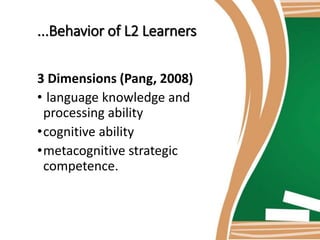
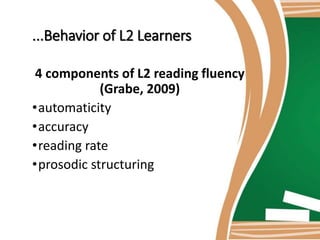
This document discusses the language-based approach to teaching reading. It explains that this approach helps students focus on how language is used in literary texts. Students engage with texts through language activities rather than just studying facts. The document also provides examples of lesson plans using this approach, including pre-reading discussion, reading aloud, and a post-reading activity where students make scrapbooks about heroes from the text. The rationale is that these activities promote language use among students through discussions, presentations, and describing characters.