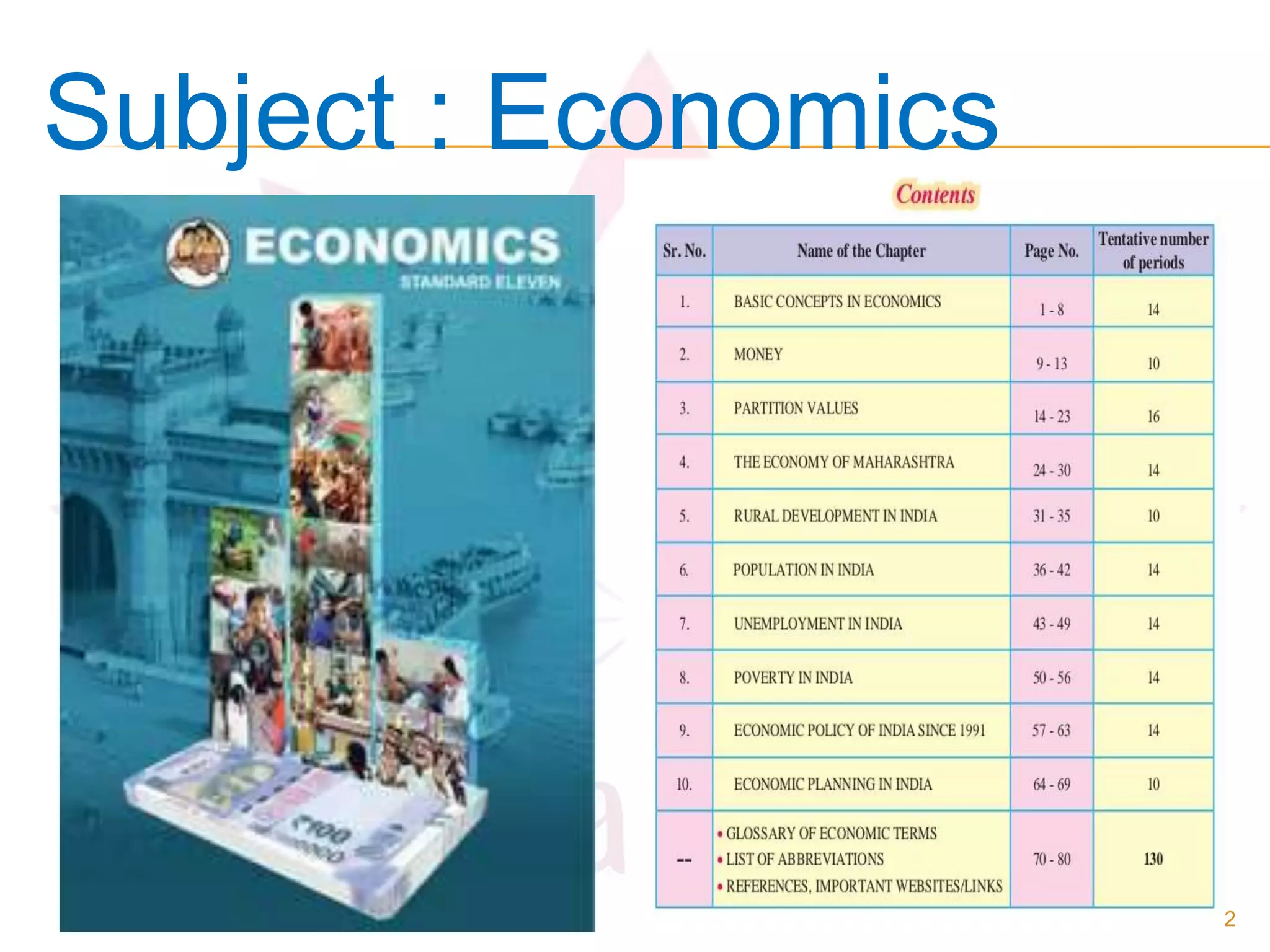
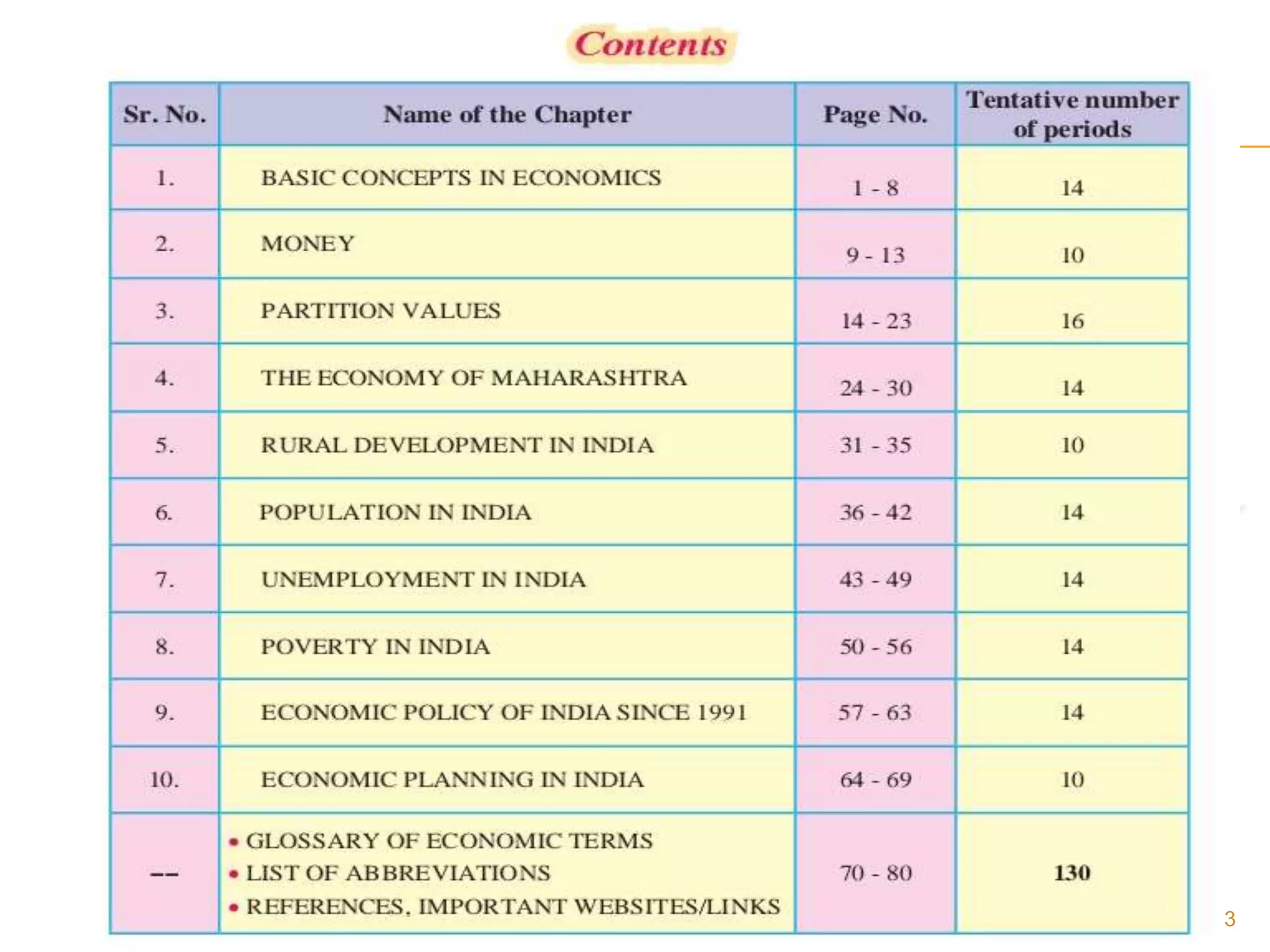
The document provides an overview of concepts in economics from an Indian textbook. It covers:
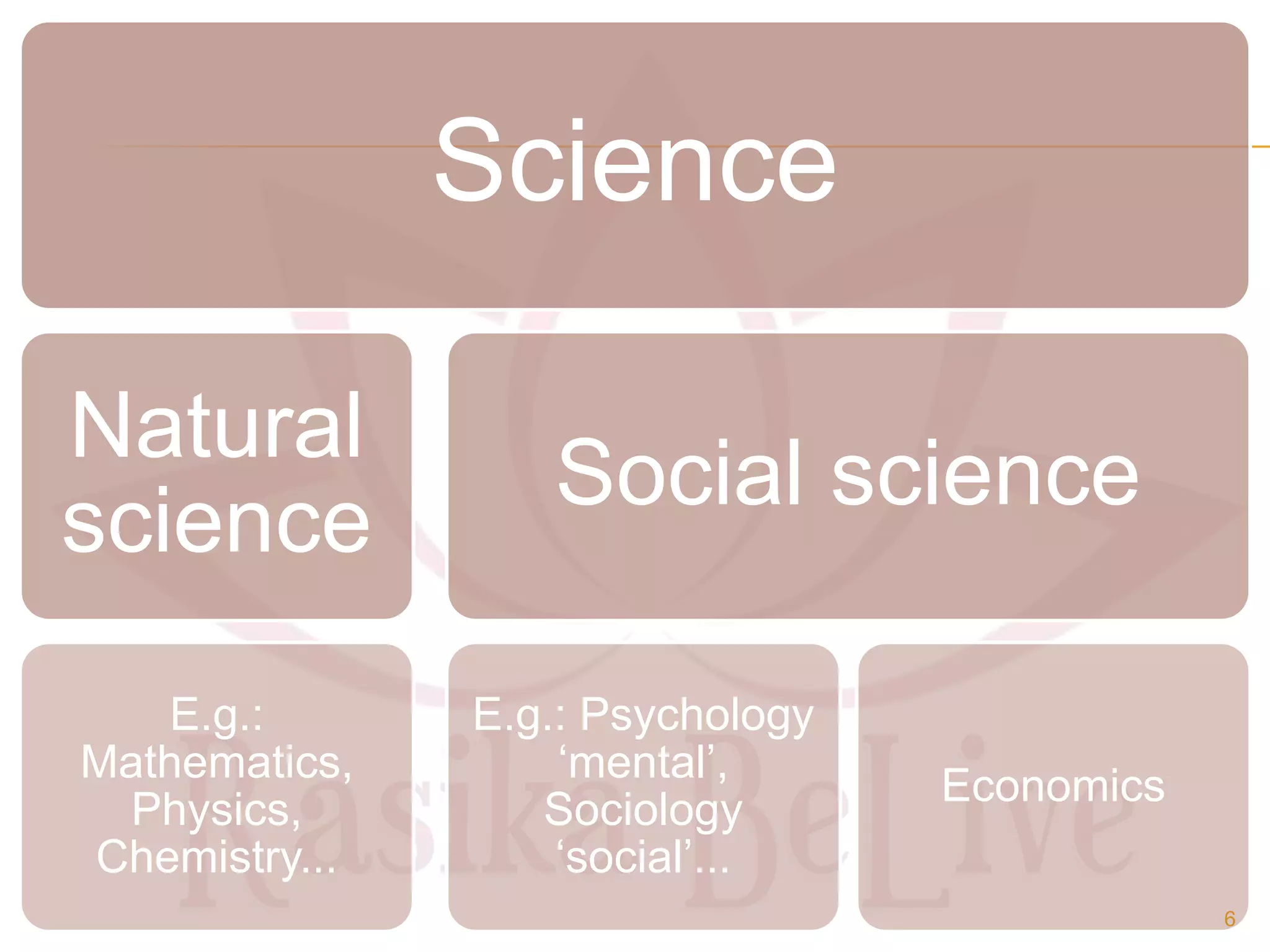
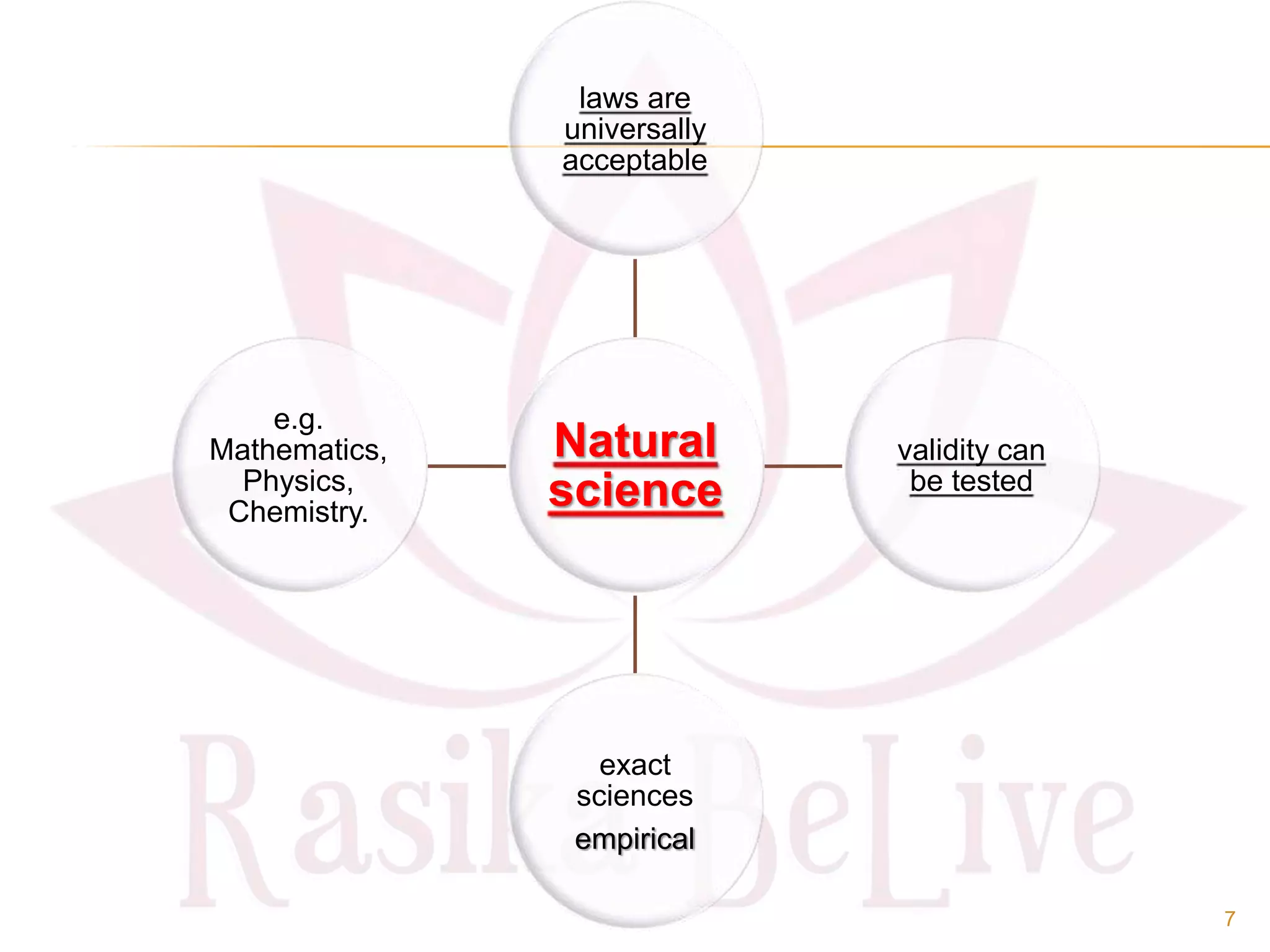
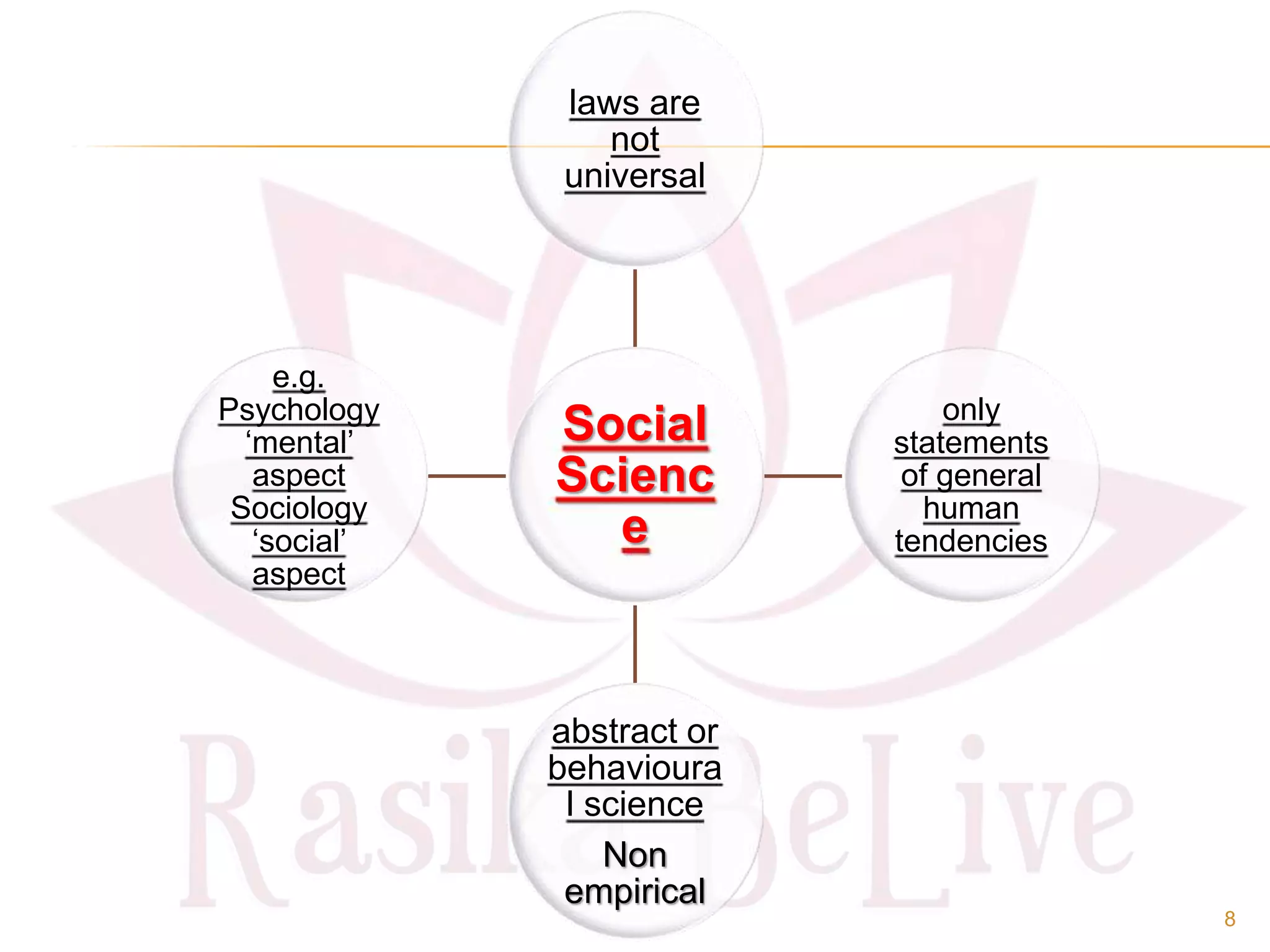
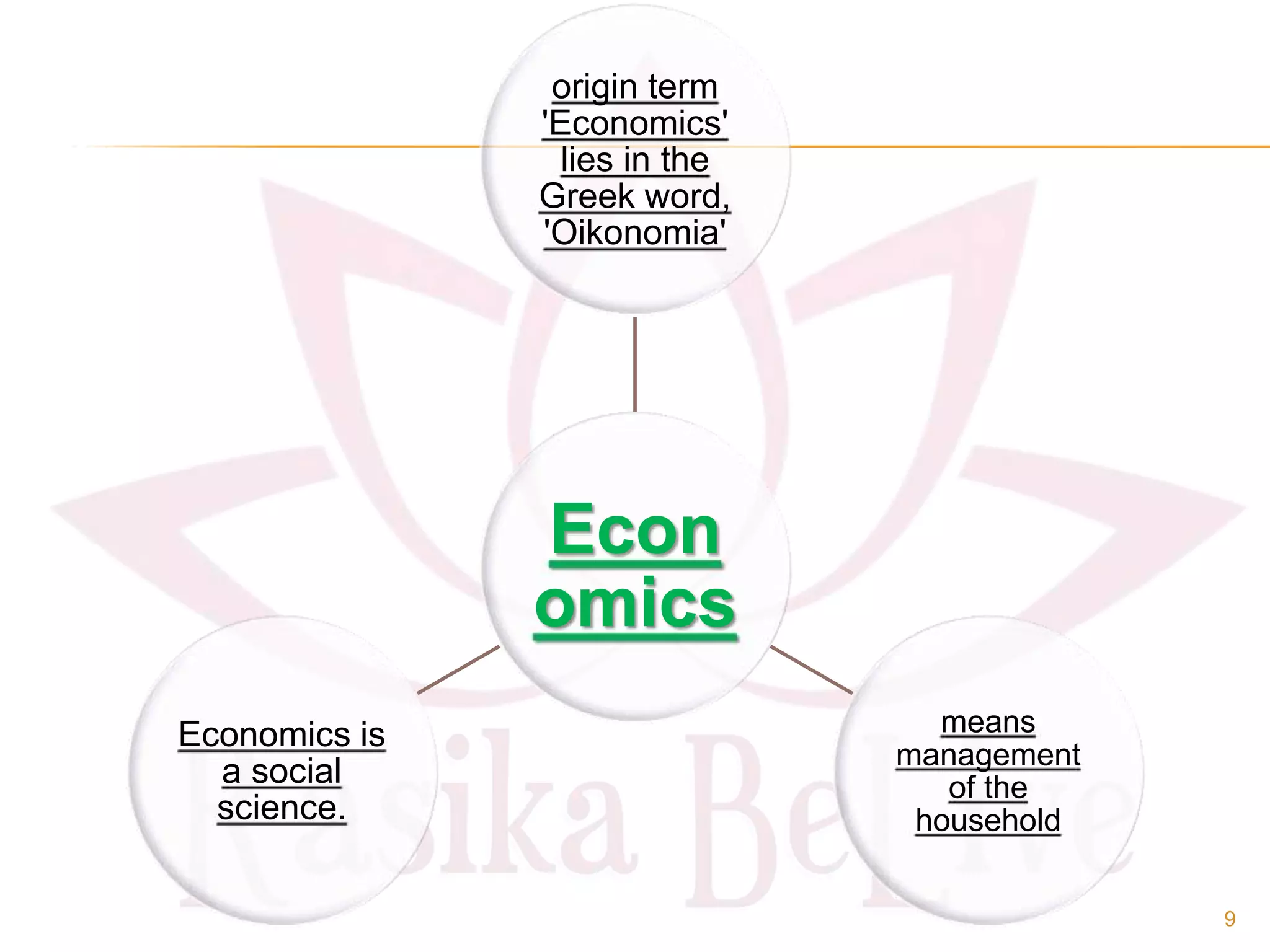
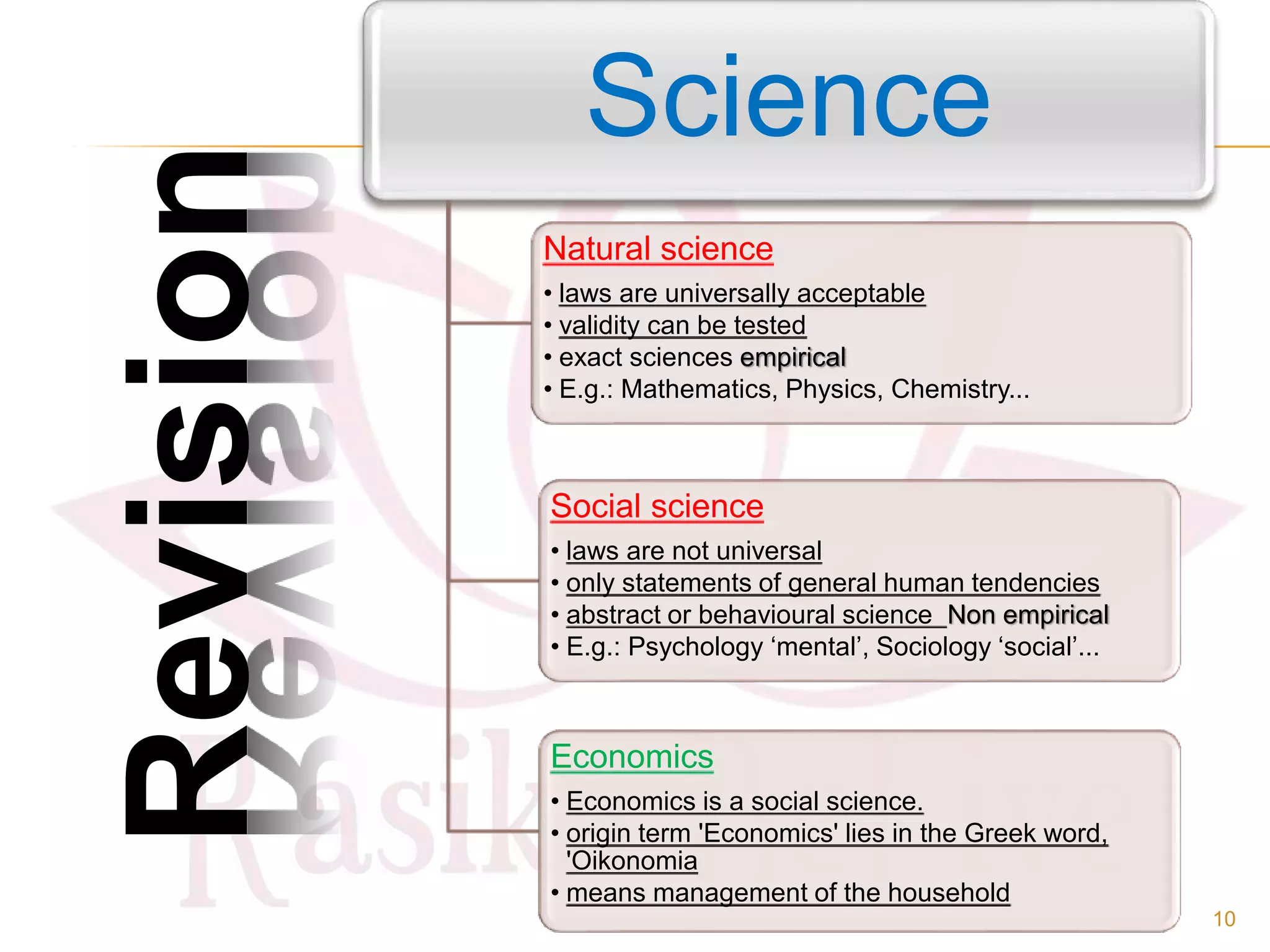
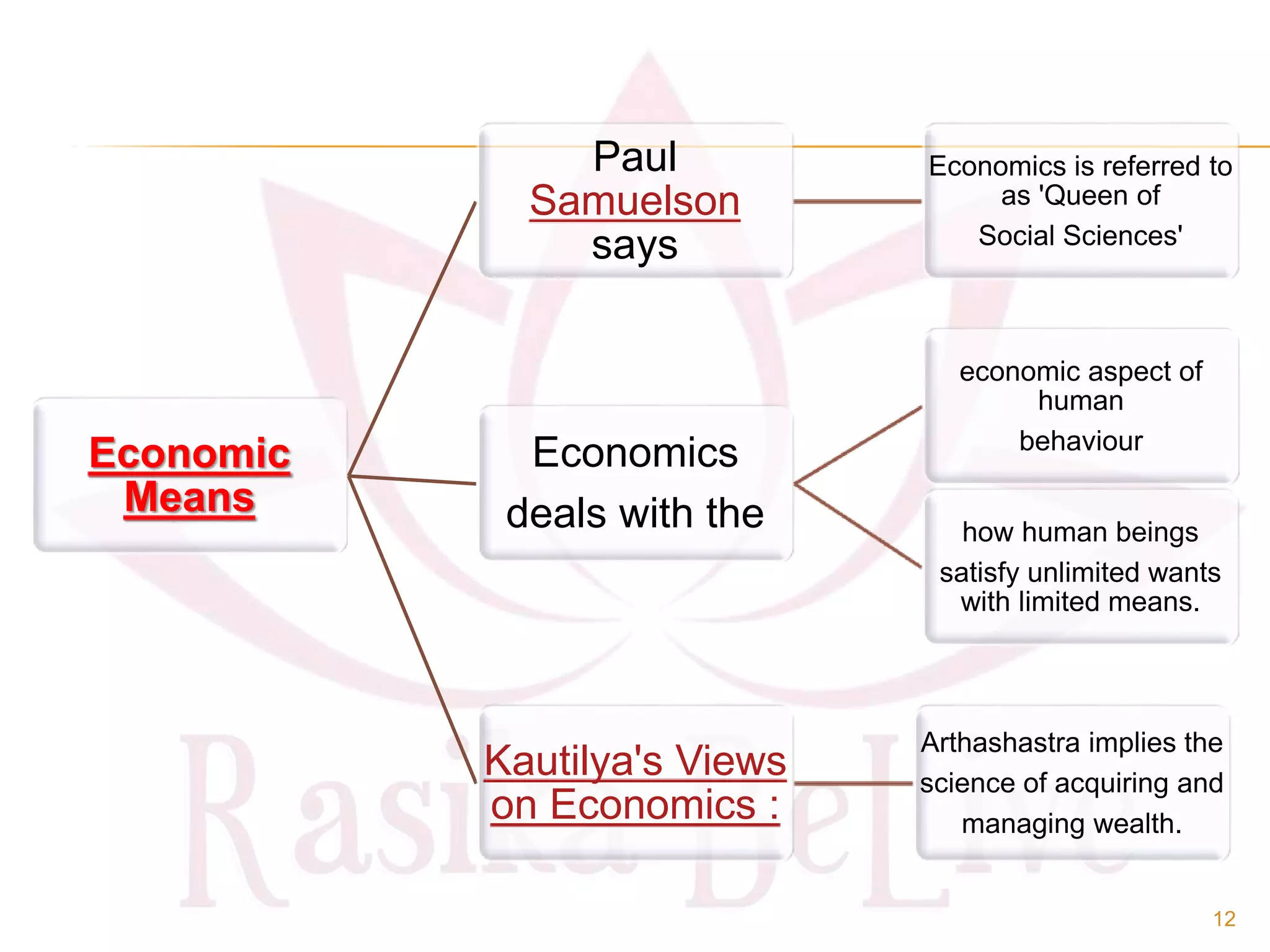
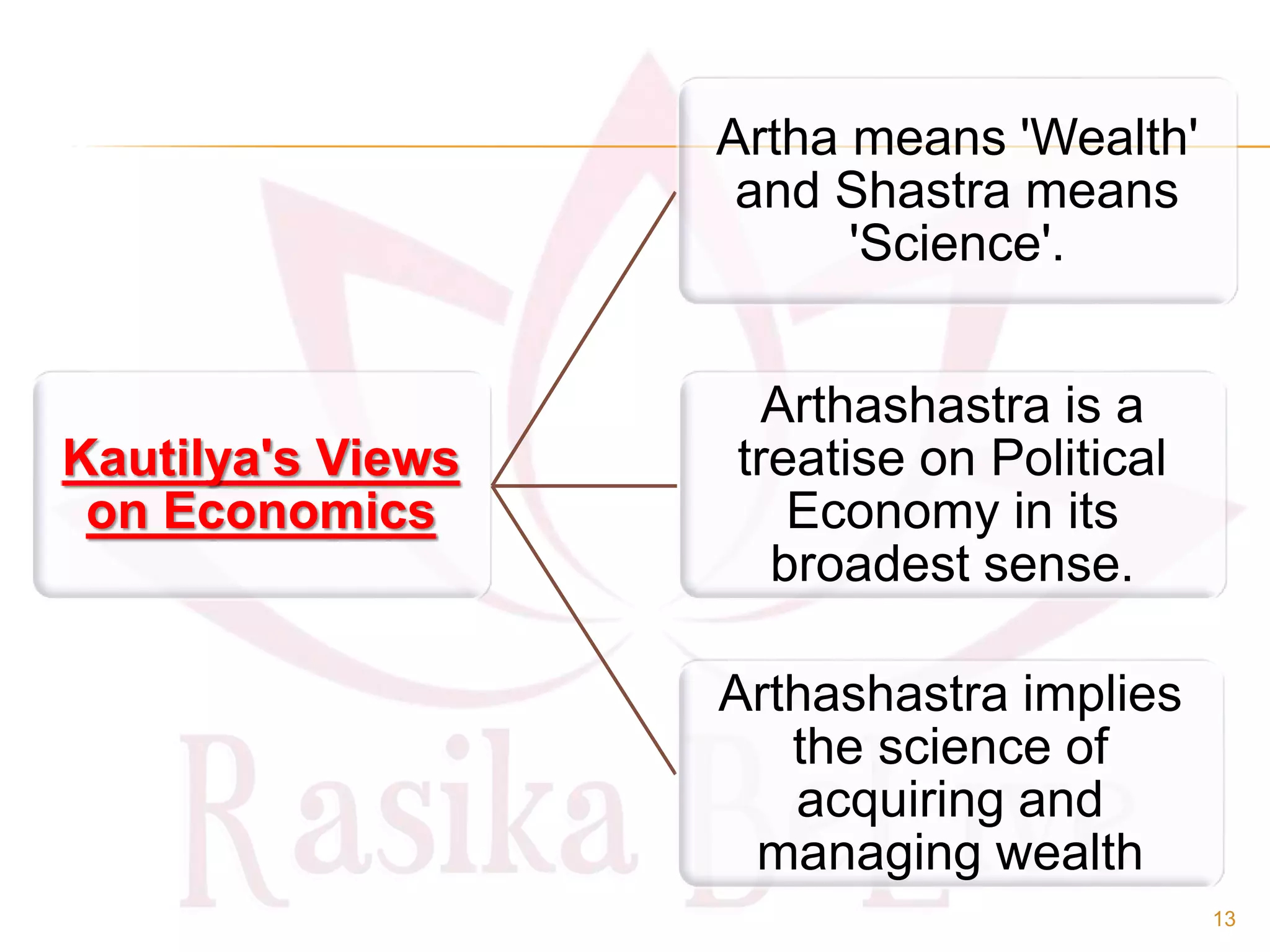
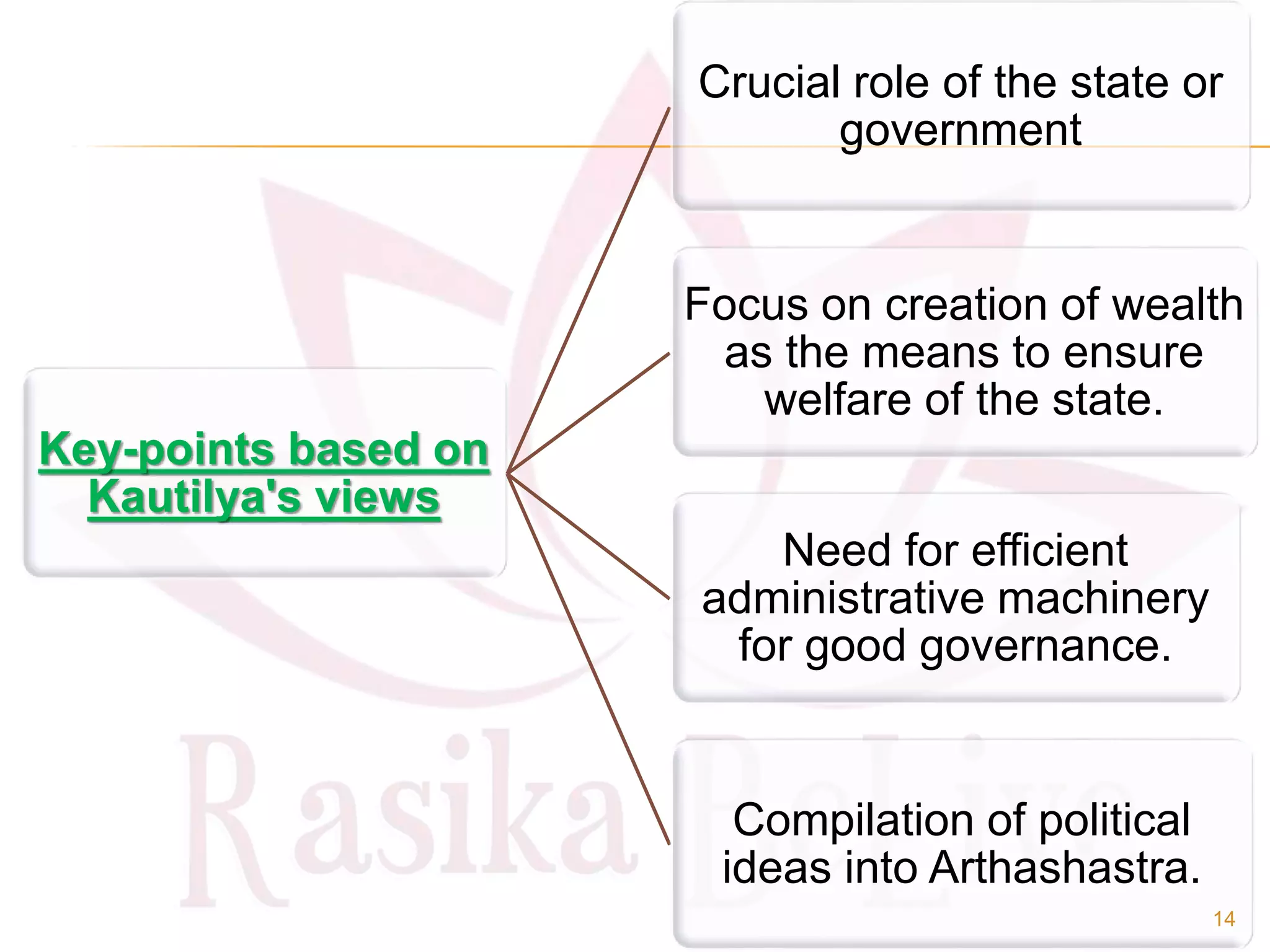
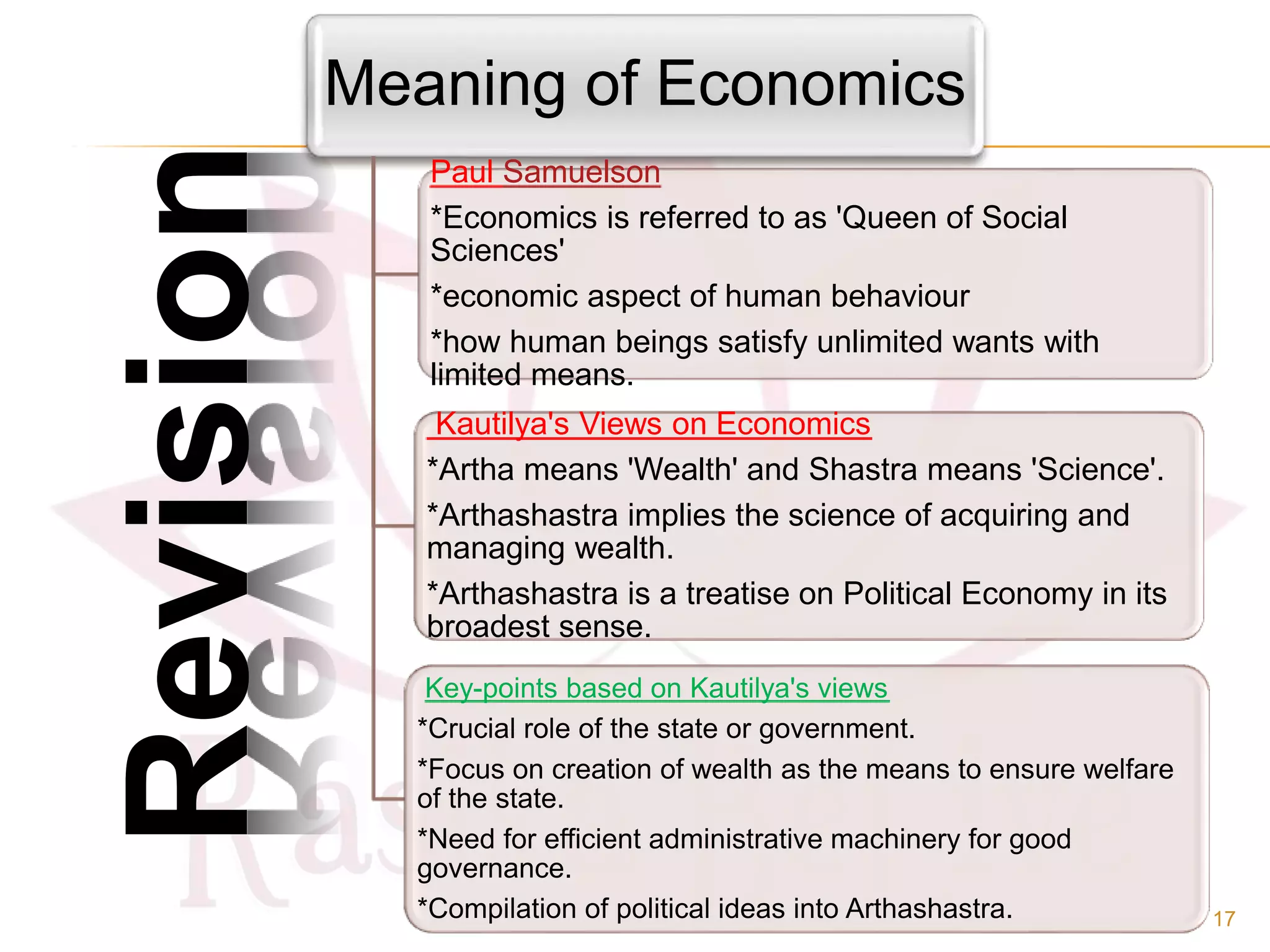
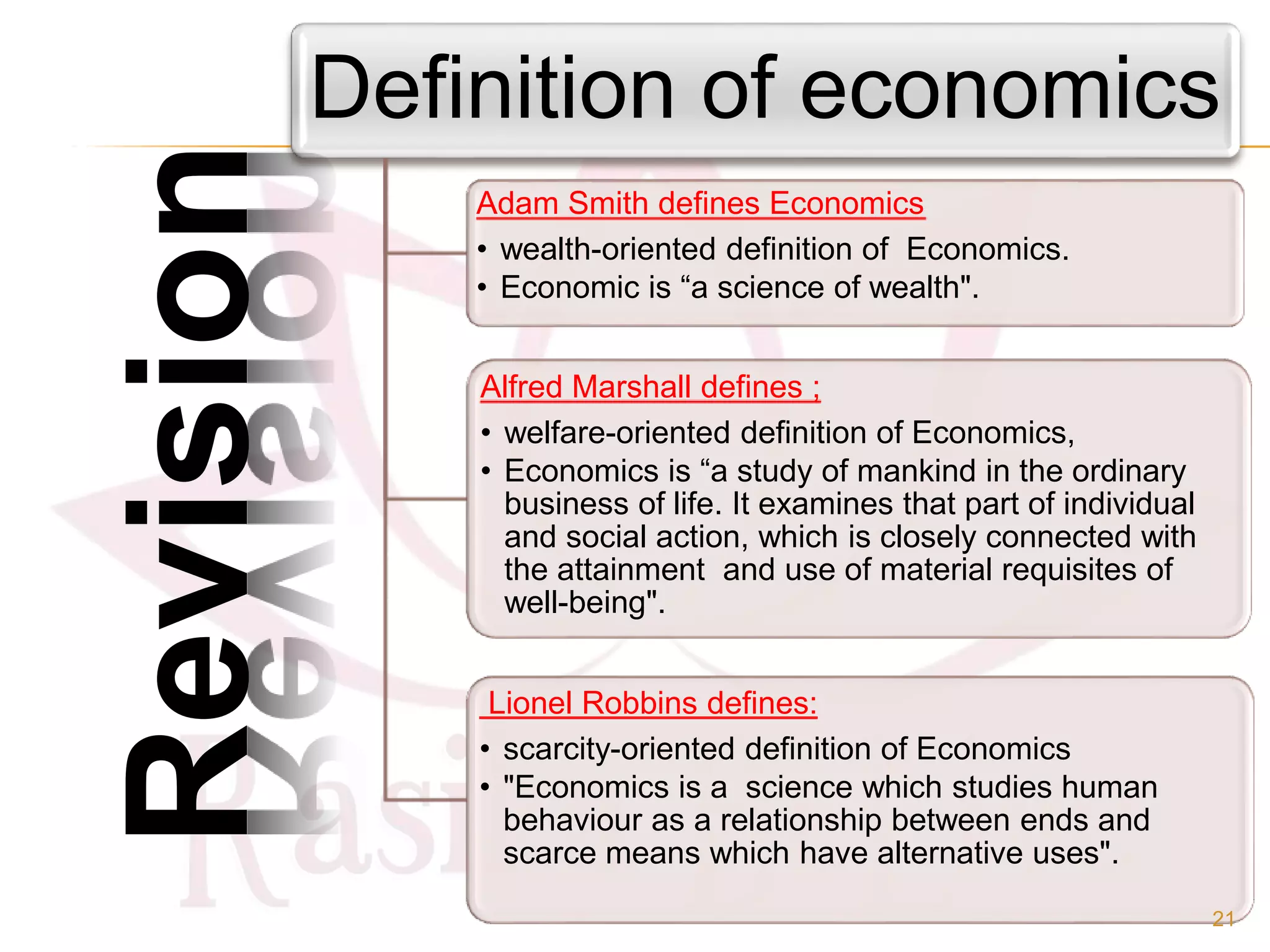
- The origin of economics as a social science and definitions from thinkers like Paul Samuelson and Kautilya.
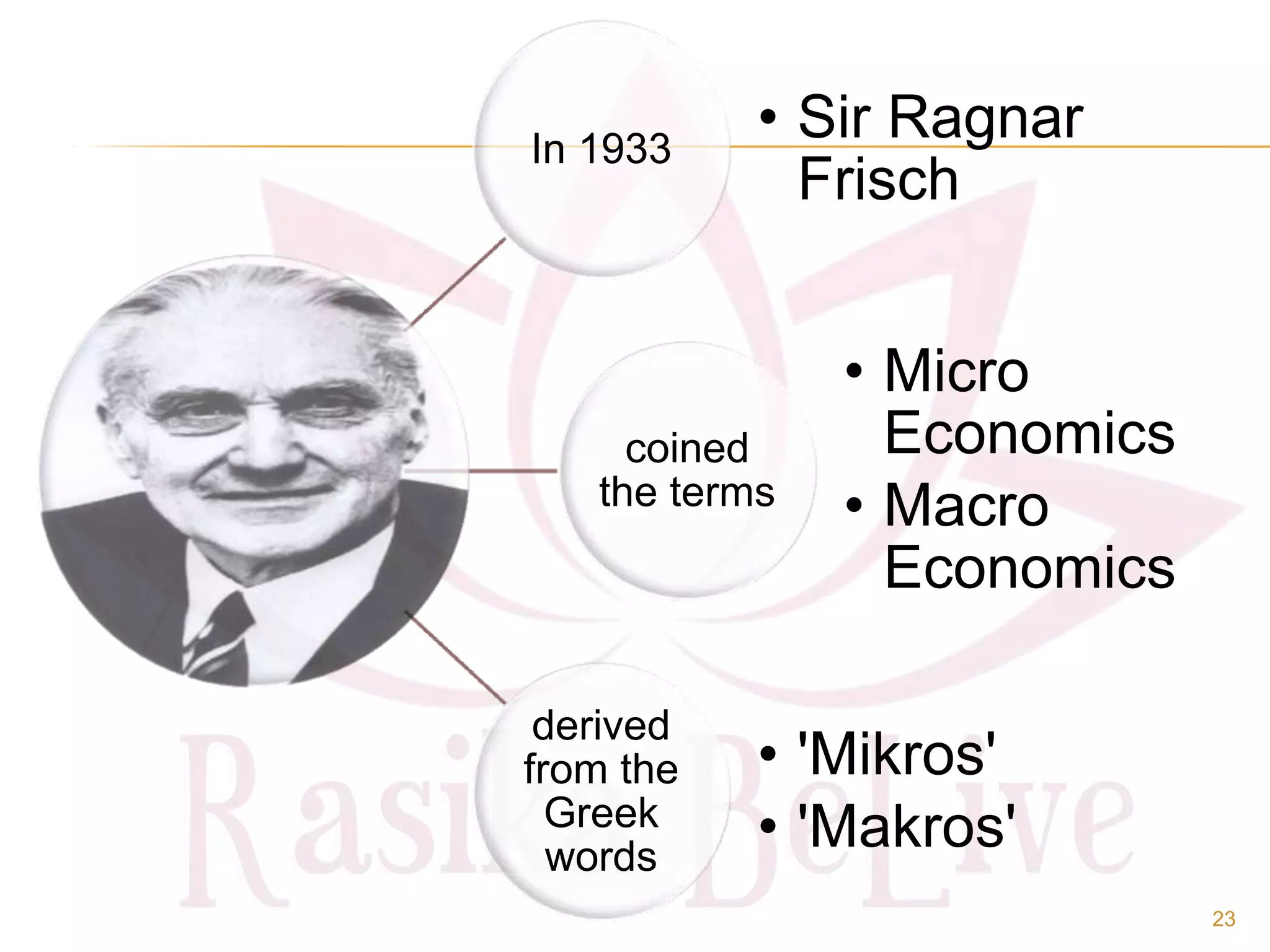
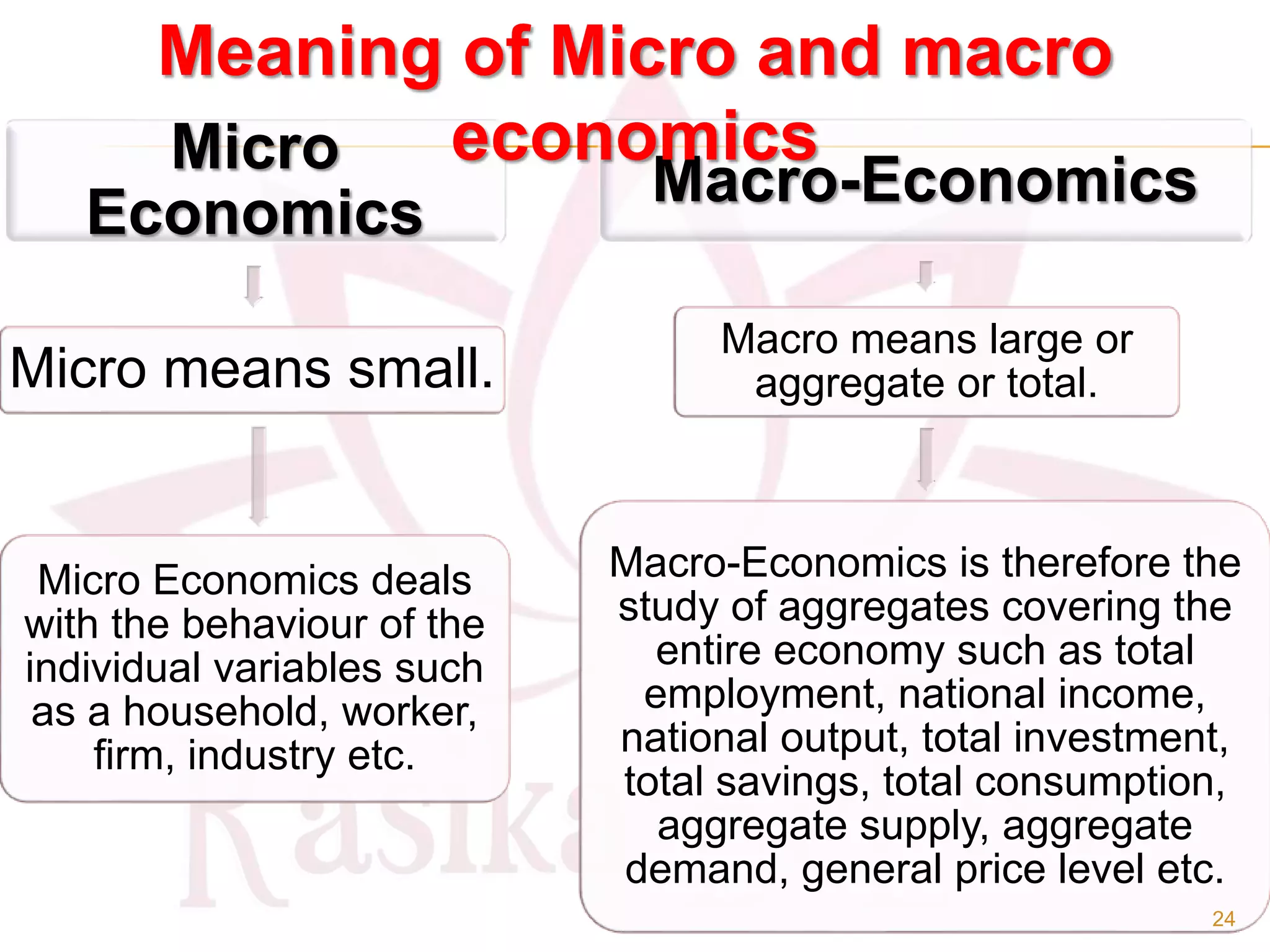
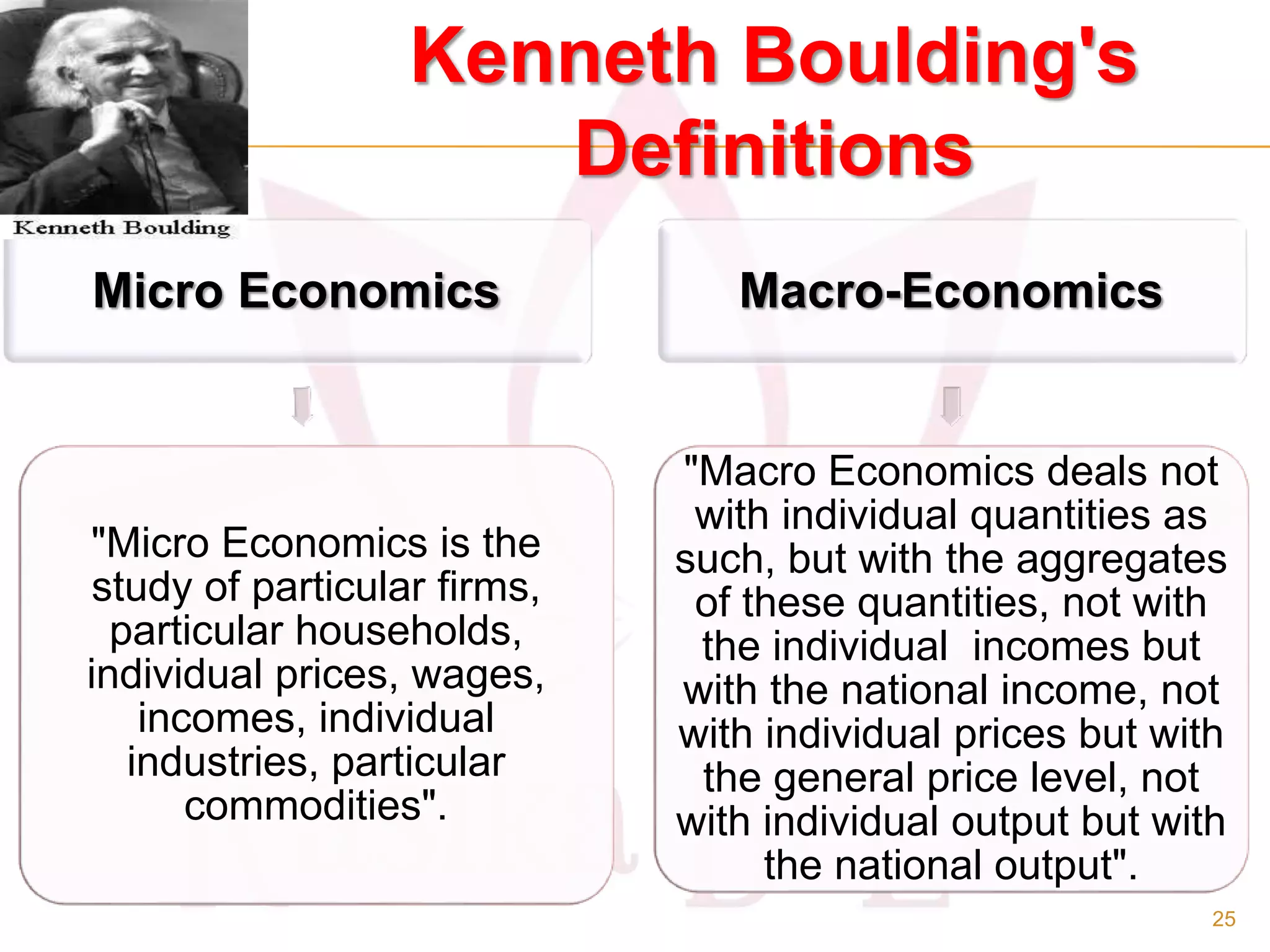
- The main branches of economics including microeconomics, which studies individual components, and macroeconomics, which looks at aggregates.
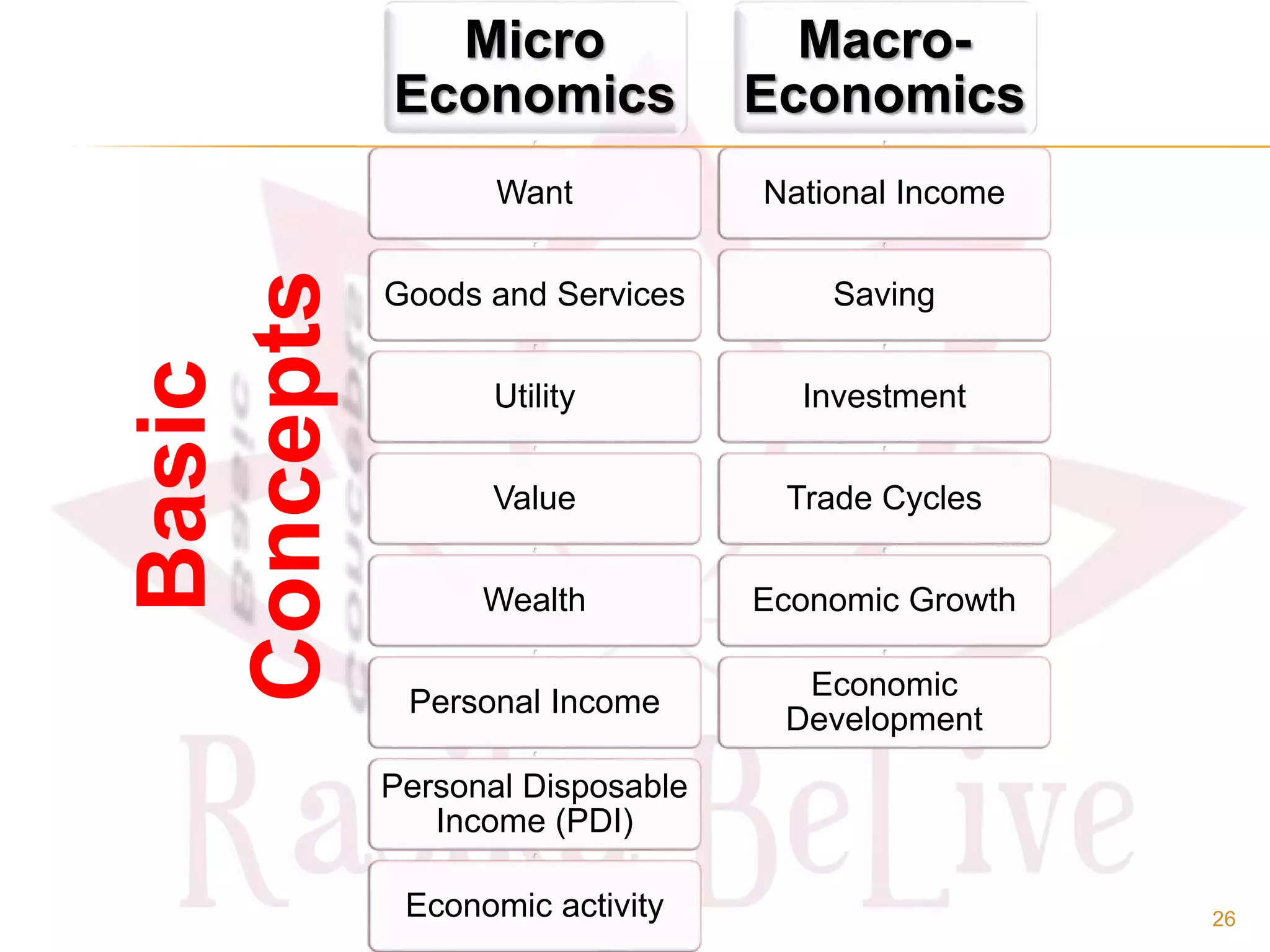
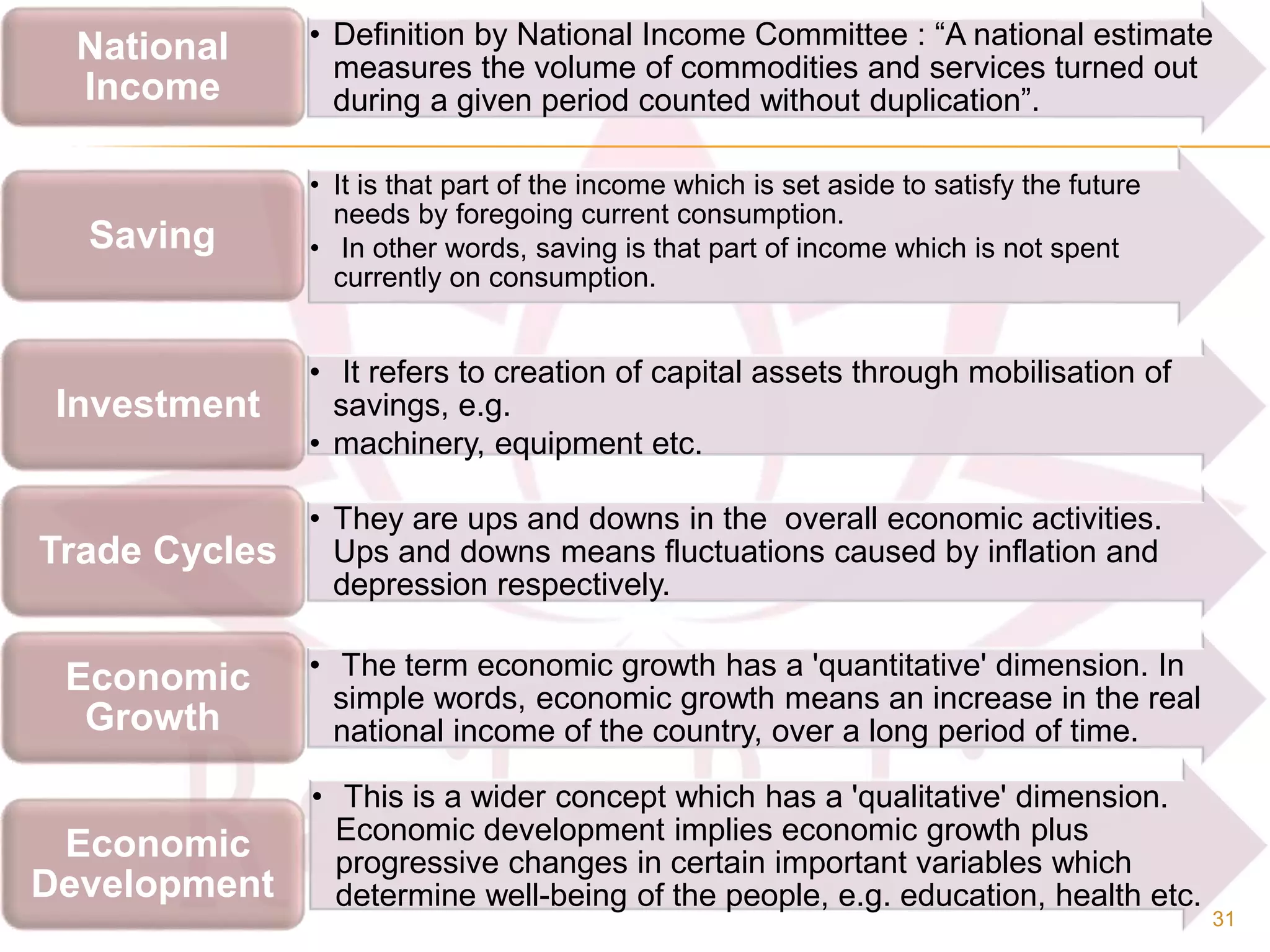
- Key concepts in microeconomics such as wants, goods, utility and wealth. And concepts in macroeconomics including national income, savings, and economic growth versus development.
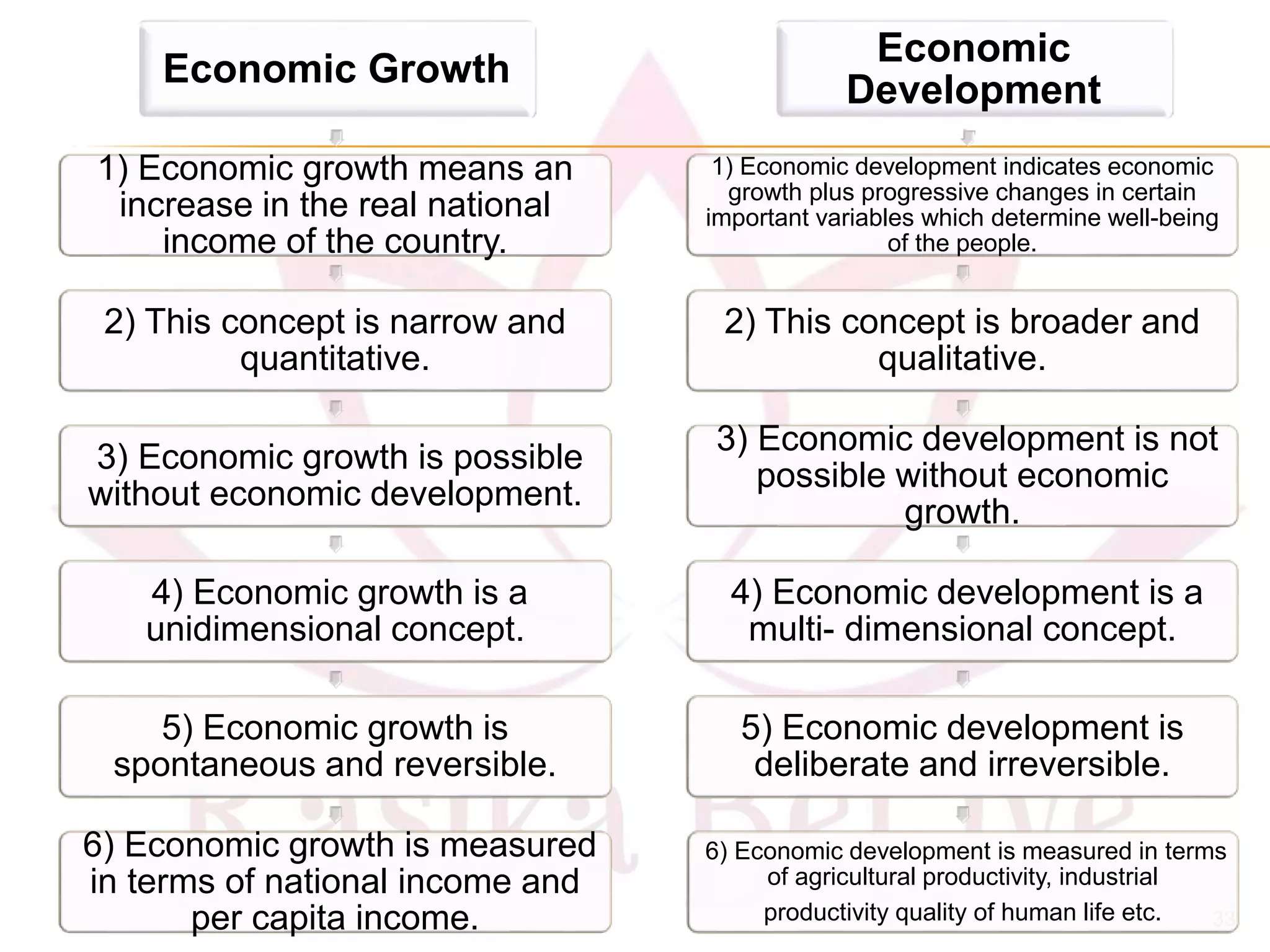
- Differences between economic growth, defined as a rise in national income, and development which also considers social progress.
In 3 sentences it summarizes the main topics around definitions and branches of