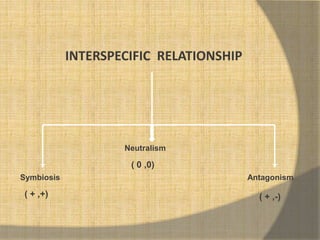
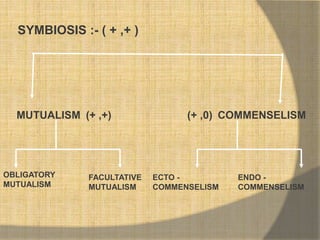
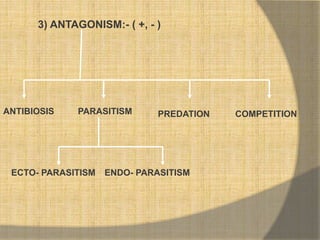
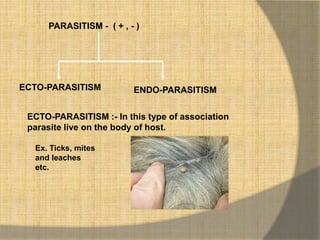
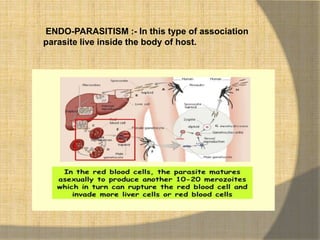
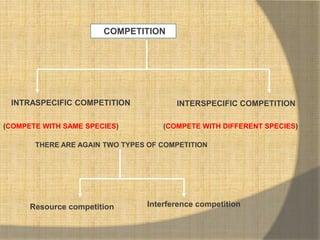
This document defines ecological relationships and describes different types of interspecific relationships between species. There are three main types of interspecific relationships: symbiosis, which includes mutualism and commensalism; neutralism; and antagonism. Antagonism includes antibiosis, parasitism, predation, and competition. Specific examples are provided to illustrate different forms of these relationships, such as obligatory and facultative mutualism, endo- and ecto-parasitism, predation between herbivores and carnivores, and resource and interference competition.