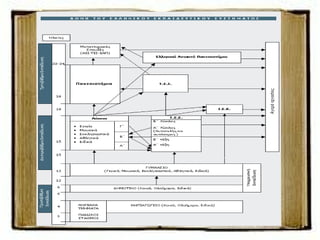
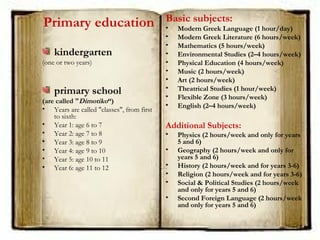
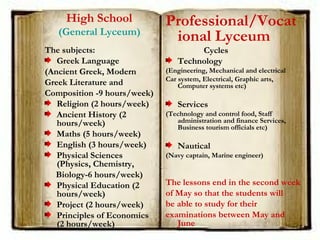
This document summarizes the education system in Greece. It outlines three main levels - primary, secondary, and tertiary education. Primary education consists of kindergarten and primary school (Dimotiko). Secondary education is divided into junior high school (Gymnasio) and high school (Lykeio), which can be either general or vocational. Tertiary education includes universities, technological institutes, and vocational training institutes. The education system is overseen by the Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs and includes public and some private schools.