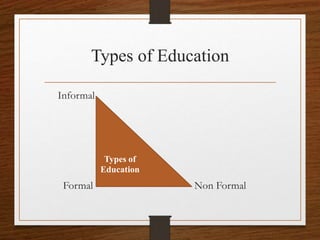
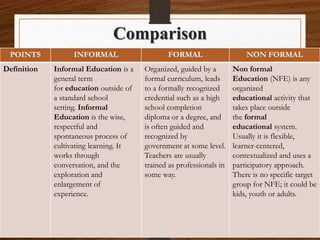
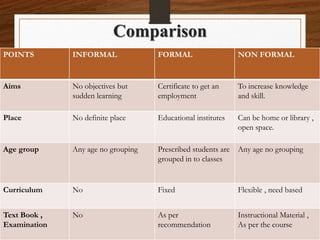
Education is defined as the process of imparting knowledge and skills through instruction and study. It involves bringing about desirable changes in behavior and is directed towards a socially acceptable end. The main types of education are formal, non-formal, and informal. Formal education takes place in institutional settings and leads to certificates and degrees. Informal education occurs through daily experiences and exposure to one's environment. Non-formal education is flexible and takes place outside formal systems, using participatory approaches. The real purpose of education is to help people become better individuals by developing enlightenment, knowledge, personality, and leadership qualities.