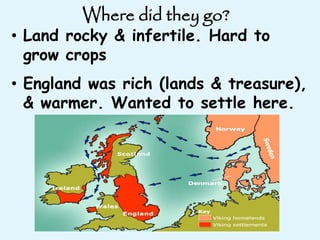
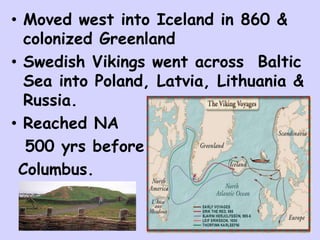
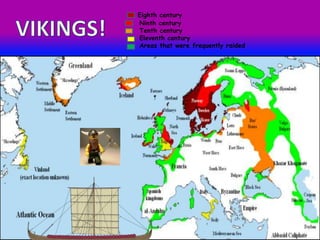
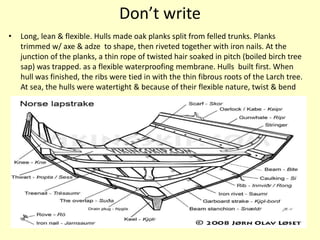
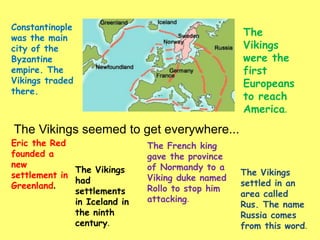
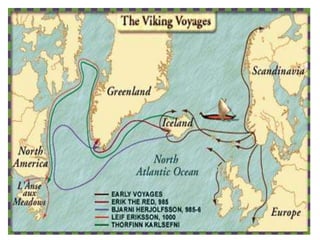
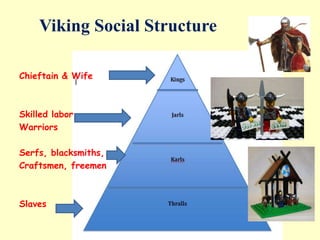
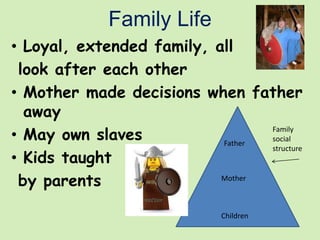
The Vikings were Scandinavian seafaring warriors from Norway, Sweden, and Denmark who raided, traded, explored, and settled across Europe from the late 8th to late 11th centuries. They used longships to raid coastal areas and sail up rivers as far as Russia, the Middle East, and North America. The Vikings attacked monasteries and towns for their riches and often captured people to ransom or sell into slavery. They established settlements in Iceland, Greenland, and Vinland in North America. The Viking way of life centered around farming, fishing, crafts, and battle. They had a polytheistic religion and buried their dead with treasures.