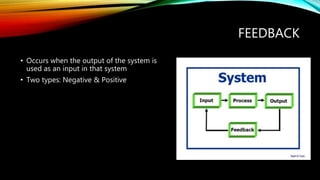
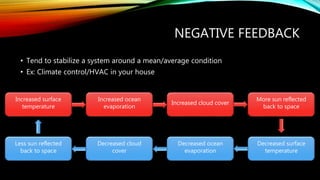
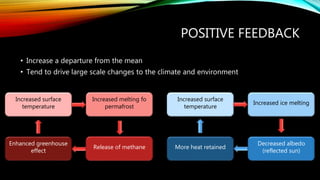
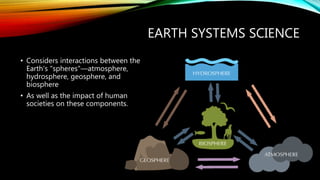
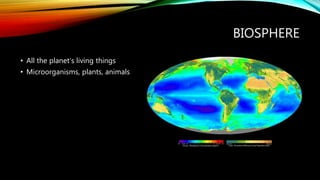
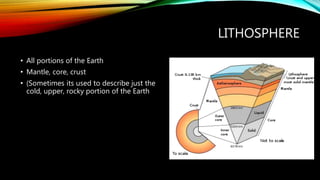
This document discusses key concepts in systems science. It defines a system as interconnected parts forming a whole and describes open systems that exchange matter and energy with surroundings and closed systems that do not. Feedback occurs when a system's output becomes its input and can be negative, stabilizing around an average, or positive, driving large changes. Earth system science considers interactions between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, and biosphere as well as human impacts. The hydrosphere includes all water, the biosphere all living things, the lithosphere the solid Earth, and the atmosphere the air surrounding Earth.