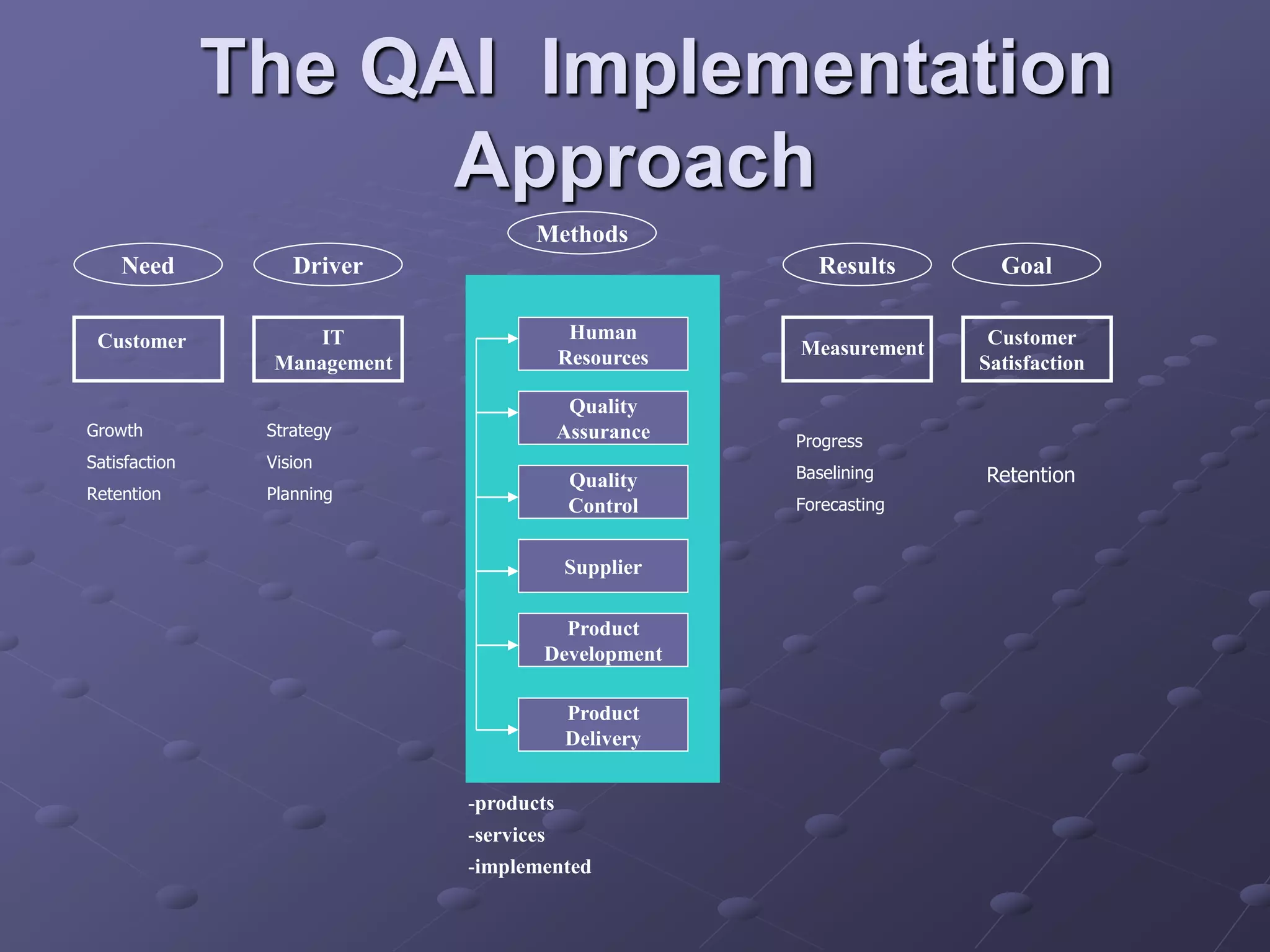
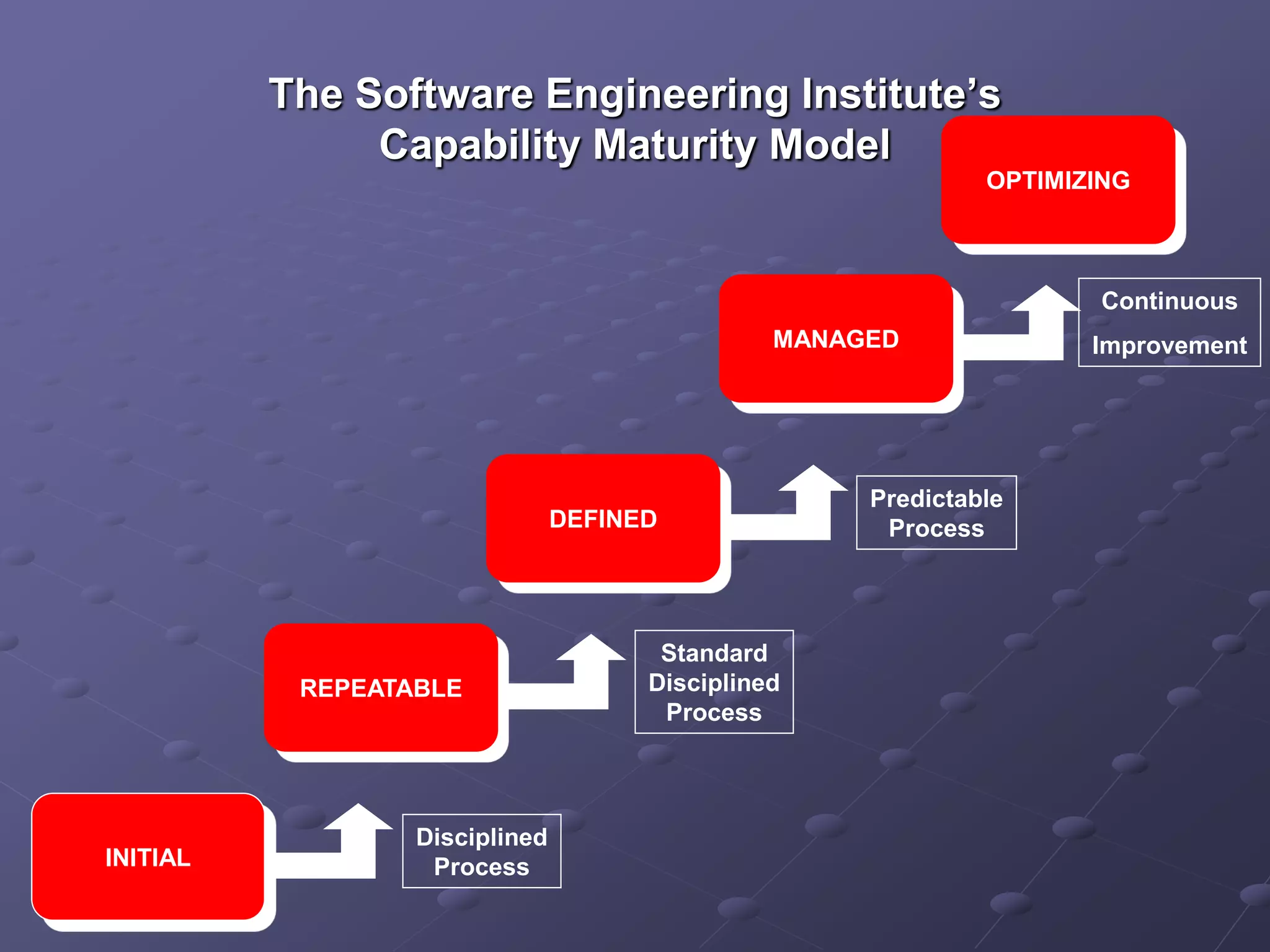
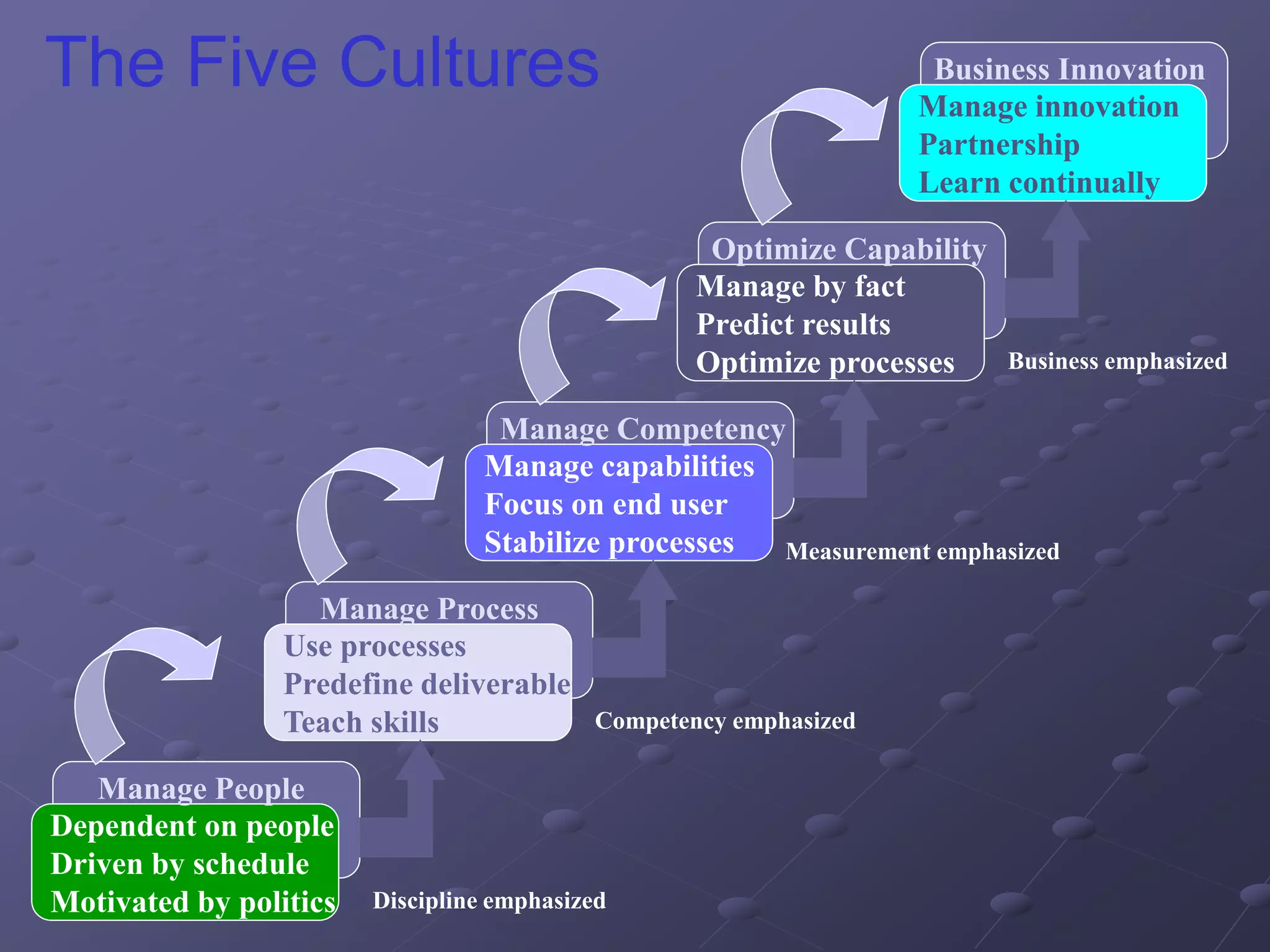
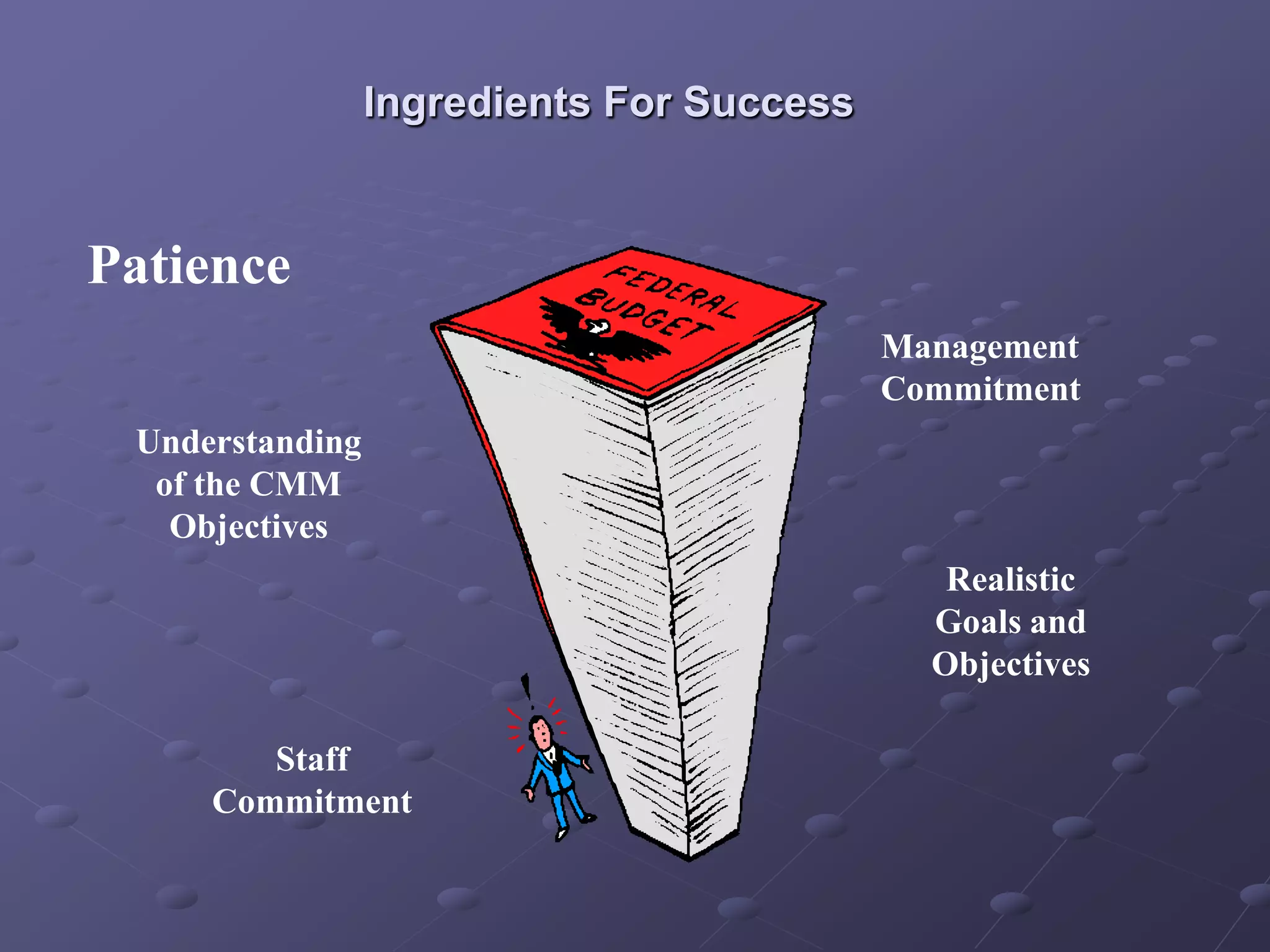
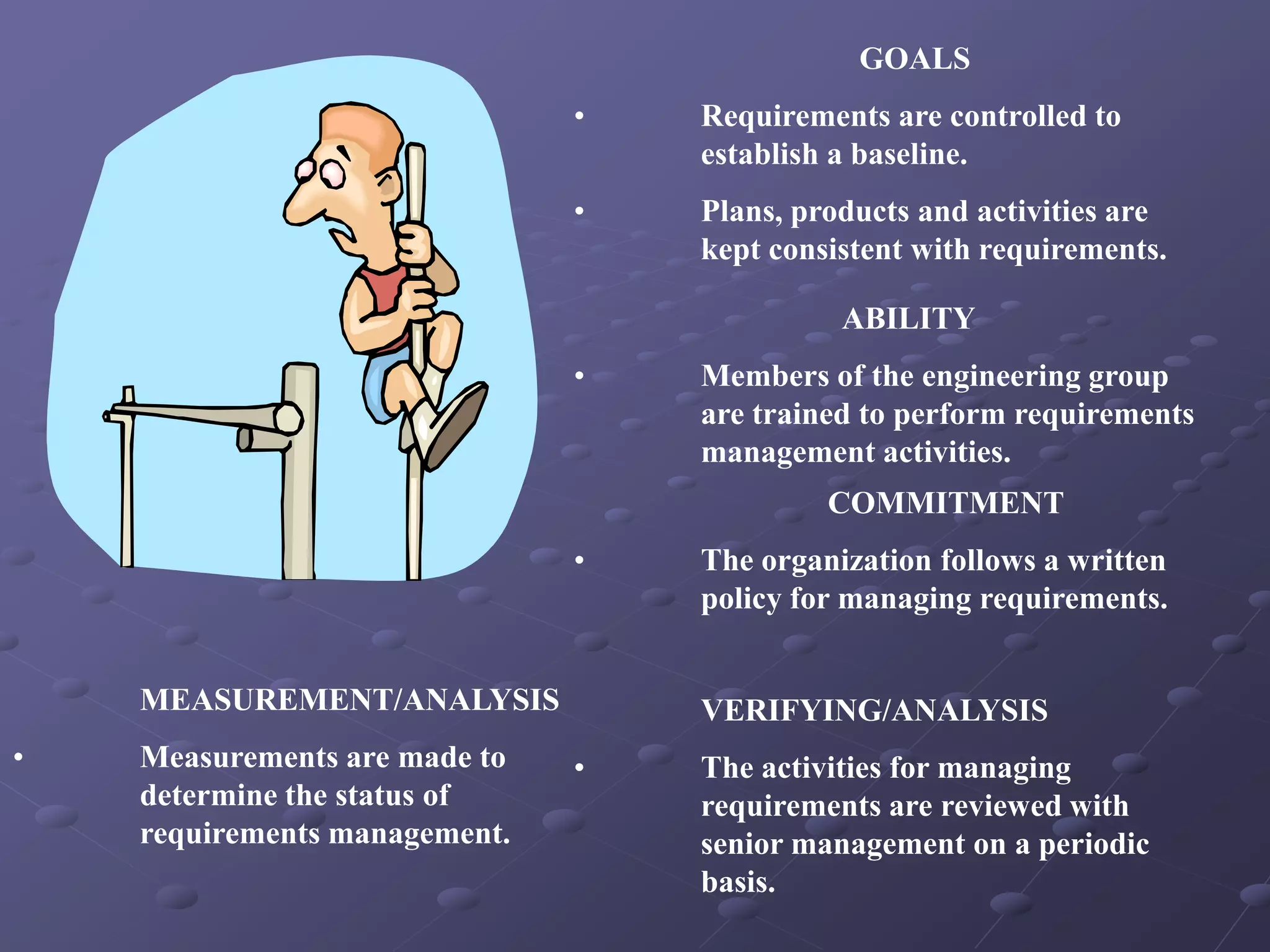
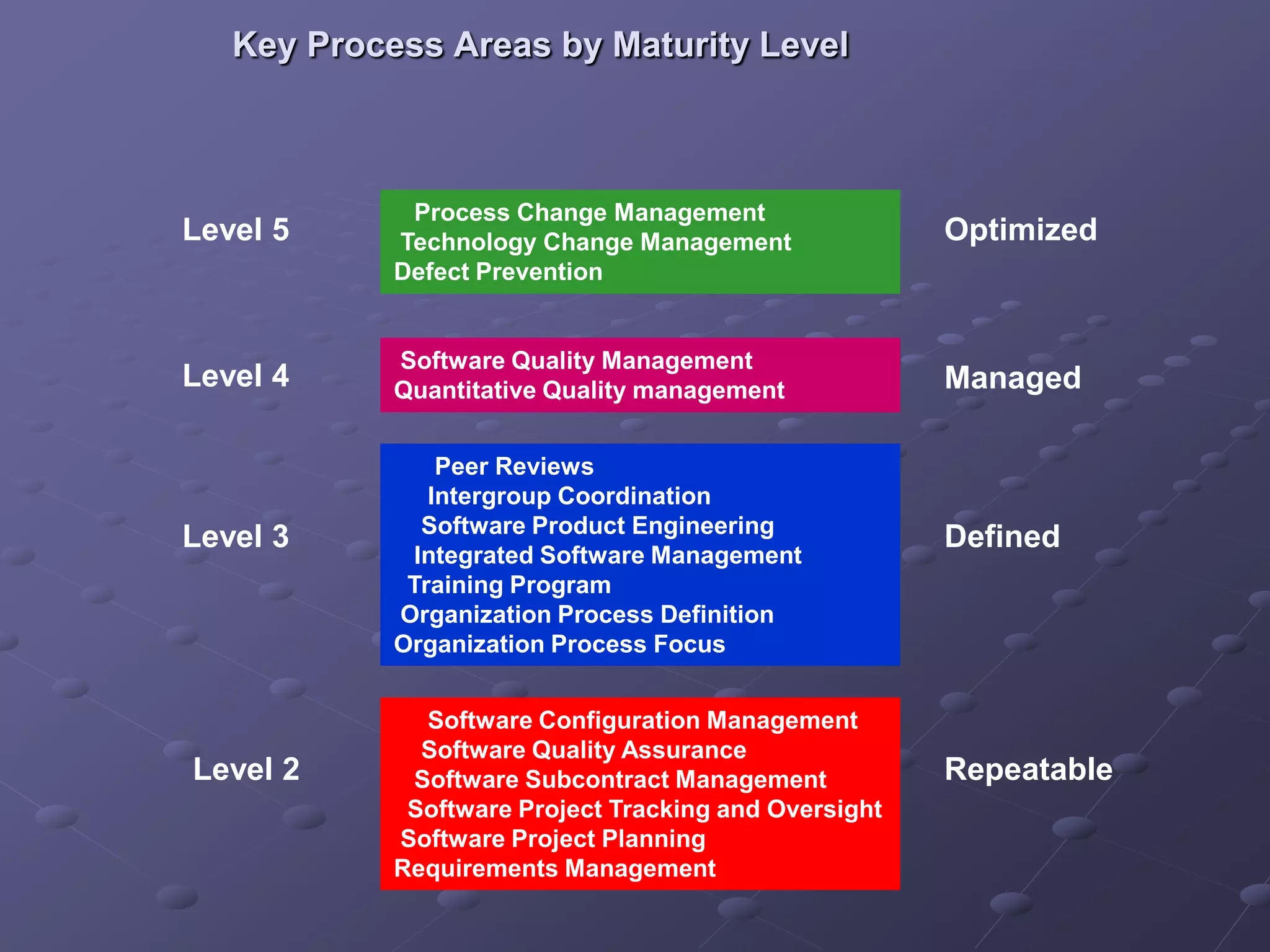
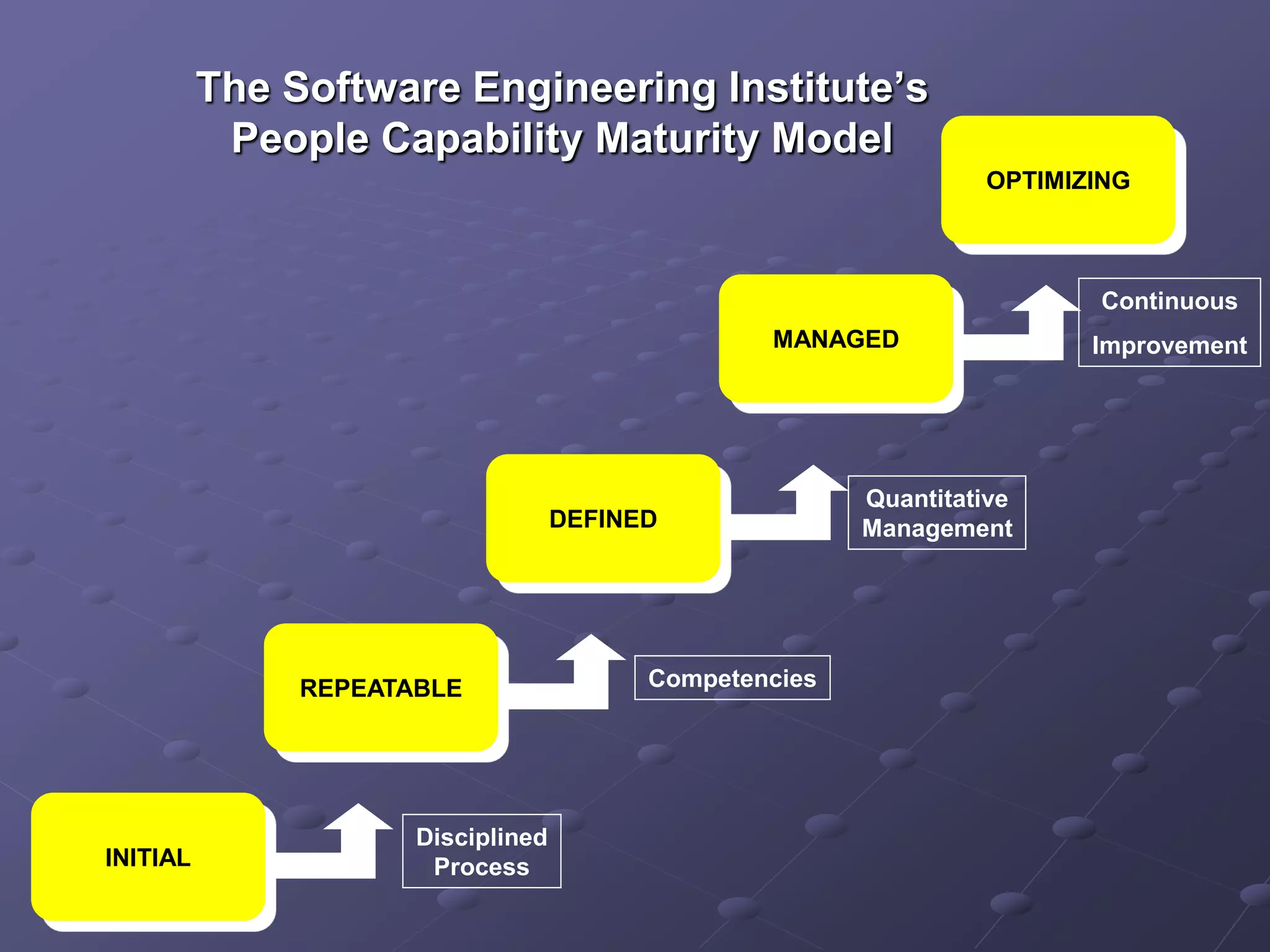
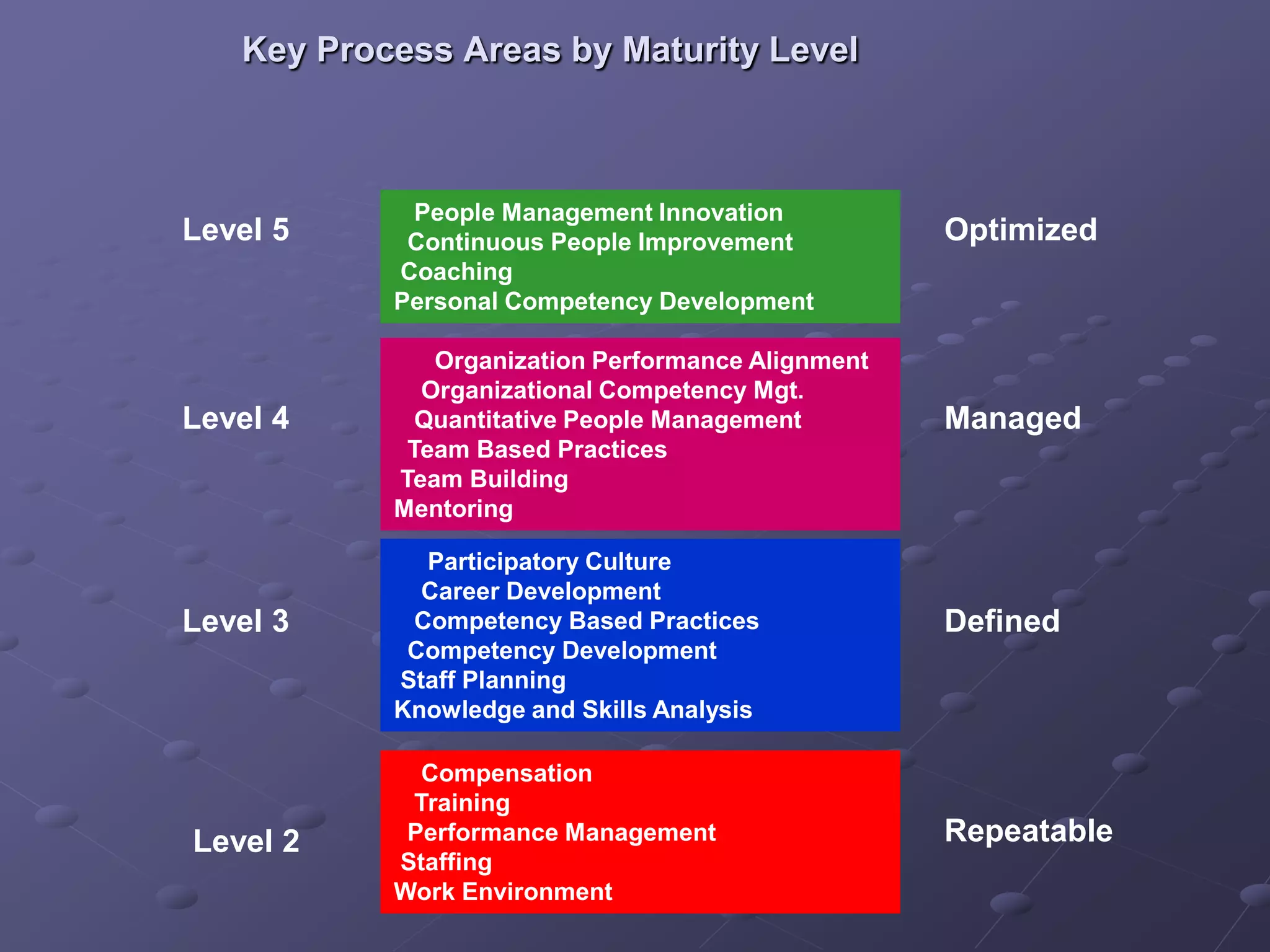
The document provides an overview of quality assurance and software engineering concepts, including key certifications like CSTE and CSQA, and the Capability Maturity Model (CMM). It outlines significant quality management principles, practices, and stages of maturity within processes, emphasizing continuous improvement and effective process management. Additionally, it discusses the organizational commitment and skill development necessary for implementing these quality frameworks successfully.