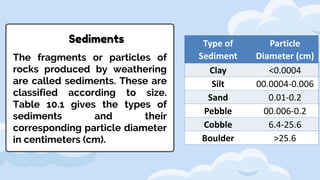
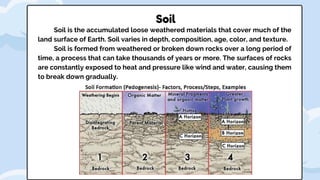
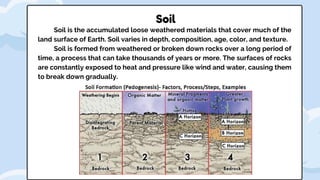
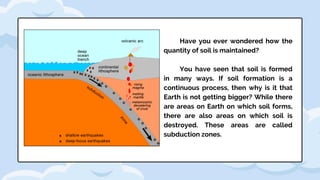
Rock weathering breaks down Earth's crust through physical and chemical processes. Physical weathering breaks rocks into smaller pieces through mechanical means like temperature changes, plant and animal activity, and abrasion. Chemical weathering alters the chemical composition of rocks through reactions with water, oxygen, carbon dioxide and acids. The rate of weathering depends on factors like climate, rock type, and exposure. Weathering produces sediments and soils that cover much of the Earth's surface.