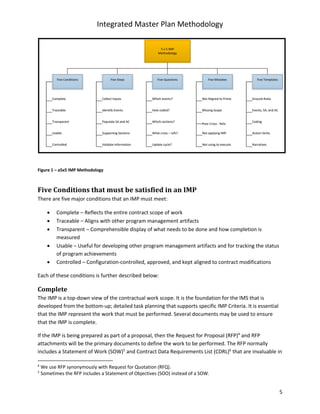
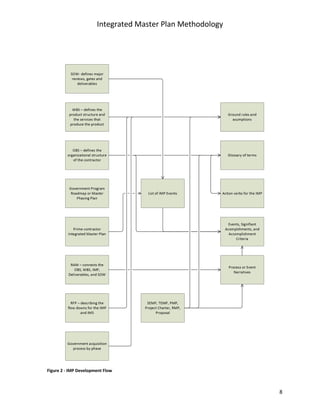
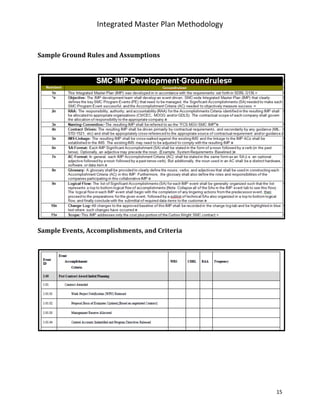
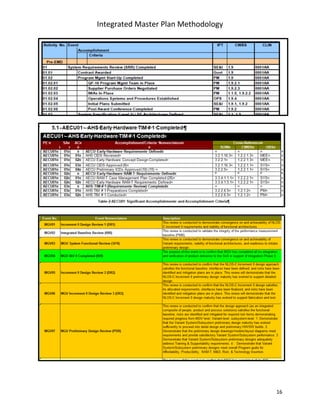
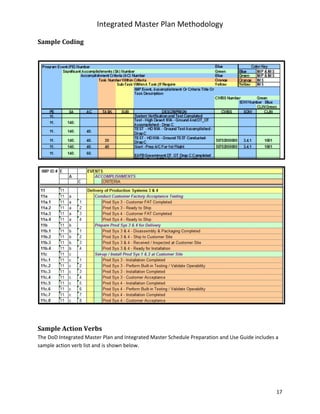
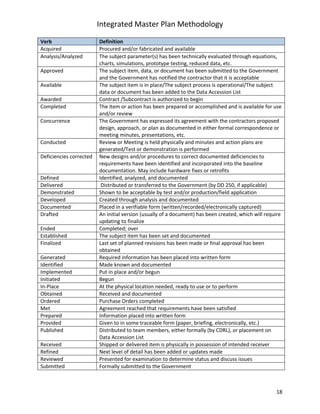
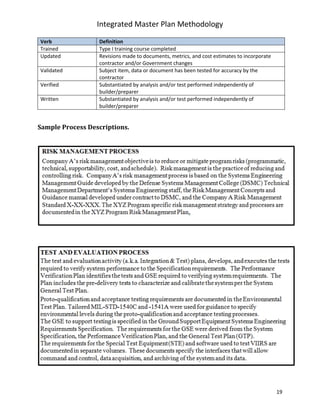
The document describes a methodology for developing an Integrated Master Plan (IMP). It outlines five conditions an IMP must meet, five steps in the development process, five common questions about IMP development, five common mistakes, and provides five templates/samples for key IMP sections. The methodology is intended to help program and project teams create effective IMPs that integrate execution plans and align with contractual requirements.