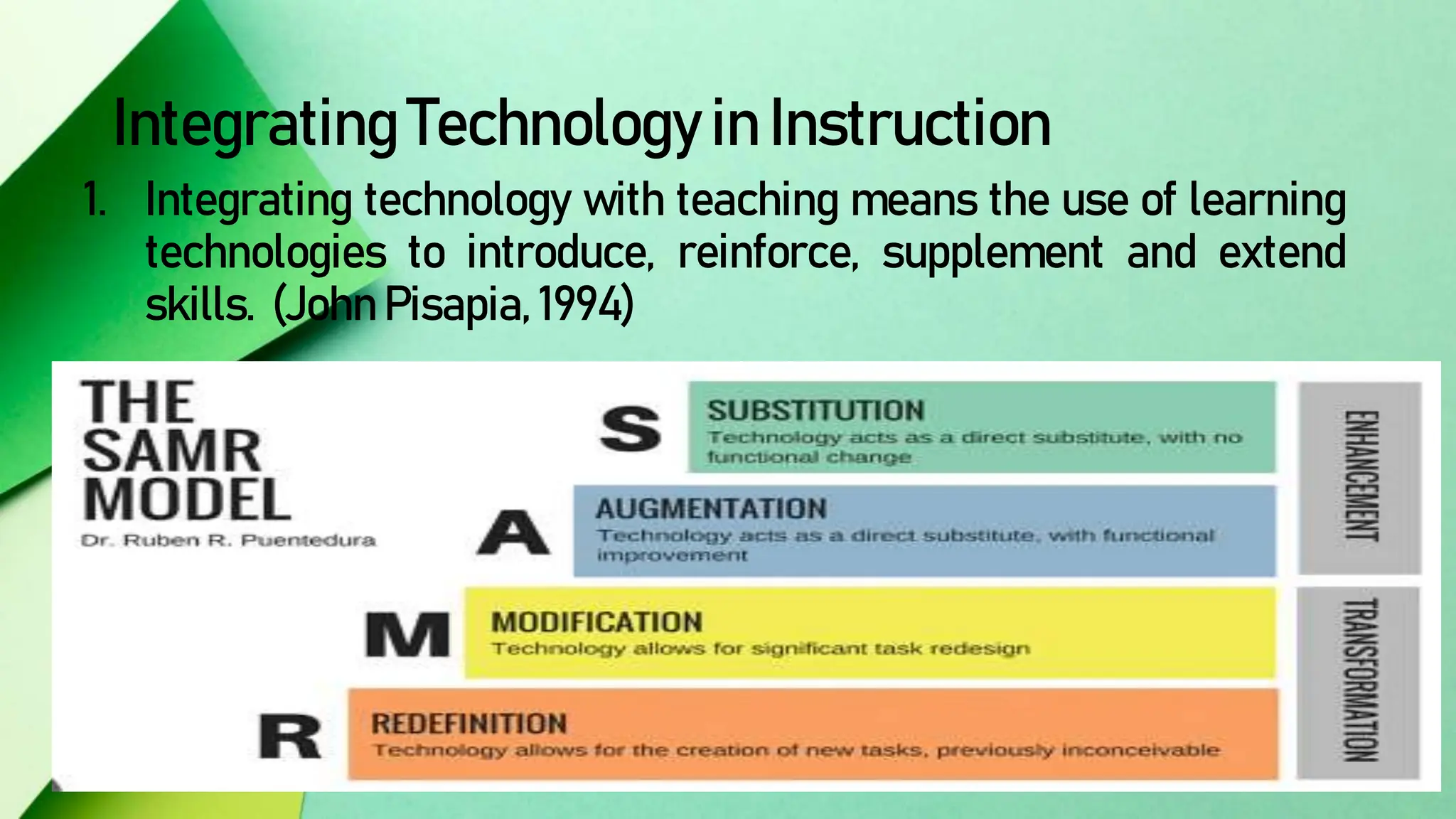
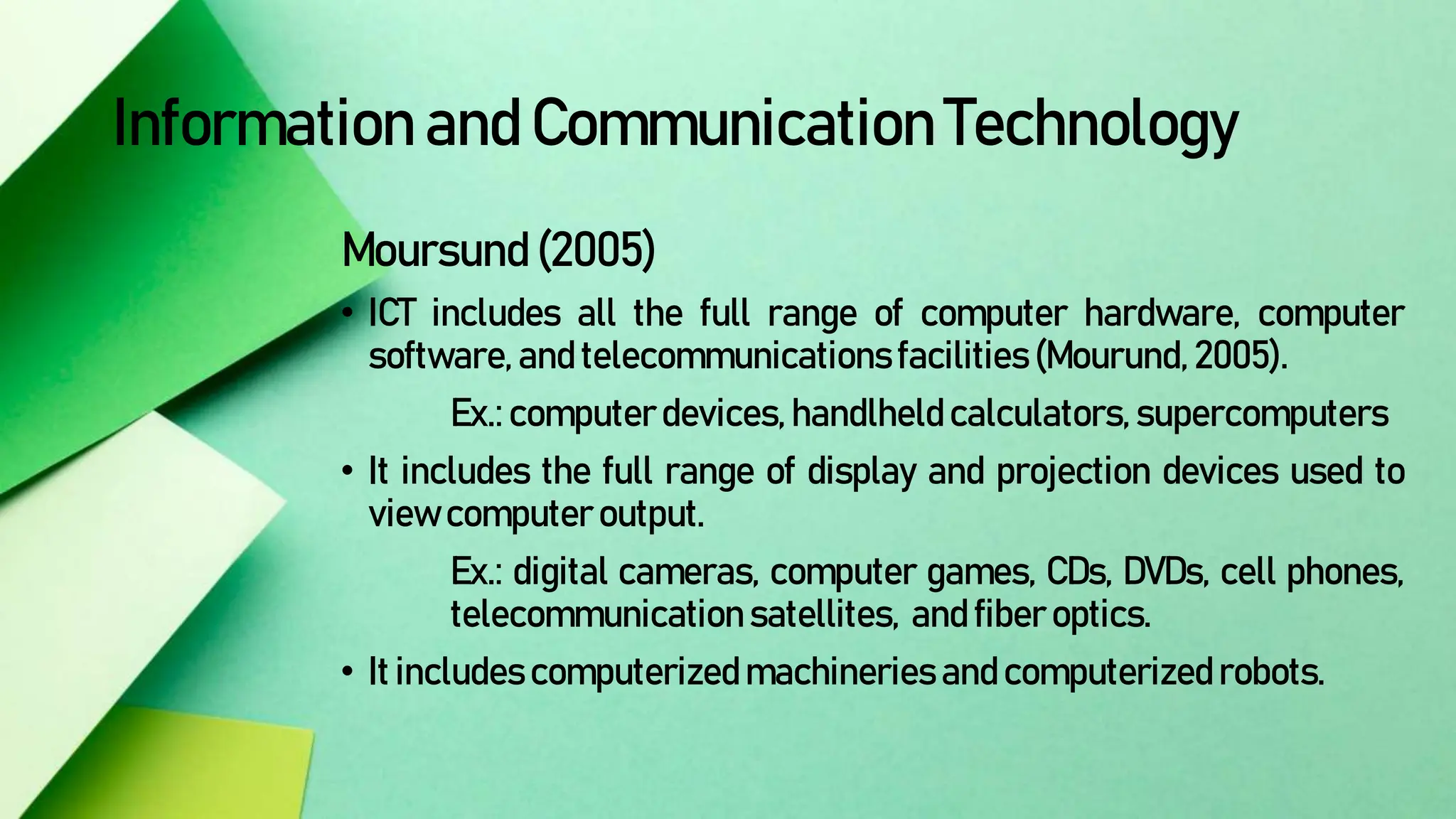
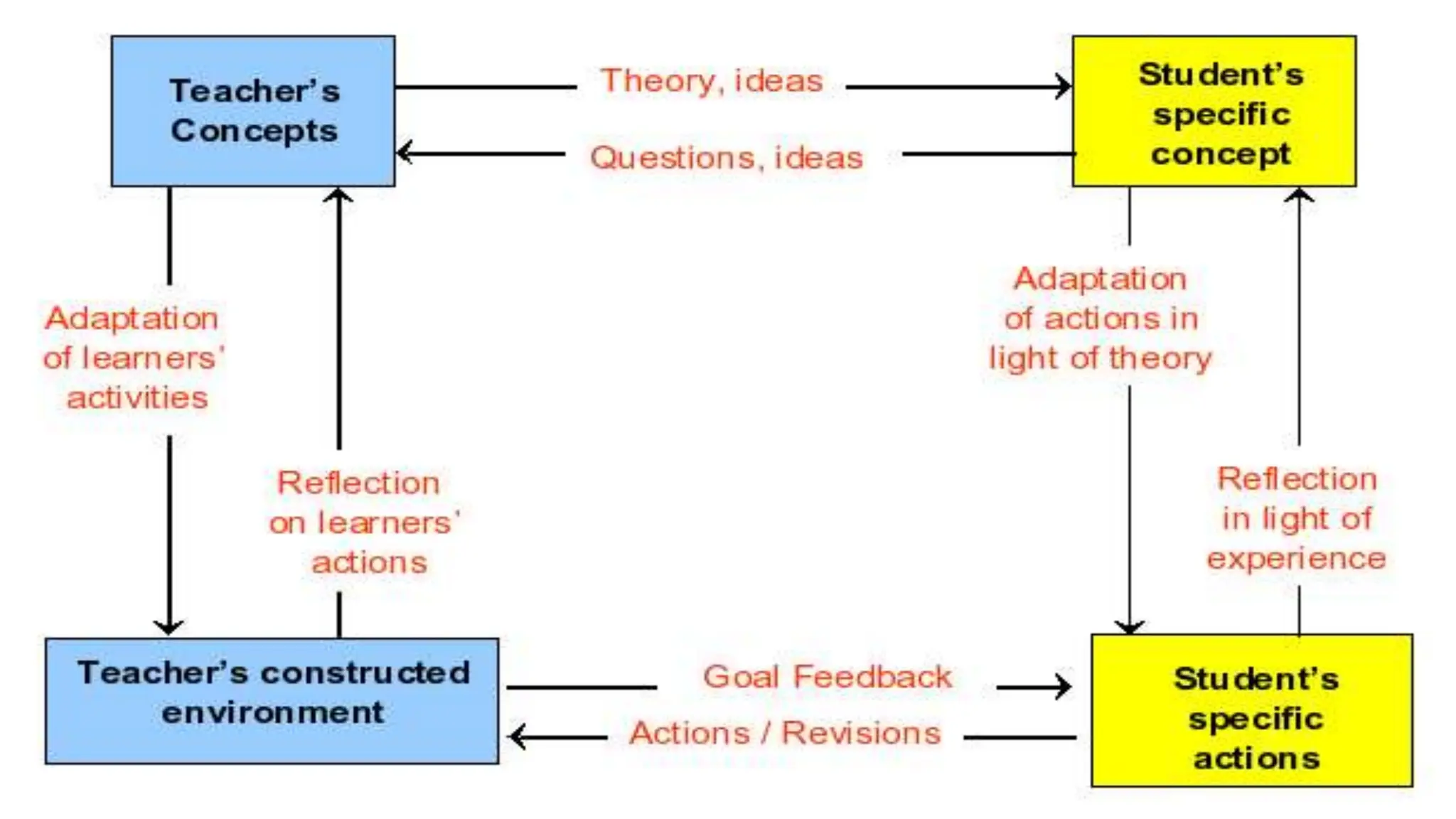
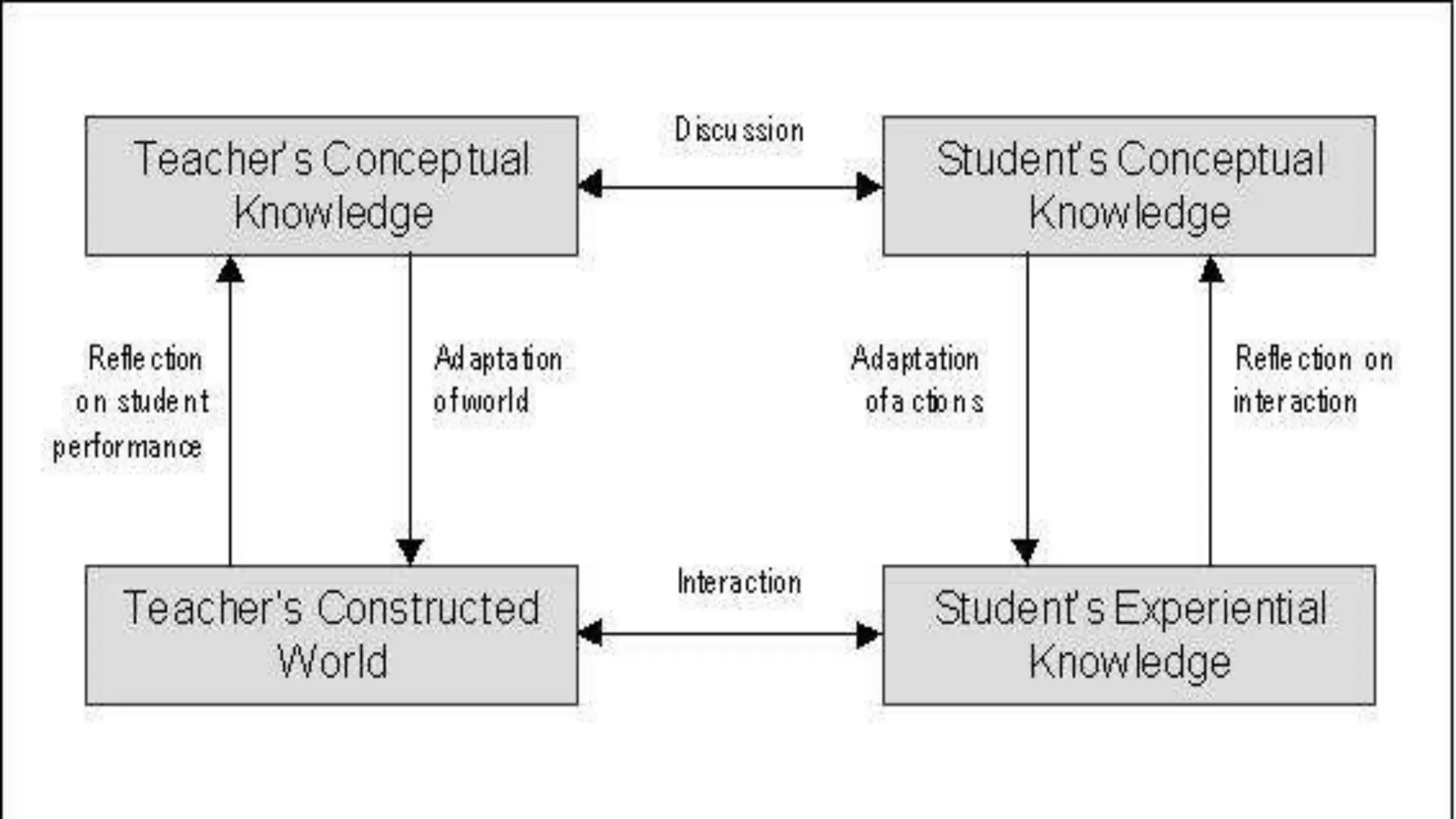
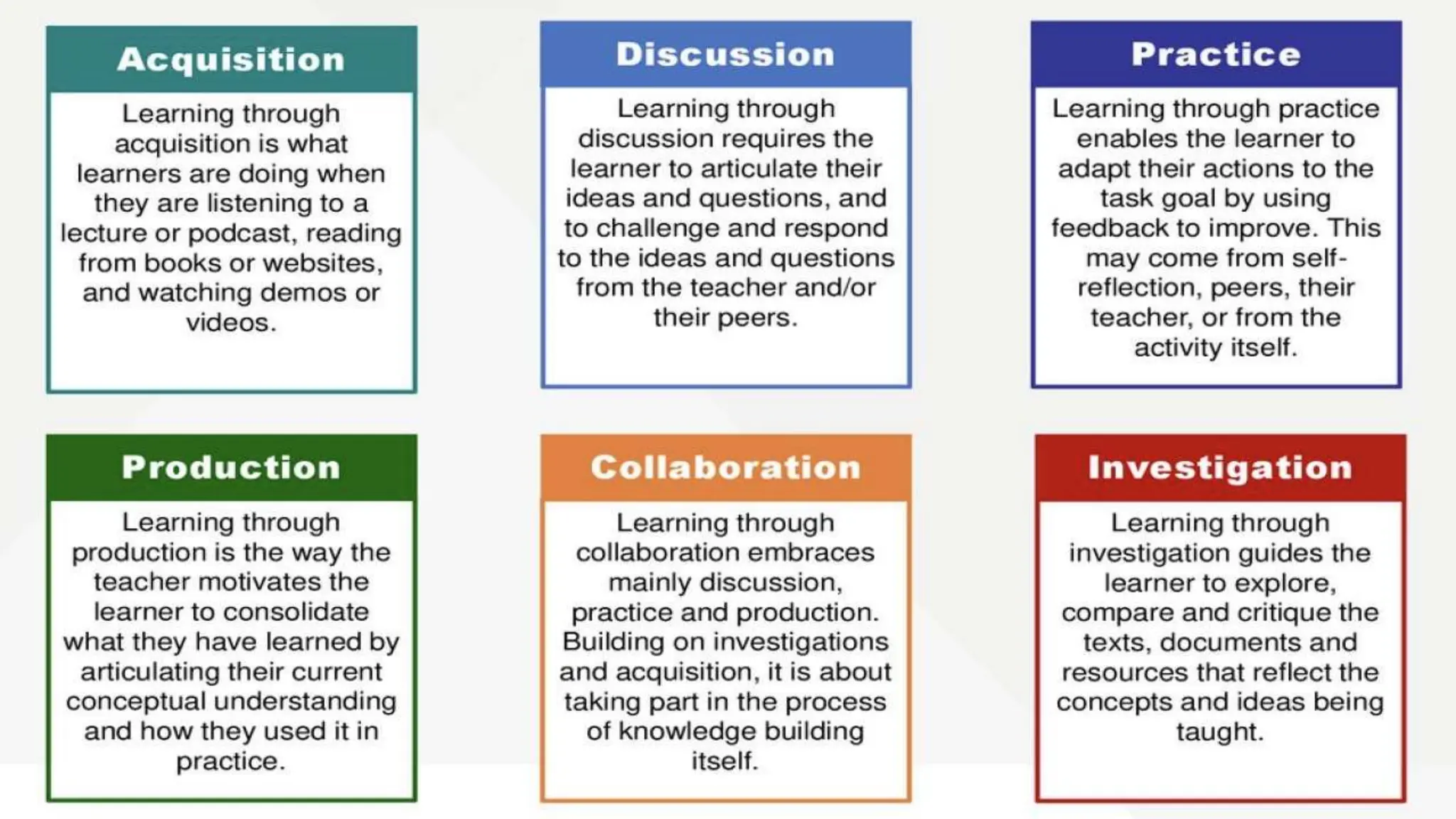
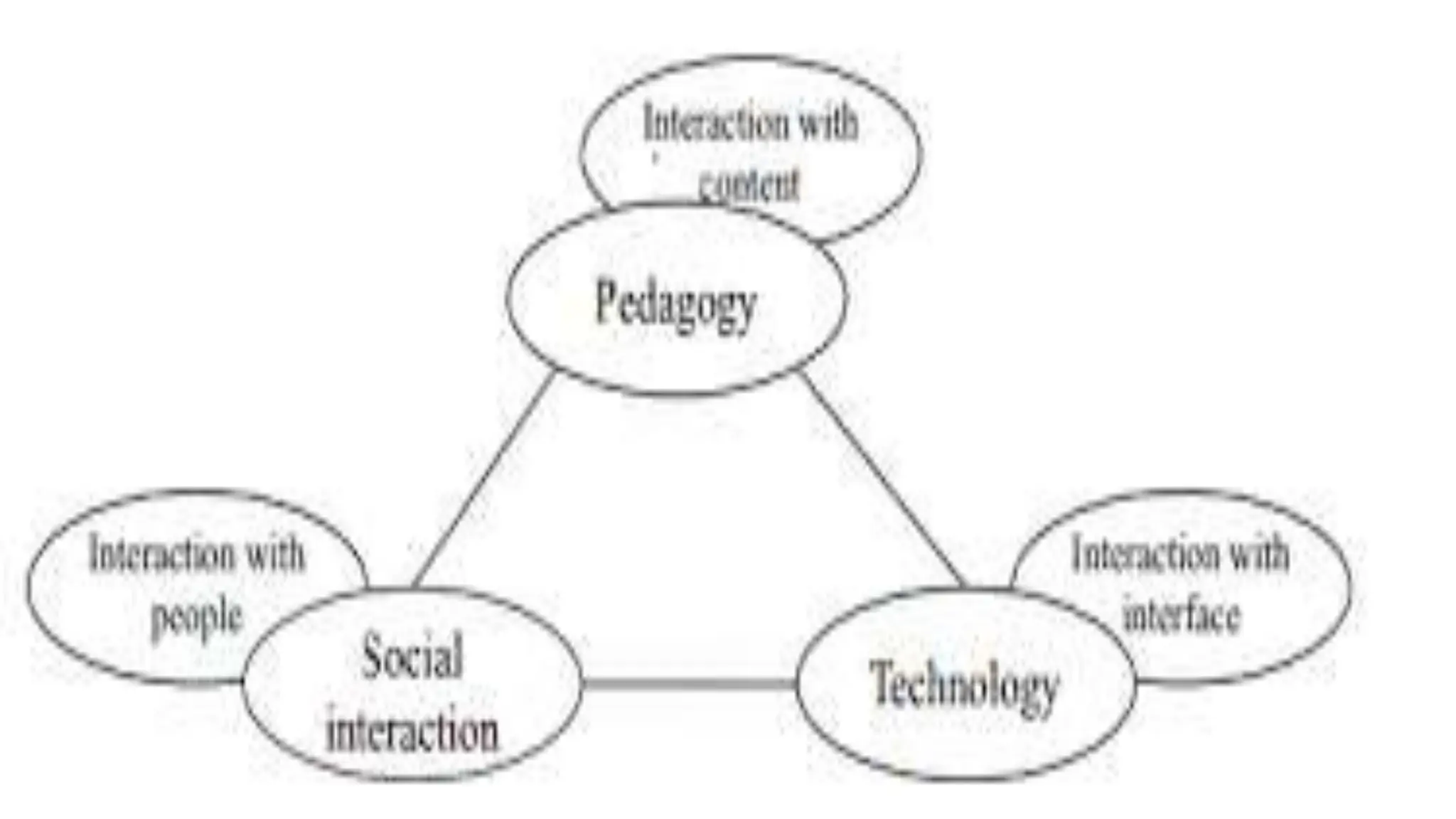
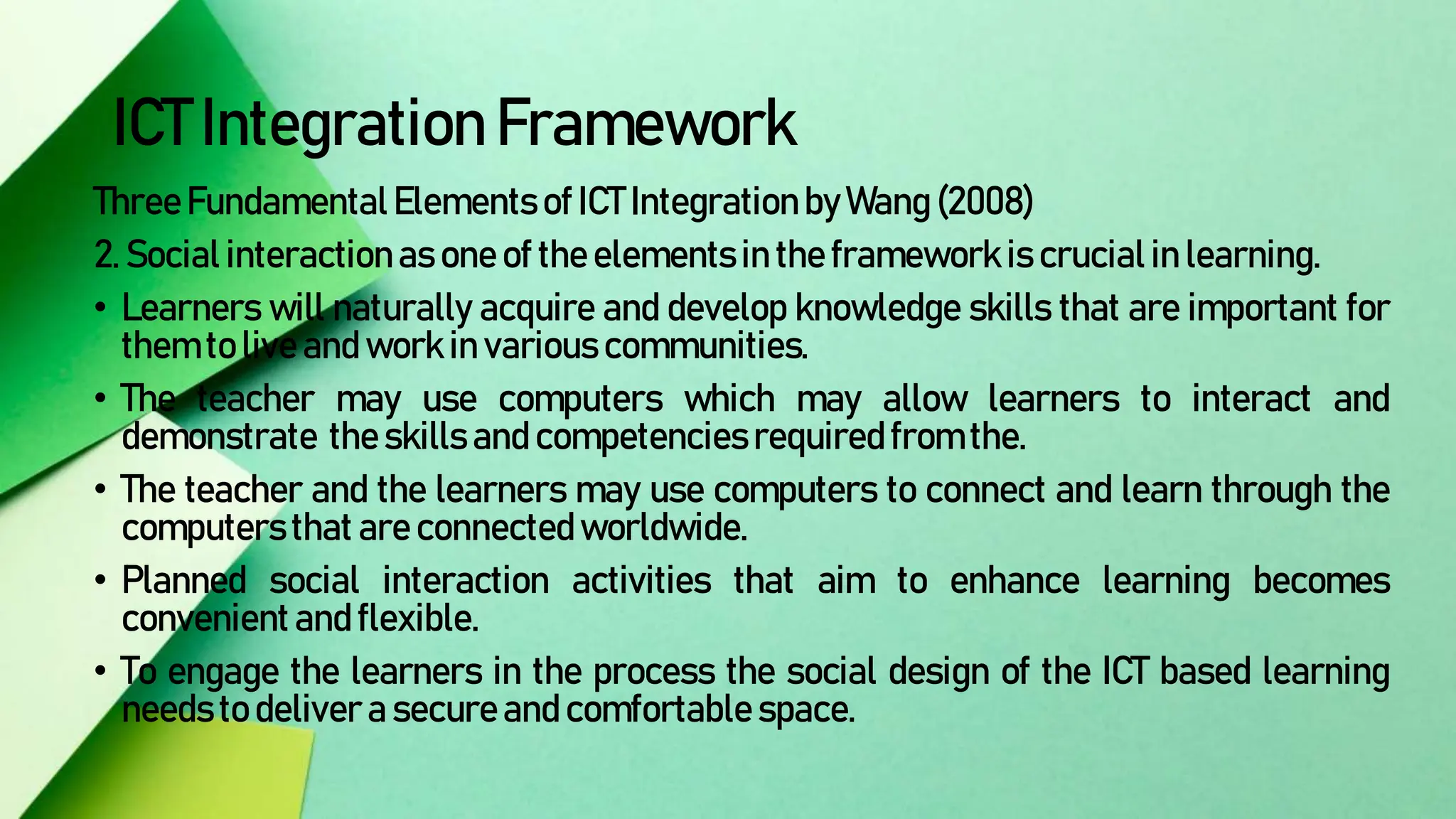
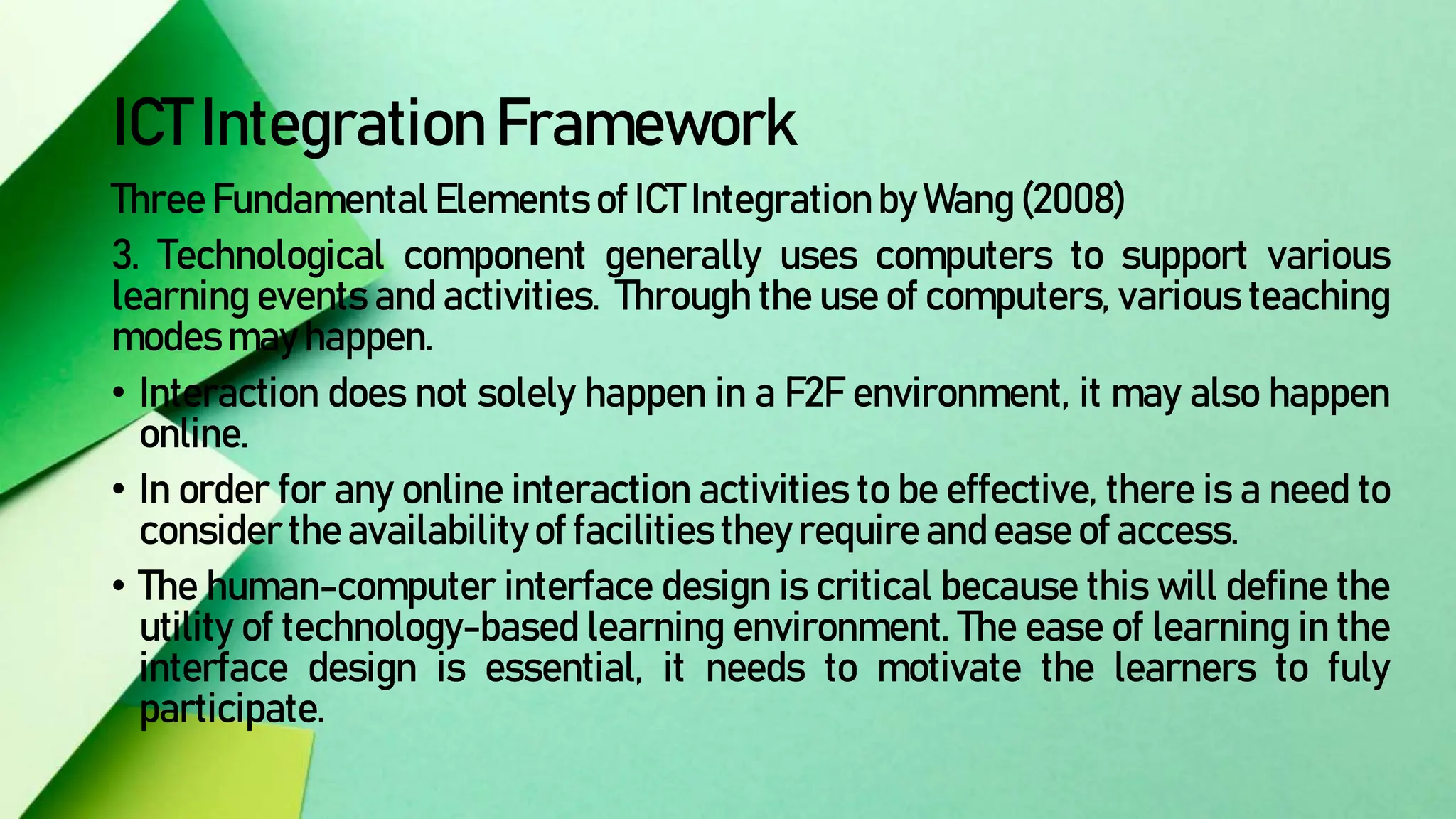
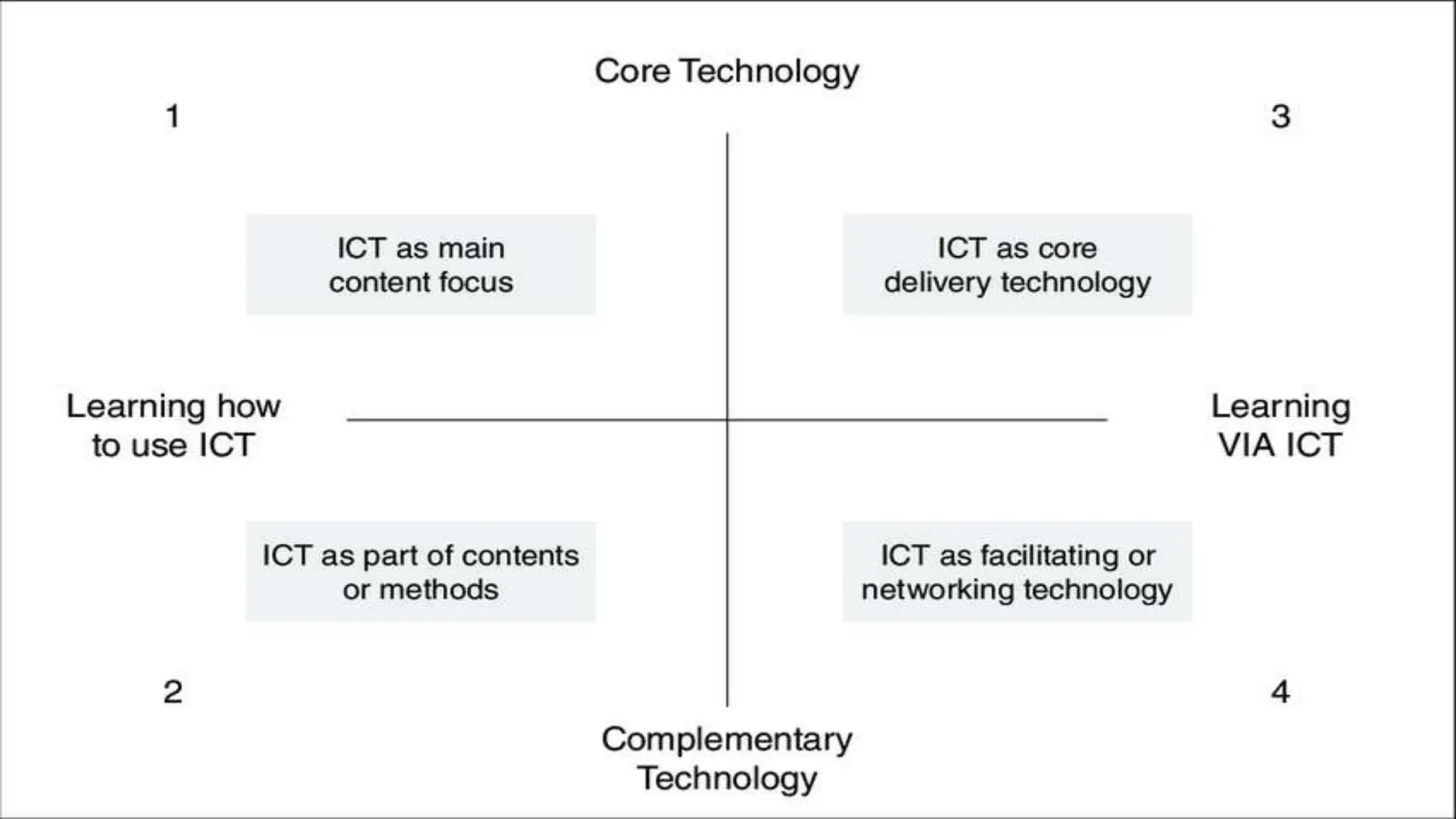
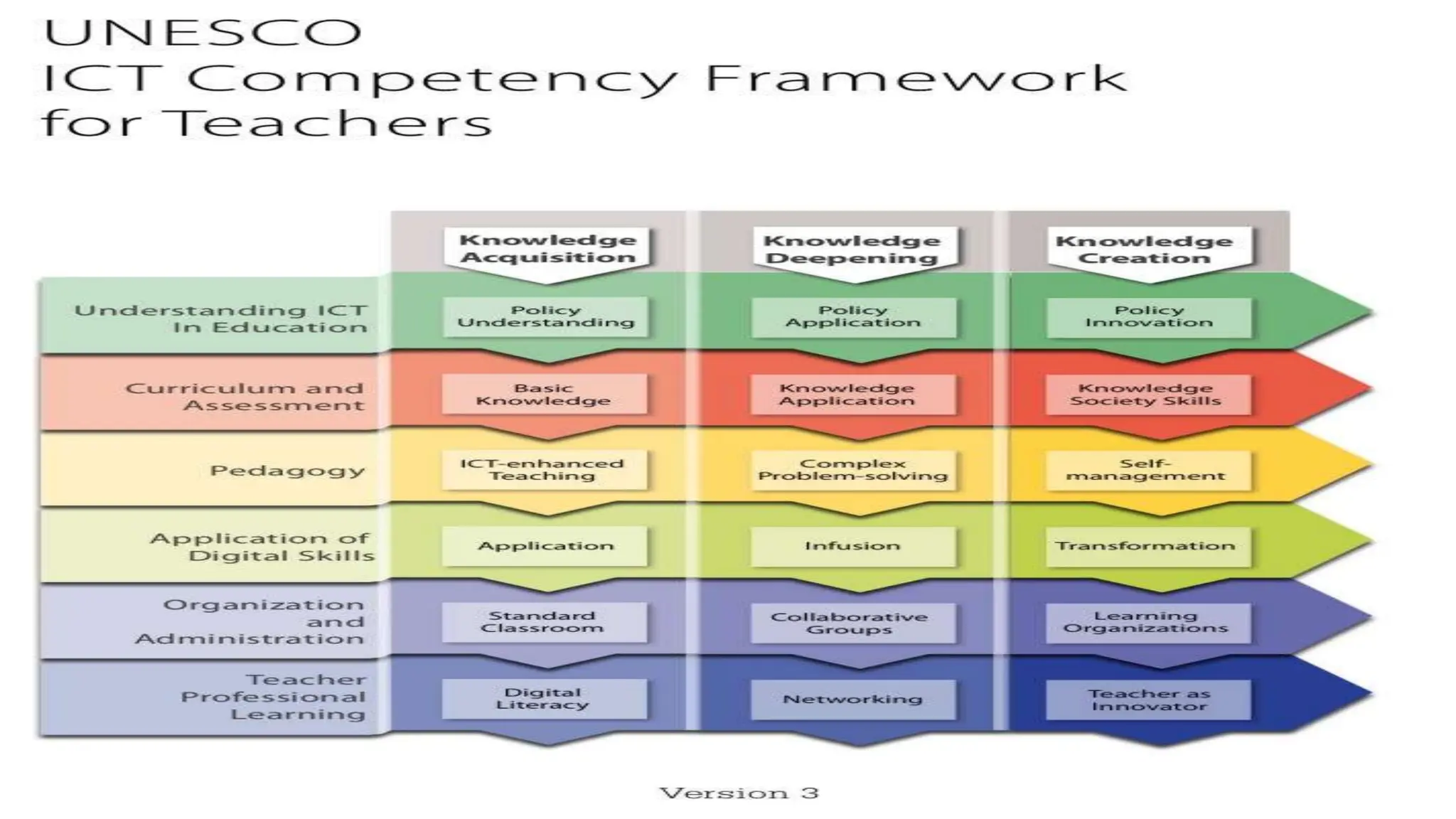
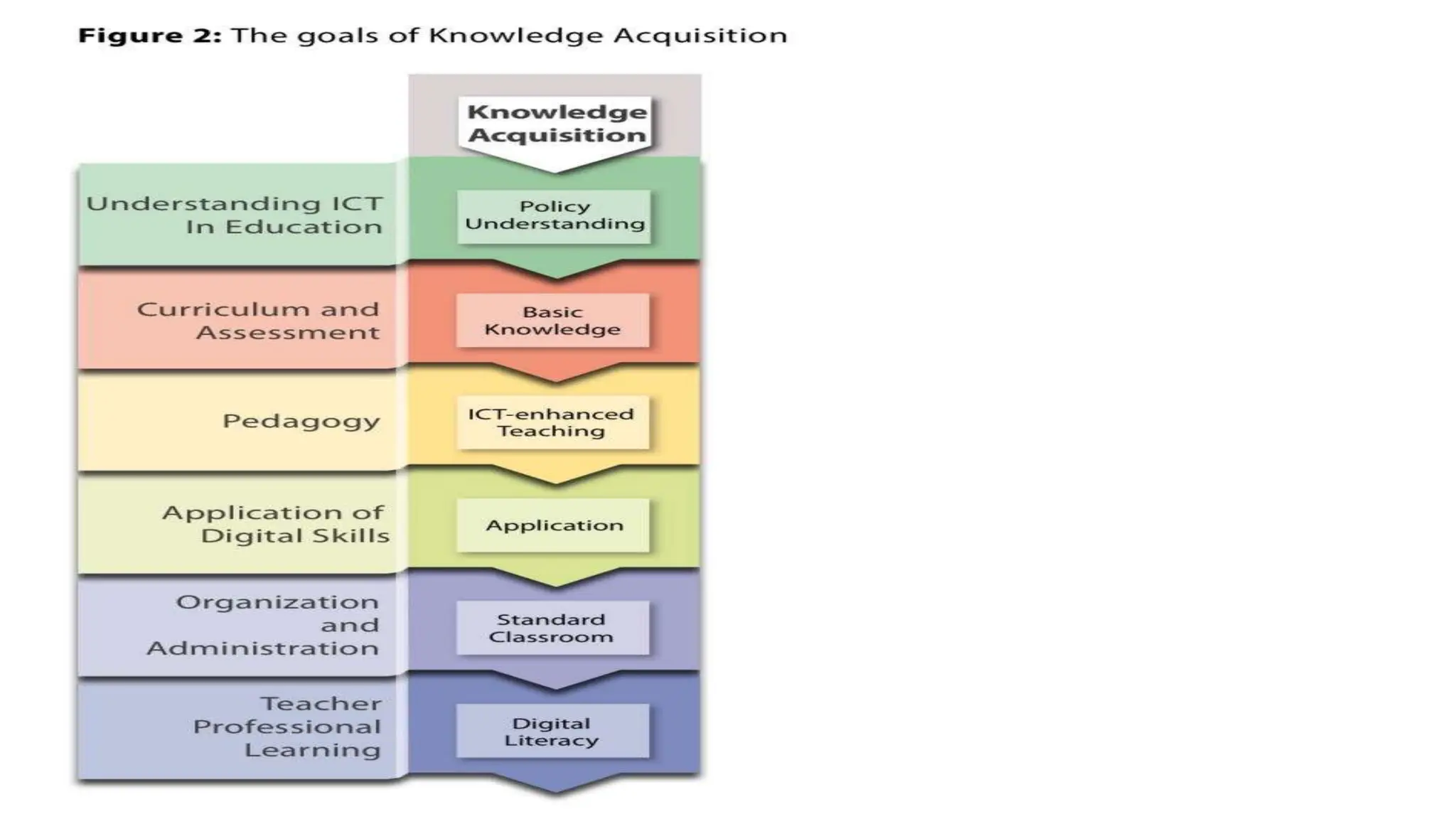
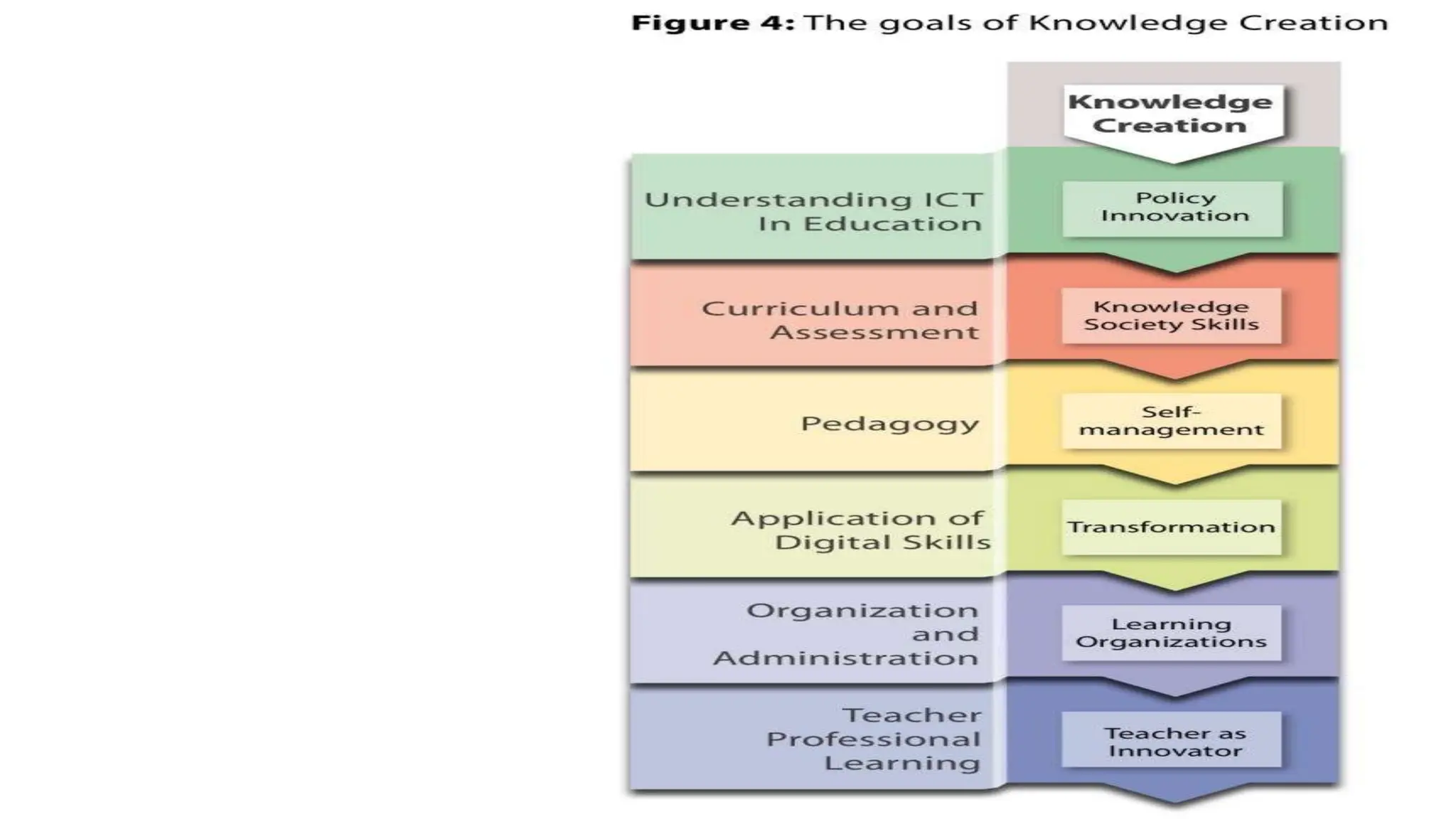
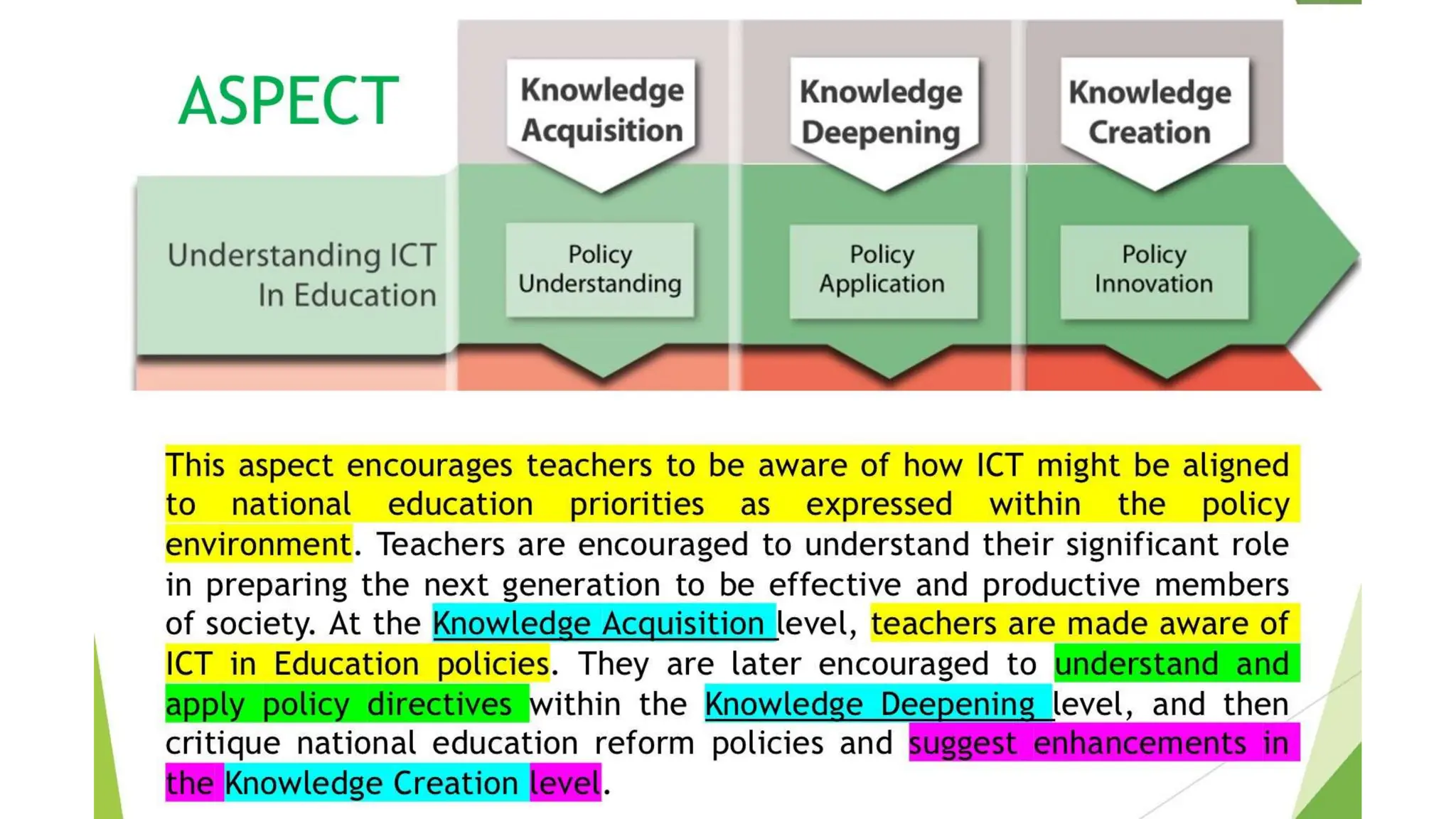
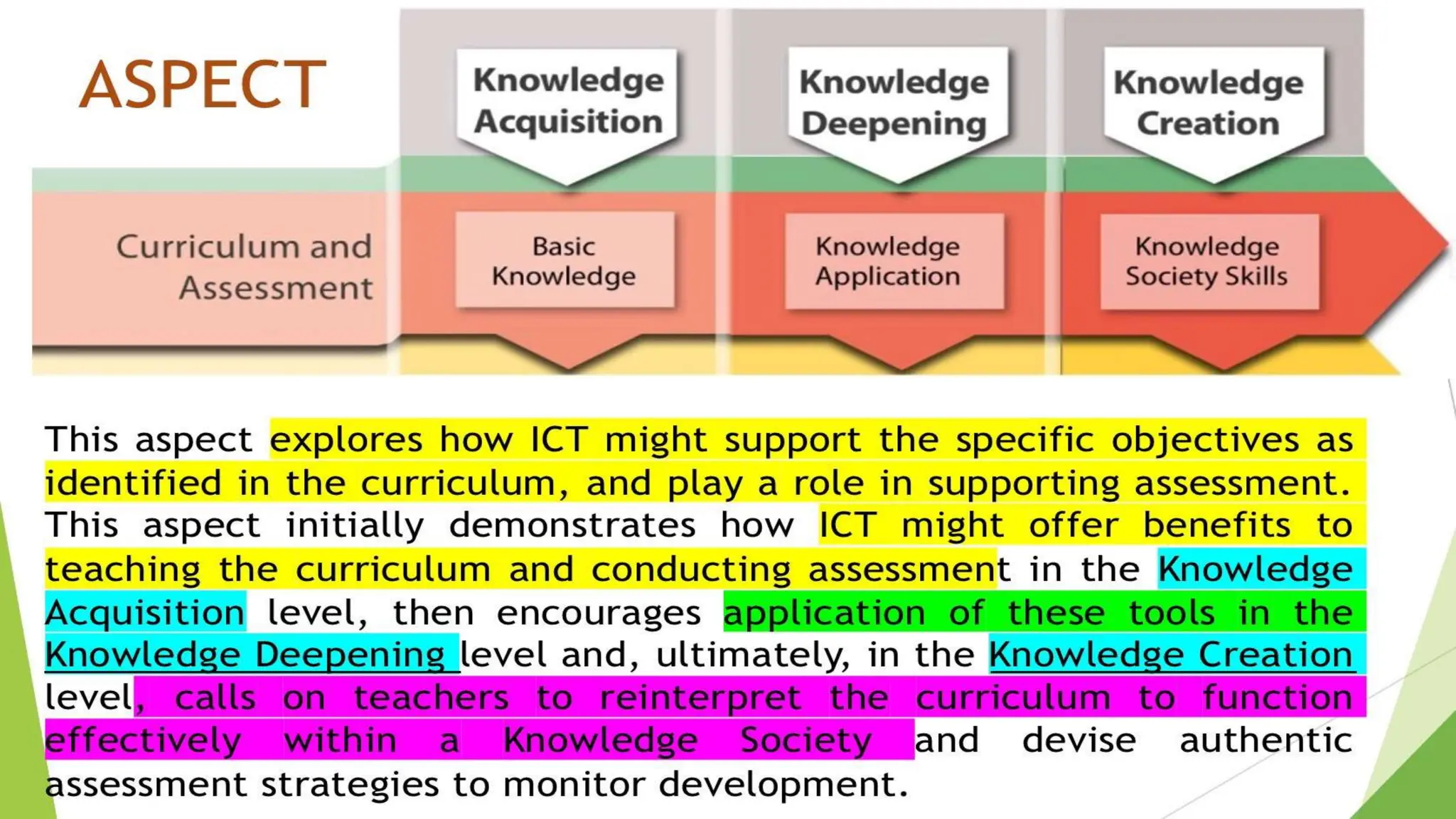
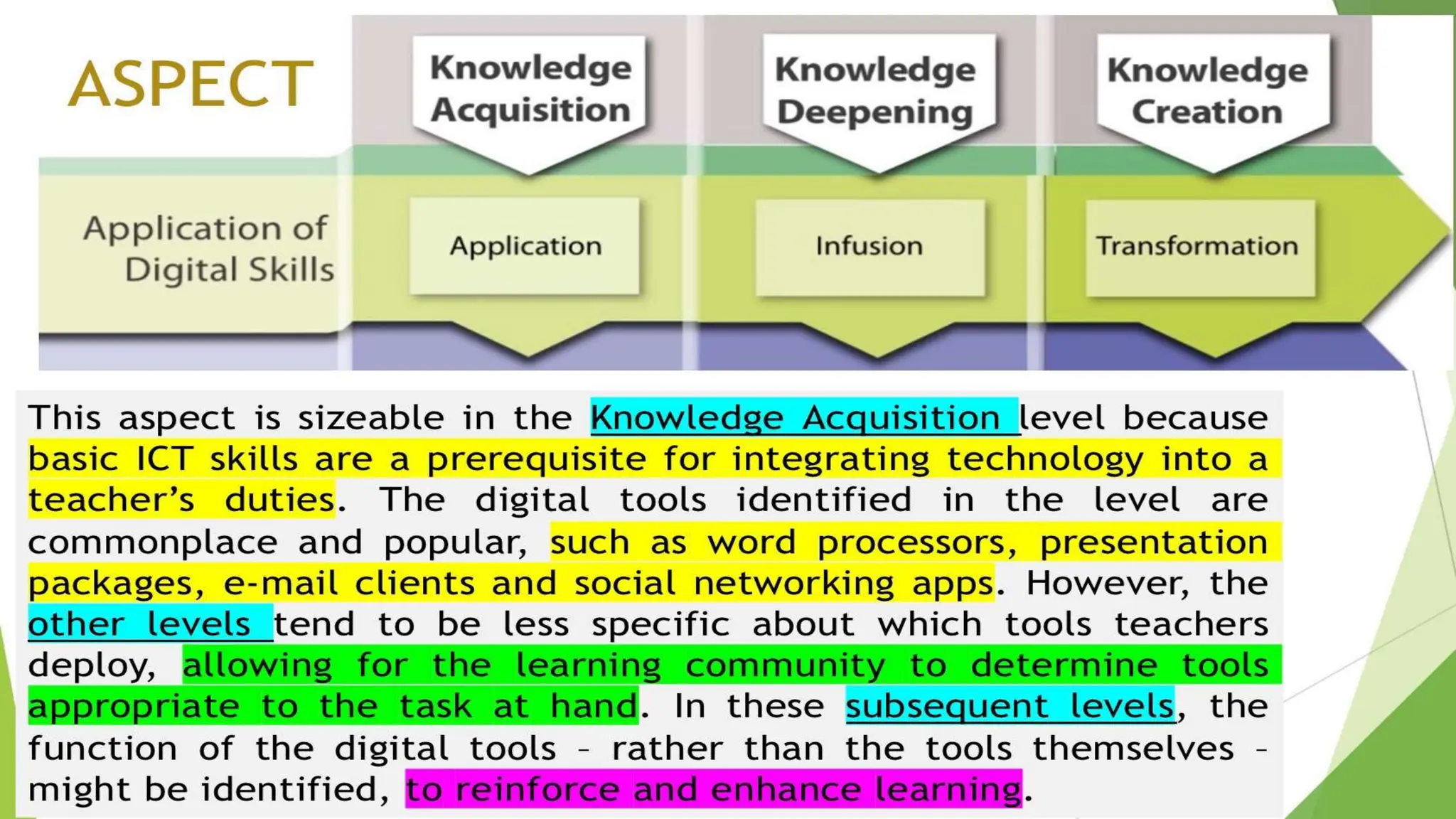
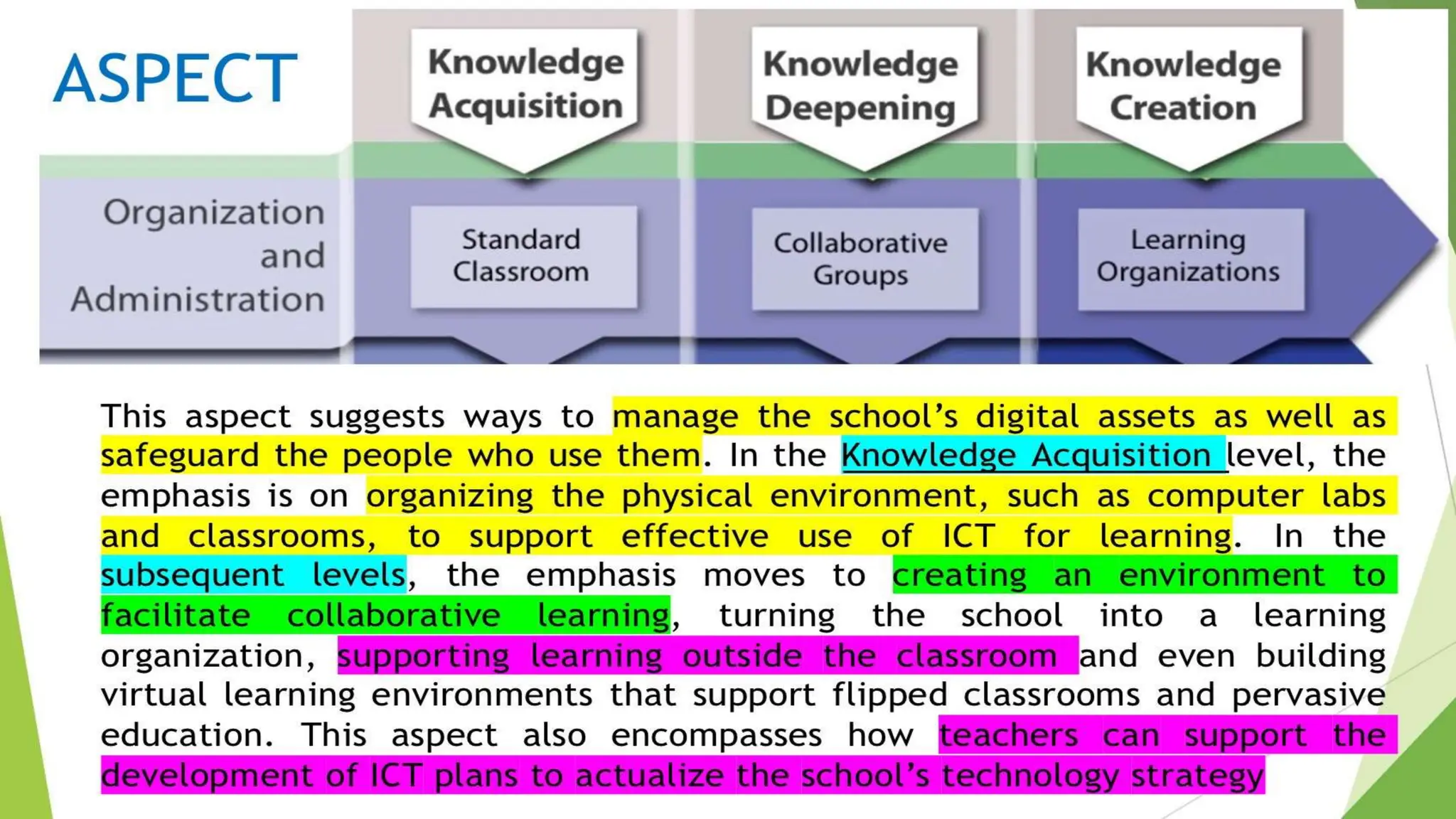
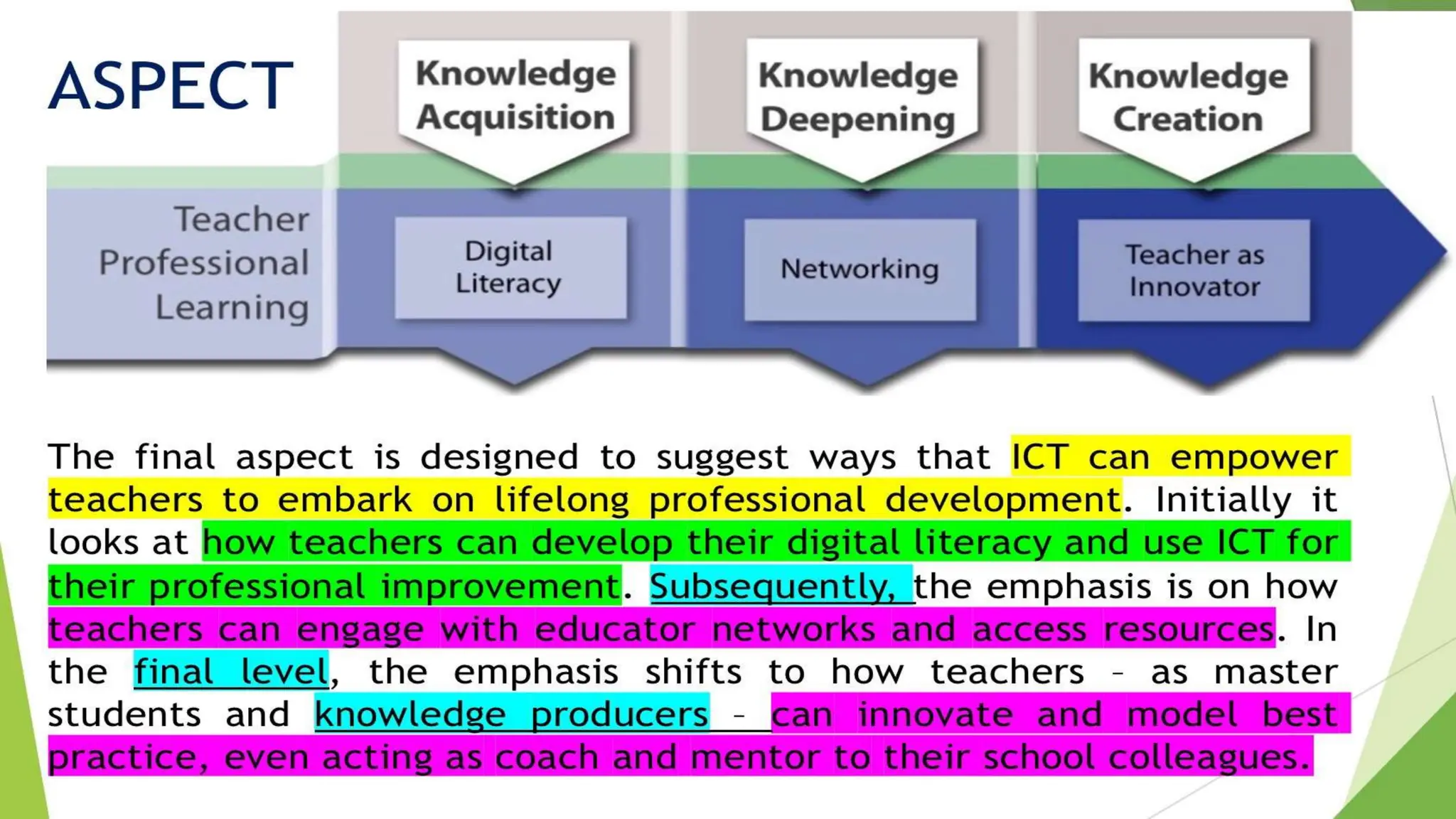
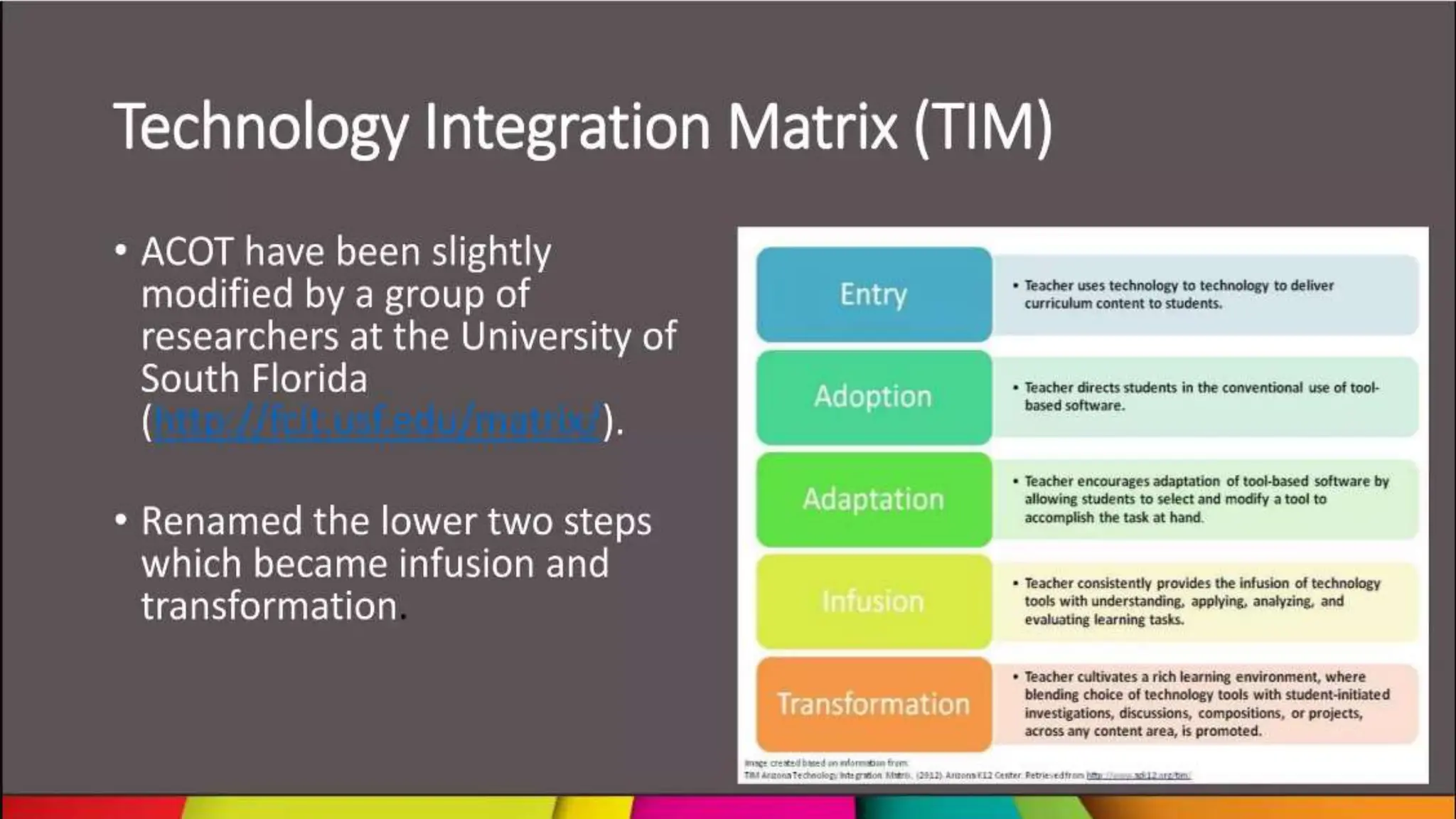
The document discusses integrating technology in instruction and teaching. It provides definitions of integrating technology from various sources which emphasize selecting appropriate technologies to help students obtain and present information. It also discusses that effective integration considers both infrastructure and pedagogy to change how and what is learned. Models of technology integration include stages from initial student direction to transformative stages where students self-direct learning. Frameworks for integration discuss ensuring sound pedagogical principles and considering social interaction, pedagogy and technology. Teacher training categories and competency frameworks aim to equip teachers to achieve goals like enabling informed choices and participation in society.