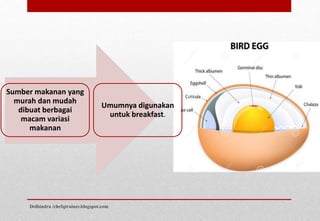
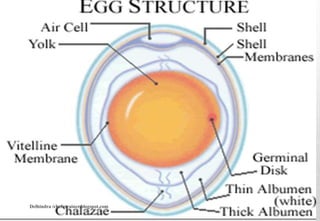
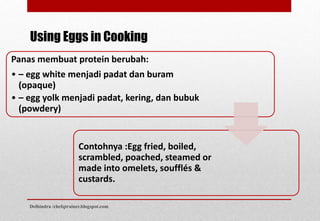
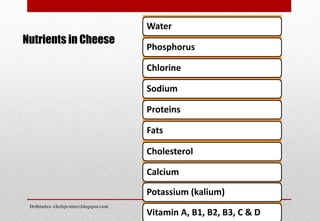
Dokumen ini menjelaskan tentang telur dan produk susu, mencakup struktur dan manfaat gizi dari telur, serta proses pembuatan dan klasifikasi berbagai jenis keju. Selain itu, dijelaskan juga berbagai jenis susu dan produk susu seperti yogurt, krim, dan mentega, beserta penggunaannya dalam memasak. Informasi ini memberikan wawasan tentang pemanfaatan secara luas dari telur dan produk susu dalam kuliner.