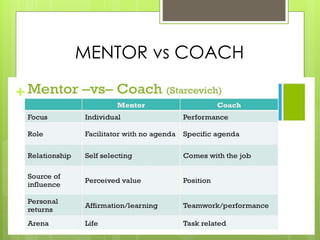
The document discusses counselling, mentoring, and coaching in higher education. Counselling involves talking through problems with a professional to gain insight and work towards acceptance or change. Mentoring pairs an experienced person with a less experienced one to facilitate growth through teaching, coaching, and challenging. Coaching focuses on improving specific skills and meeting goals set with the coach through direct feedback. While related, counselling, mentoring, and coaching each have distinct purposes, processes, and roles for those involved.