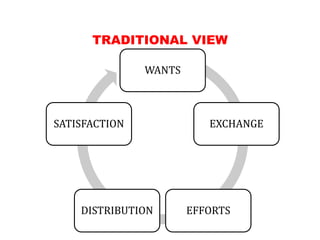
This document provides an overview of key concepts in economics. It defines economics as the study of choice and decision making given scarce resources (Adam Smith). It discusses the history of economics beginning with Adam Smith and the Wealth of Nations. It also covers core economic concepts like production, consumption, goods, services, markets, supply and demand, competition, interest rates, different types of economies, and more. The document serves as a high-level introduction to economics and the fundamental topics within the field.