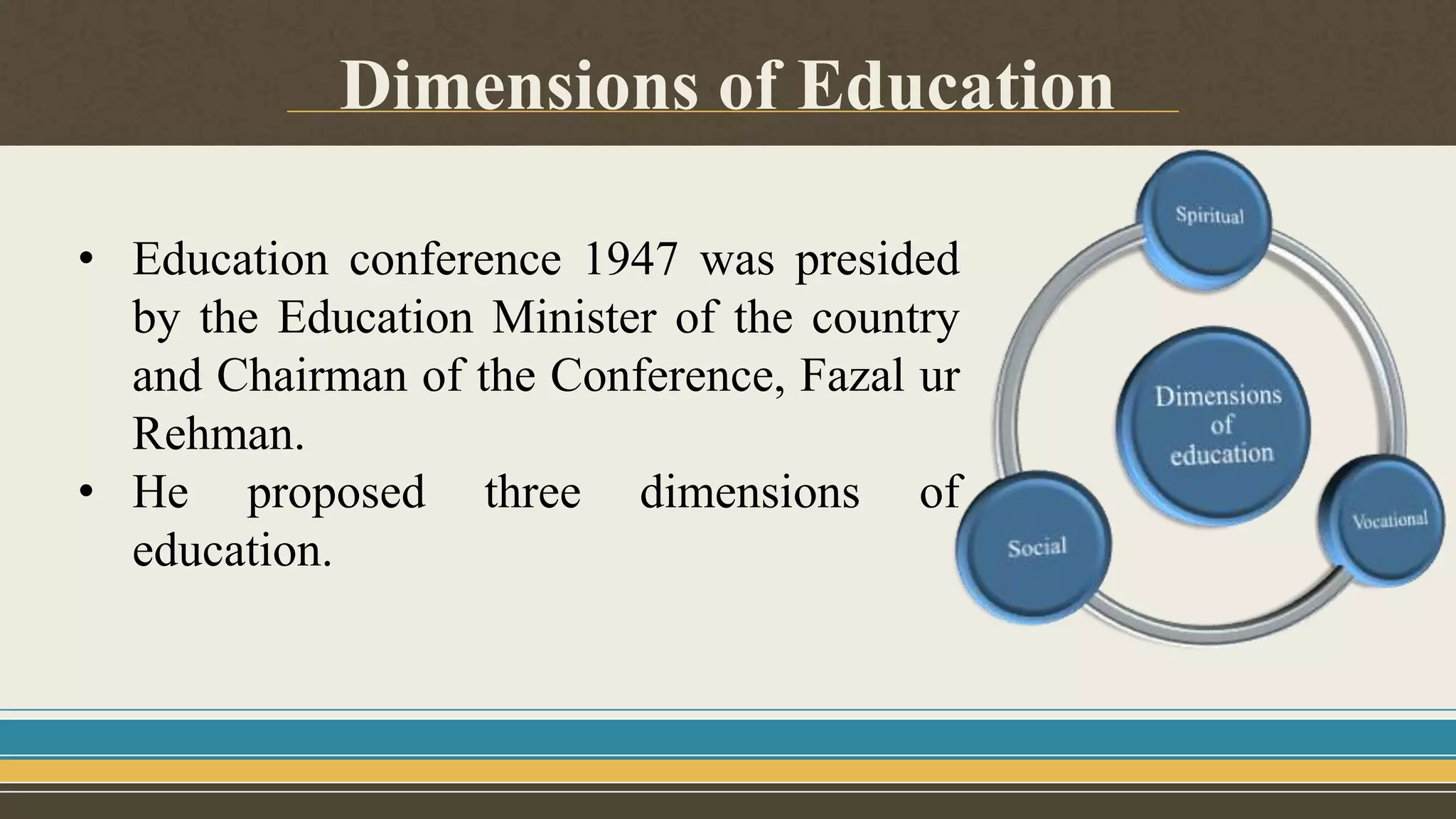
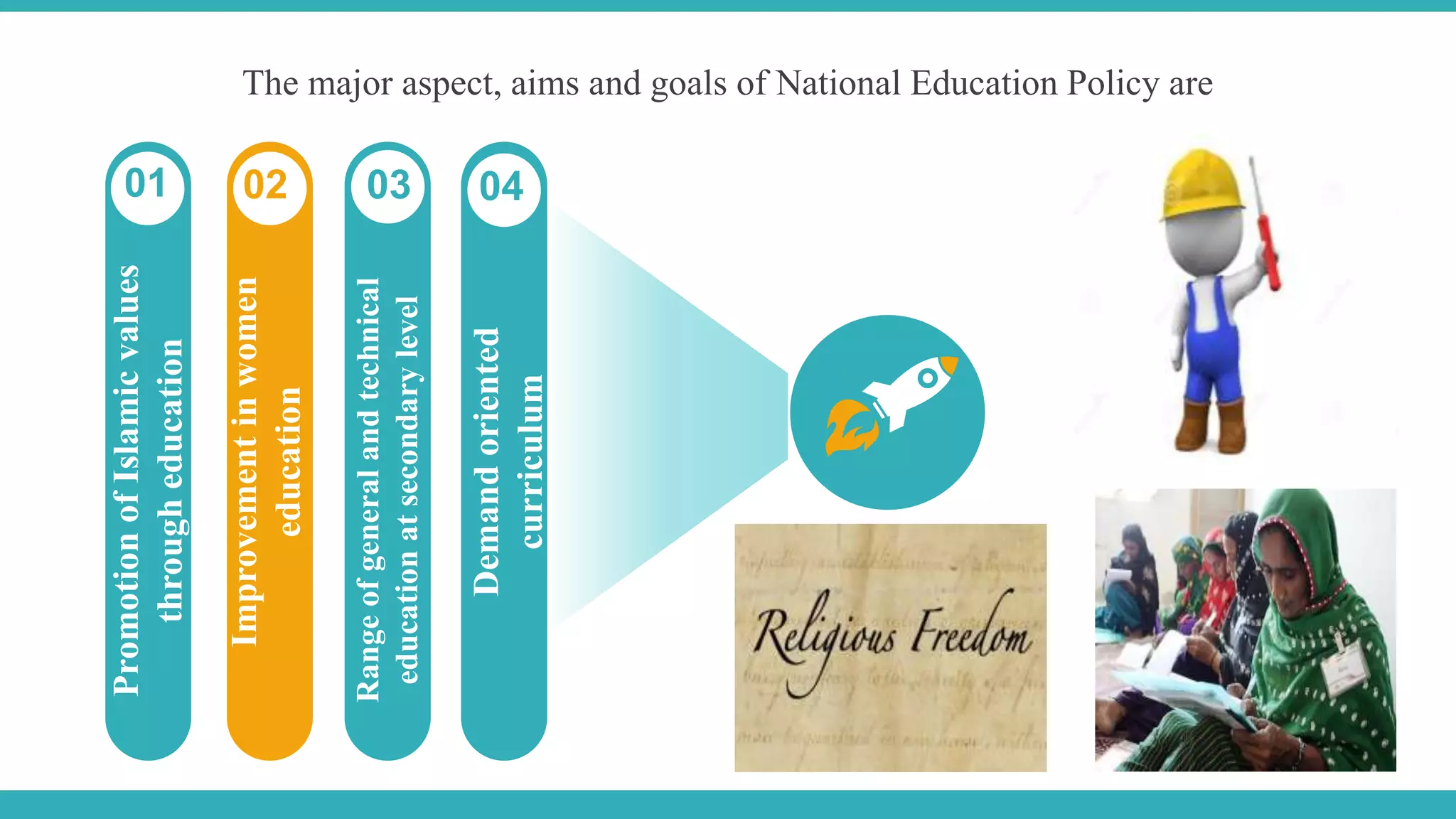
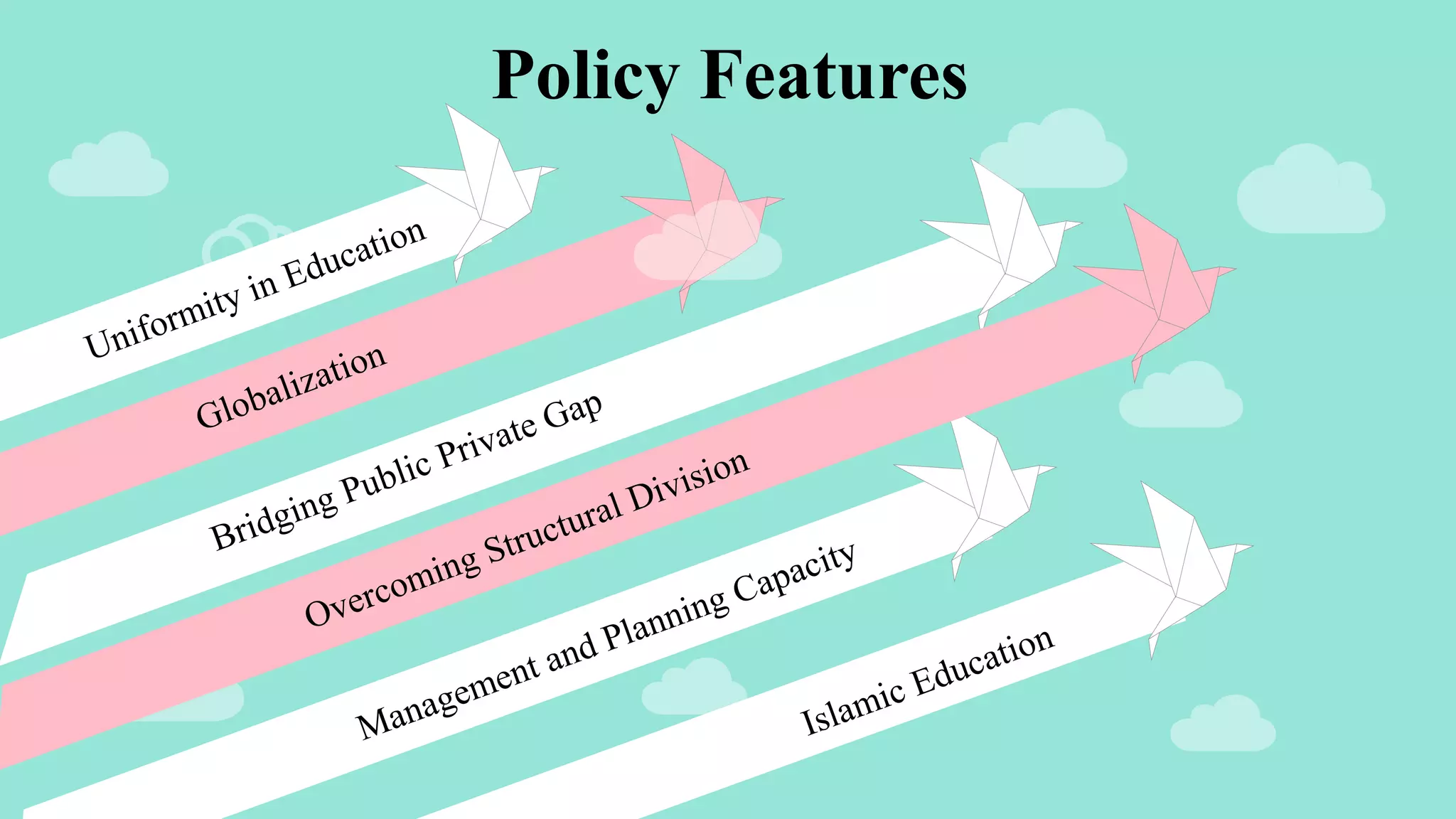
The document outlines the evolution of education policies in Pakistan from 1947 to 2009, highlighting significant conferences and policies that shaped the education system. Key milestones include the first education conference in 1947, various national education policies over the decades that aimed to address issues such as literacy, technical education, and gender equality in education. Despite the introduction of numerous policies, challenges in implementation and resource allocation have hindered their effectiveness.