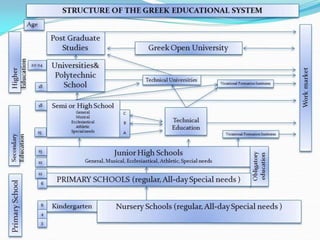
Education in Greece has its origins in Ancient Greece and was considered essential for participation in Greek culture. Nowadays, education in Greece is compulsory between ages 6-15 and includes early education, primary school, secondary school, and higher education. Primary school is for ages 6-12, secondary school is divided into junior high from 12-15 and high school from 16-18, and higher education programs are mostly 4 years. The system is centralized and overseen by the Ministry of Culture, Education and Religious Affairs.