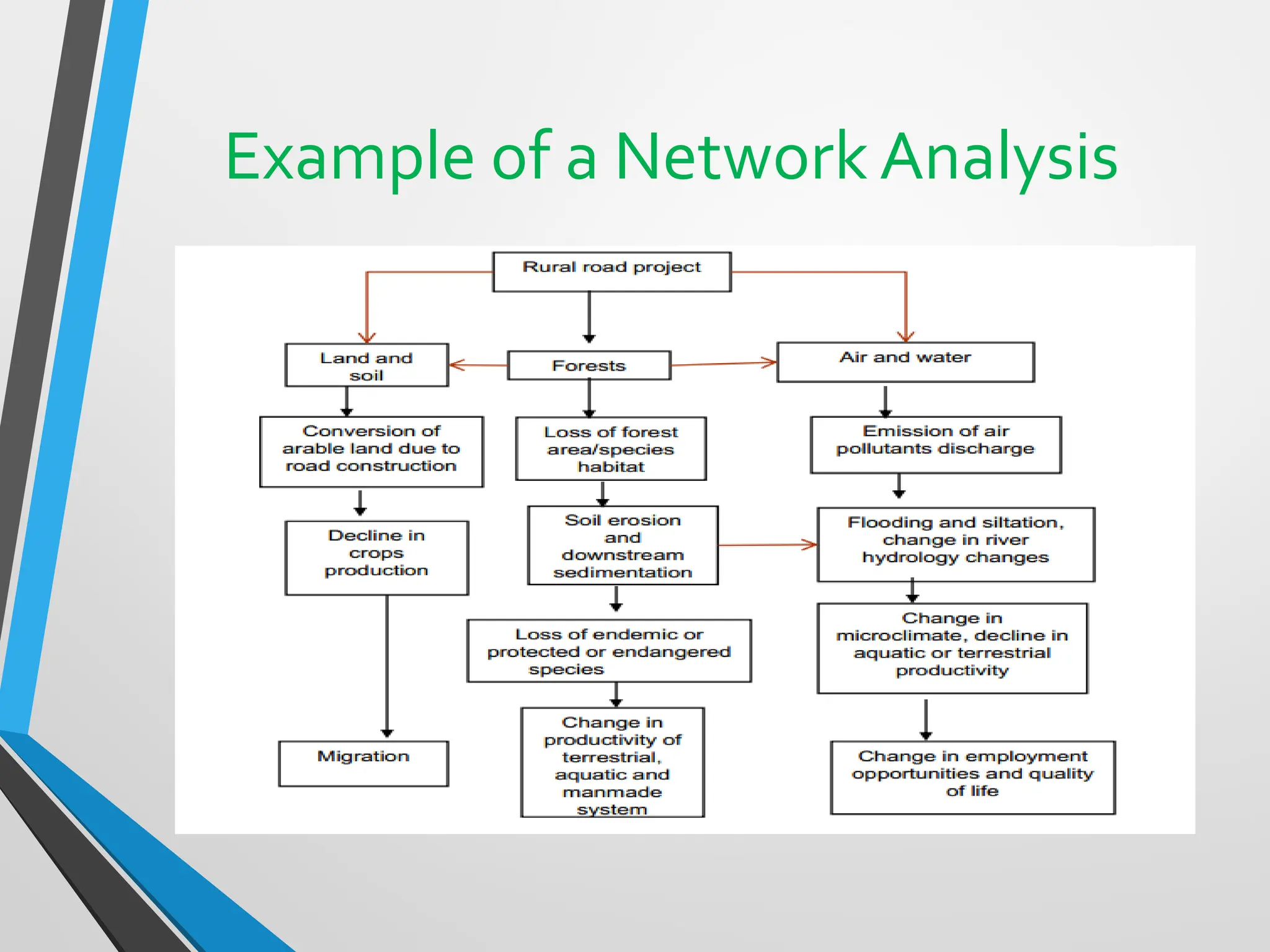
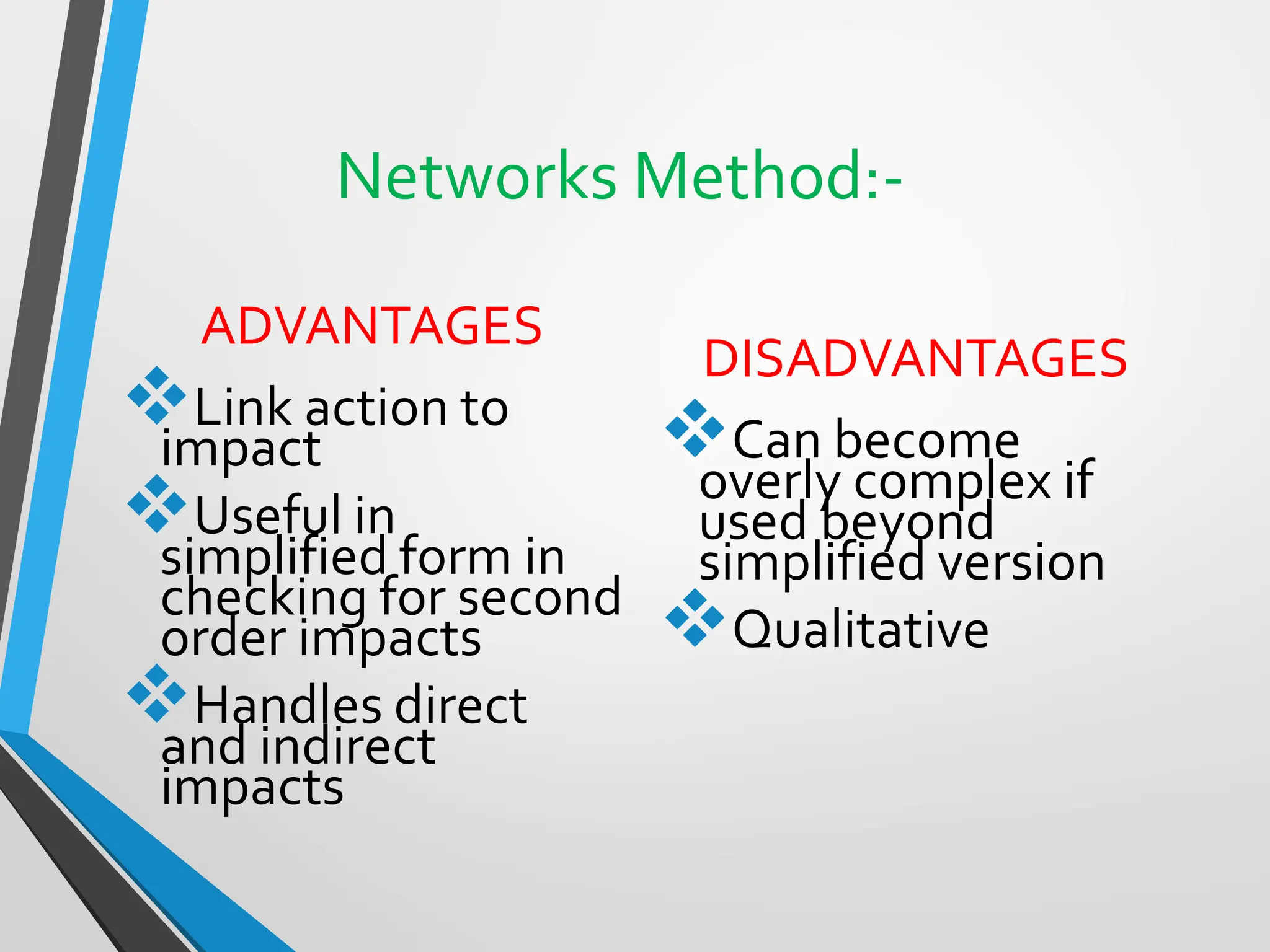
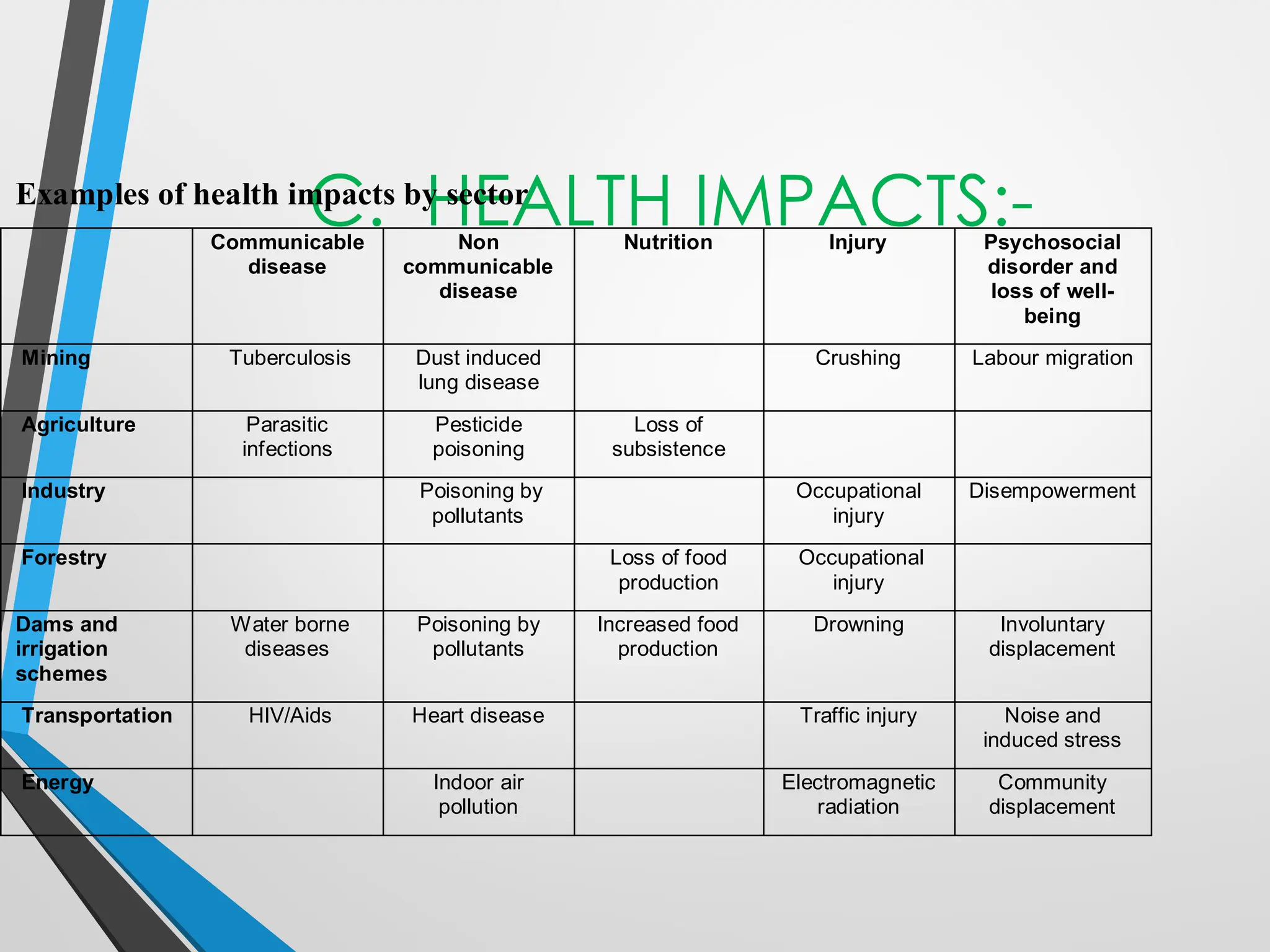
This document discusses Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) methodologies, emphasizing the importance of appropriate, unbiased, and economical approaches in assessing environmental impacts. It outlines various methods for impact identification, prediction, and evaluation, including ad hoc methods, checklists, matrices, networks, and overlays, each with their advantages and disadvantages. It concludes with a focus on the effectiveness of EIA systems, emphasizing the need for accurate information and timely decision-making in mitigating environmental impacts.