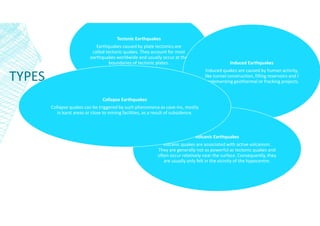
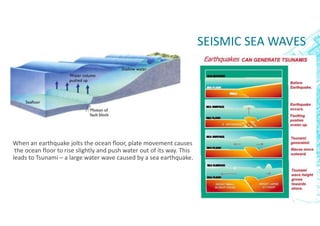
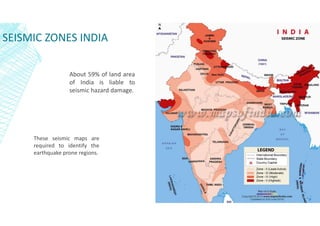
This document discusses earthquakes, including what causes them, different types of earthquakes, and factors related to earthquakes such as magnitude, intensity, and tsunamis. Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates suddenly slip past one another. The main types of earthquakes are tectonic, induced, volcanic, and collapse earthquakes. When constructing buildings in seismic areas, it is important to choose stable foundations and avoid resonance effects. Earthquake magnitude is measured by the Richter scale, while intensity is measured by the Mercalli scale and relates to destructive impact at a location. Large earthquakes can also trigger tsunamis by displacing ocean water.