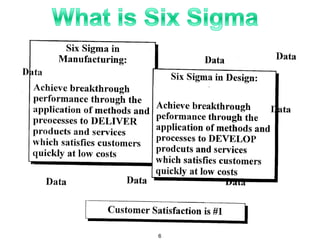
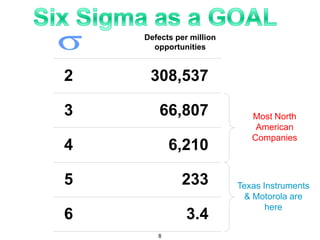
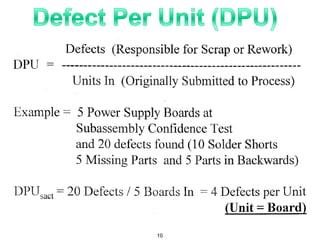
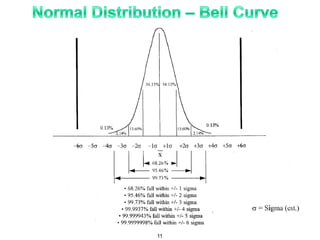
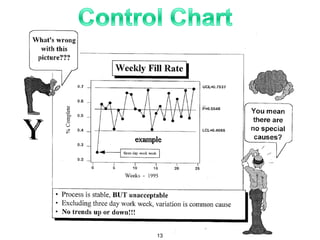
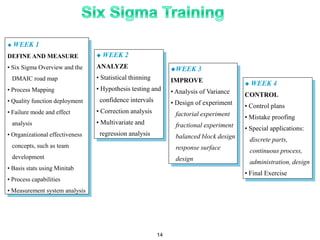
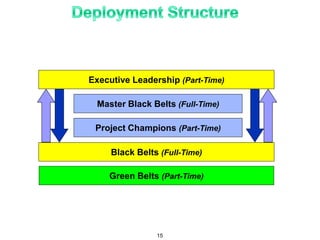
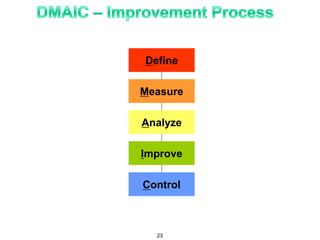
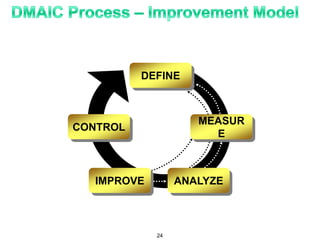
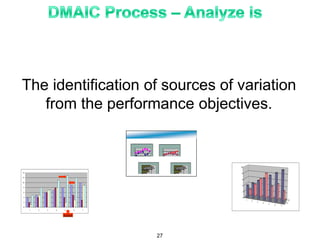
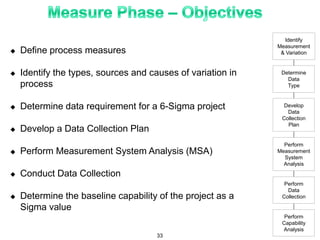
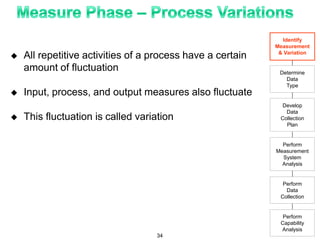
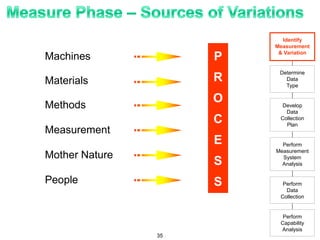
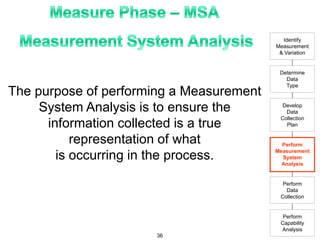
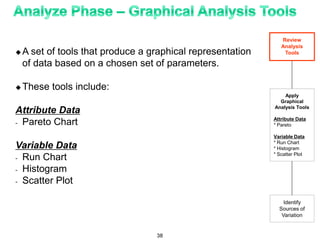
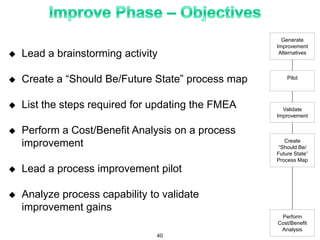
The document provides an overview of Six Sigma as a strategic tool for enhancing customer satisfaction and business performance by reducing variability. It discusses the roles of Green Belts and Black Belts in implementing Six Sigma projects, the structure of the training program, and the stages of the Six Sigma process (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control). It also highlights the historical context of Six Sigma, including its origins at Motorola and examples of companies that have successfully adopted the methodology.