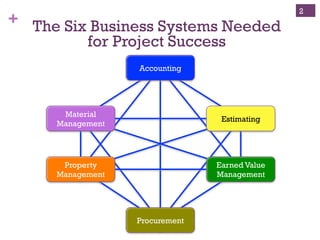
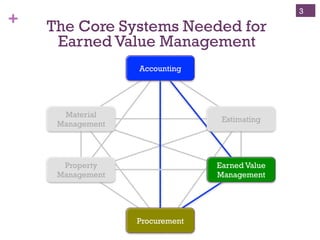
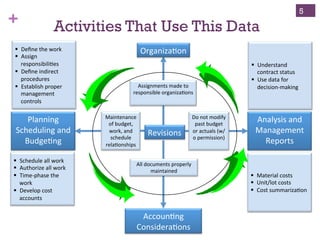
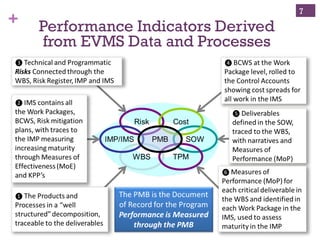
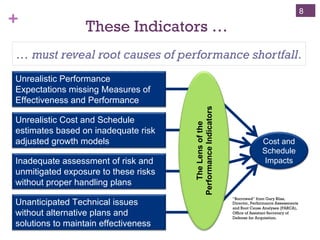
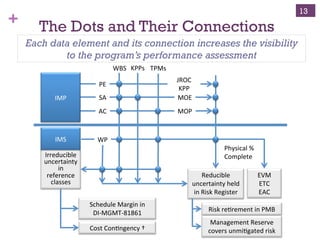
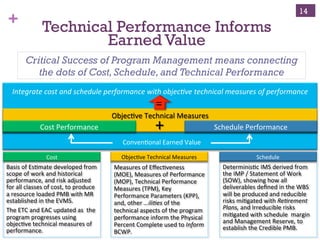
The document outlines the essentials of Earned Value Management (EVM), emphasizing its integration of people, processes, and tools for effective project management. It details critical business systems, core components, performance indicators, and success factors essential for successful EVM implementation. Additionally, it highlights the importance of objective technical measures and the relationship between cost, schedule, and technical performance in achieving project success.