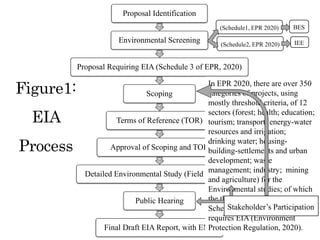
The document summarizes the environmental impact assessment (EIA) process in Nepal and identifies challenges. It outlines the key steps in an EIA, which includes scoping, terms of reference, detailed studies, public consultation, and report preparation and approval. Major challenges include perceptions of EIA as just a formality, low-quality reports, lack of alternative analysis, delays in approval, and ineffective implementation of environmental management plans. The conclusions recommend strengthening implementation and following standards to make EIAs more project-specific and effective in mitigating environmental impacts.