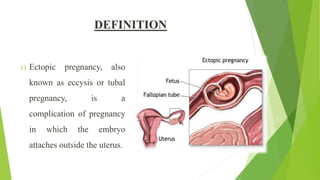
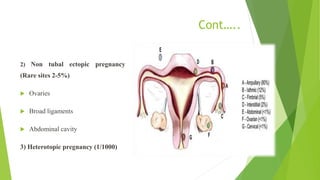
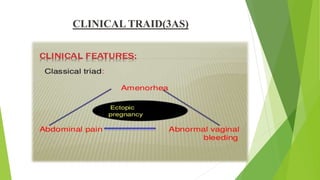
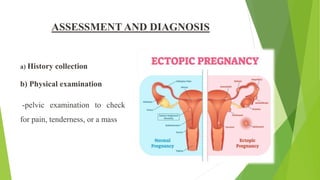
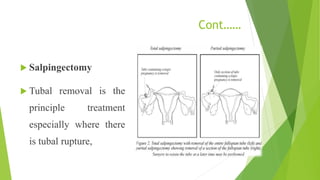
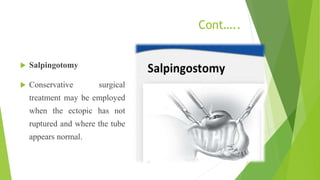
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside of the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. Risk factors include age over 35, previous pelvic surgeries or infections, fertility treatments, and structural abnormalities of the fallopian tubes. Symptoms can include abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding or spotting, and dizziness. Diagnosis involves testing hCG levels in blood and ultrasound imaging. Treatment options are medical management with methotrexate or surgical procedures like laparoscopy, laparotomy, or salpingectomy. The main complication is rupture of the fallopian tube which can lead to internal bleeding.