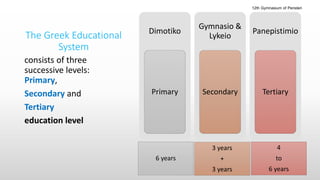
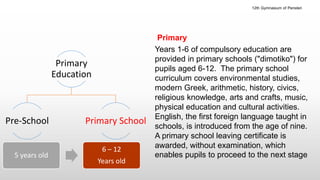
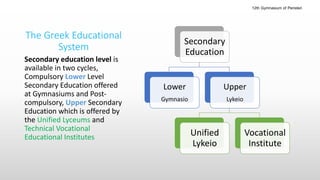
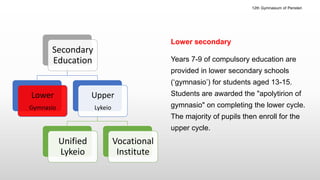
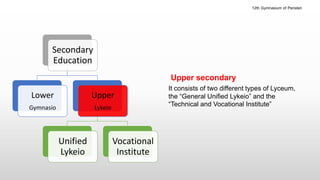
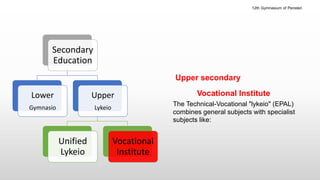
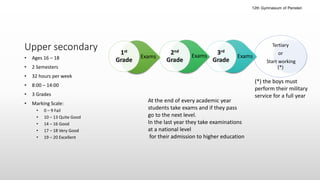
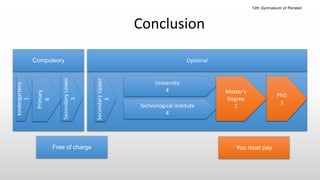
The Greek educational system comprises three levels: primary, secondary, and tertiary, all of which must adhere to the principles of equal educational opportunities as mandated by the Greek constitution. Primary education lasts from ages 6-12, secondary education is divided into lower and upper stages for ages 13-18, and higher education is provided free of charge at state institutions including universities and technological institutes. The curriculum is comprehensive, covering a wide range of subjects from languages to sciences, and students must pass examinations to advance between educational stages.