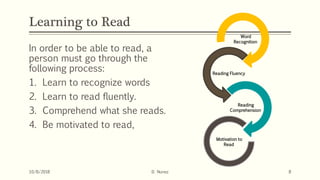
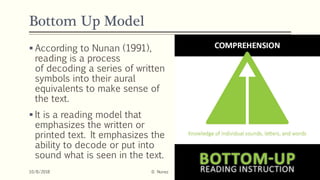
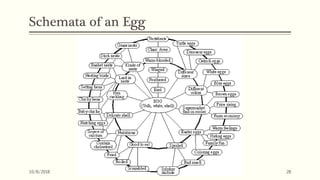
This document discusses various models of the reading process, including bottom-up, top-down, and interactive models. It defines reading as a complex process involving word recognition, comprehension, fluency, and motivation. The bottom-up model views reading as decoding written symbols, while the top-down model emphasizes using context and background knowledge to construct meaning. The interactive model incorporates both bottom-up and top-down processes. Emerging models also consider the roles of schema theory, metacognition, attitudes, and the negotiation of meaning between readers and writers.